This document discusses two common parametric surface representations: Hermite bi-cubic surfaces and Bezier surfaces.
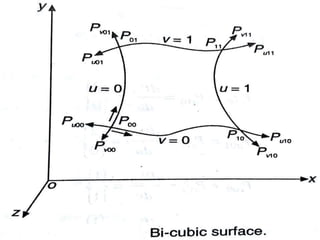
Hermite bi-cubic surfaces connect four corner points and eight tangent vectors at the corners, requiring 16 vectors (48 scalars) to determine the surface coefficients. The parametric equation uses polynomials of the parameters u and v.
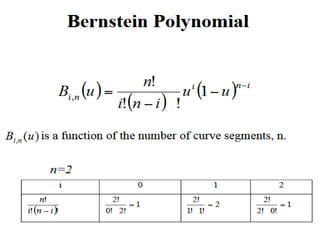
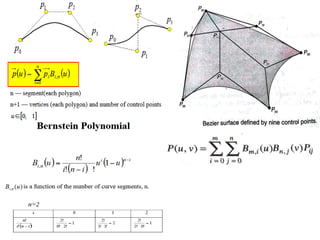
Bezier surfaces are defined by a set of control points and basic functions of the parameters u and v. The surface passes through the boundary control points but not necessarily through all interior points. Properties include partition of unity and the surface lying within the convex hull of control points.




![The equation can be expanded similar to Hermite cubic curve
where[P] , [P U] , [P V] and [P UV] are the sub –
matrices of the corner points , corner u – tangent
vectors , corner v – tangent vectors and corner
Twist.
The normal vector at N00 is: N00 = Pu00 × P v00
M is Hermite matrix
recall from Hermite curve
U AND V are parameters
of surface patch
B is corner points , corner
uv – Tangent vectors and
corner Twist.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syntheticsurfaces1111-180921084457/85/Synthetic-surfaces-6-320.jpg)





![where [MH] is the Hermite matrix and V is the geometry (or
boundary conditions) vector.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syntheticsurfaces1111-180921084457/85/Synthetic-surfaces-12-320.jpg)