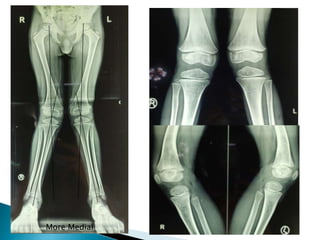
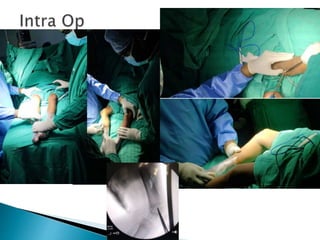
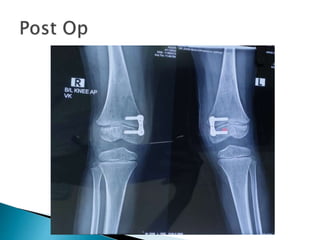
This patient is a 6-year-old boy presenting with bilateral genu valgum deformity of the knees. He has a history of vitamin D deficiency as a child. On examination, he walks with adduction of the knees such that his knees touch. Range of motion of the knees is normal. Imaging shows bilateral genu valgum deformity. Given the patient's young age and remaining growth potential, the treatment plan is to perform guided growth modulation using figure of 8 plates on both knees. This is the standard treatment for skeletally immature patients to gradually correct the deformity over time as the patient grows.