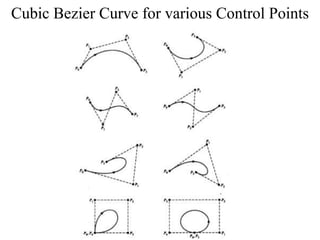
This document discusses different methods for representing curves in geometric modeling, including non-parametric and parametric representations. Non-parametric representations can be explicit, using equations relating x, y, and z, or implicit, with no distinction between dependent and independent variables. Parametric representations describe variables in terms of a parameter, allowing for multi-valued and flexible curves. Specific curve types discussed include Bezier curves, defined by control points, and B-spline curves, which separate the polynomial order from the number of control points.