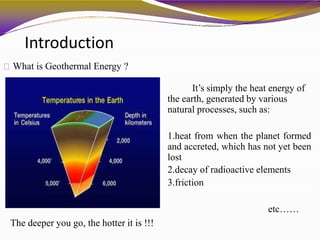
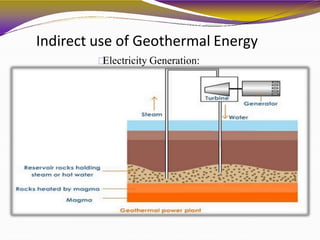
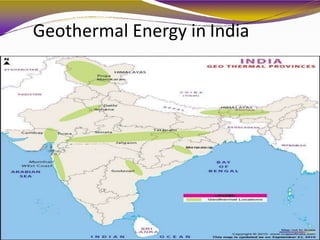
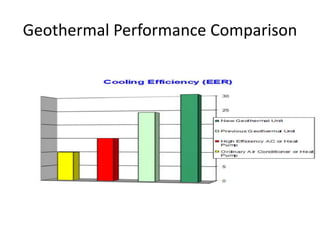
Geothermal energy is a renewable energy source that harnesses heat from within the earth. It can be extracted from geothermal reservoirs found in areas with geysers, hot springs, volcanoes, and boiling mud pots, where hot water and steam are trapped in porous rock. This heat energy can be used directly, such as for heating buildings and greenhouses, or indirectly for electricity generation in dry steam, flash steam, or binary cycle power plants. While geothermal energy has advantages of being continuously available and having little environmental impact, development is limited by high upfront costs and the risk of reservoirs running dry or releasing harmful gases.