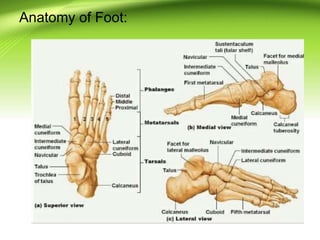
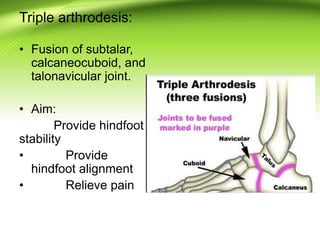
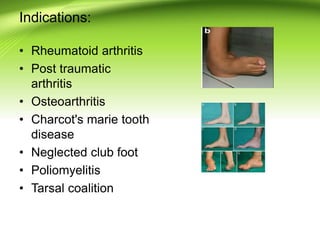
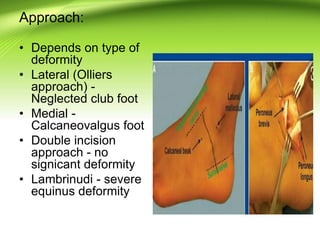
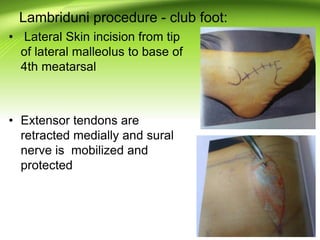
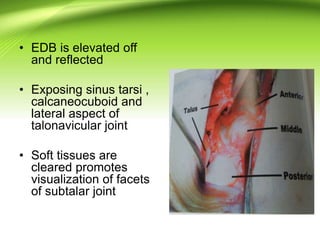
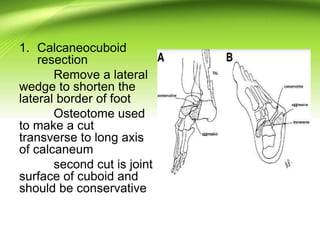
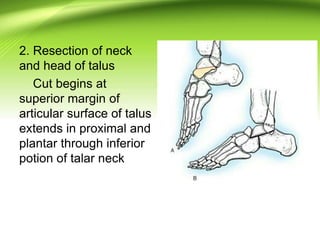
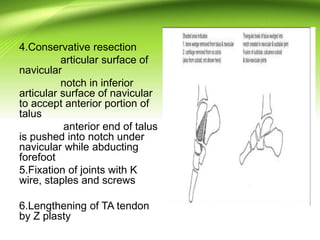
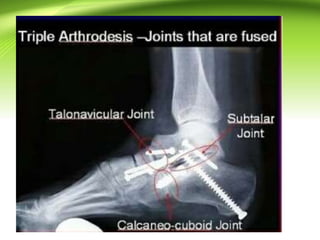
Triple arthrodesis is a surgical fusion of the subtalar, calcaneocuboid, and talonavicular joints to provide hindfoot stability and alignment and relieve pain. It is used to treat conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, post-traumatic arthritis, osteoarthritis, Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, neglected clubfoot, poliomyelitis, and tarsal coalition. The Lambrinudi procedure is used for severe clubfoot and involves wedge resections of the calcaneum, talus, and navicular followed by fixation with K-wires, staples or screws. Postoperatively, the limb is immobilized for 6 weeks followed by ankle-foot orthosis use and weight bearing