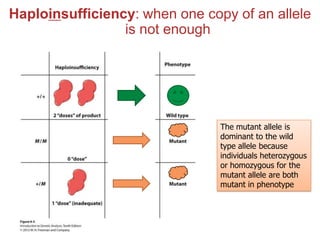
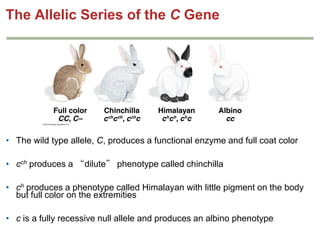
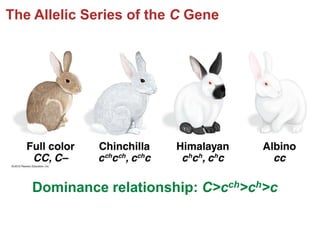
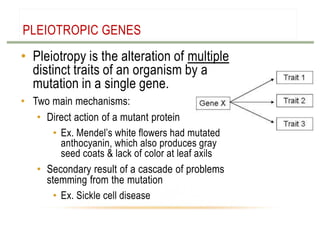
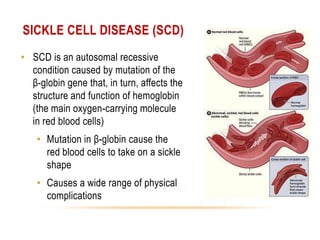
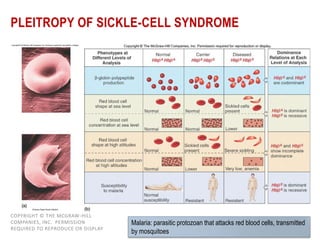
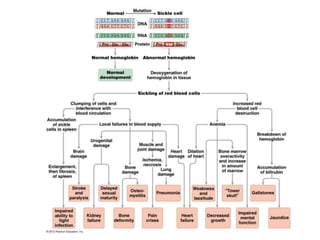
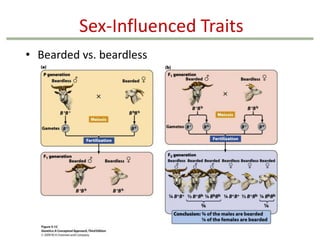
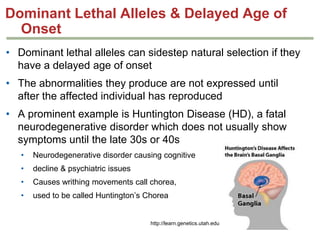
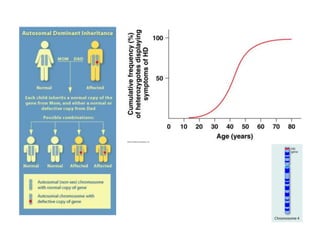
- Gene interactions refer to how genes collaborate or interact to influence phenotypes. There are several types of interactions including interactions between alleles, pleiotropy, sex-limited traits, and gene-environment interactions.
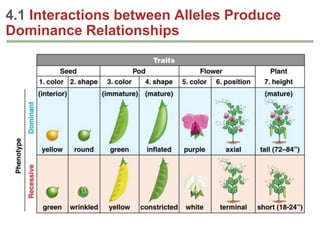
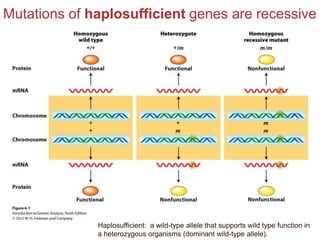
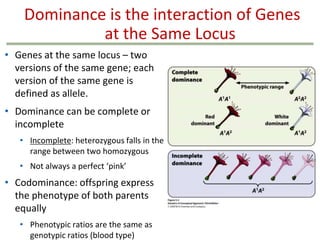
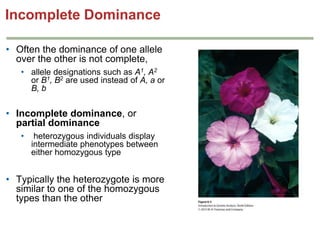
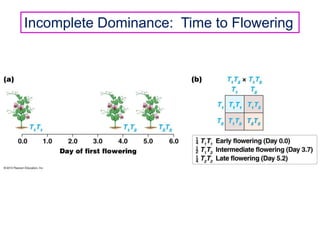
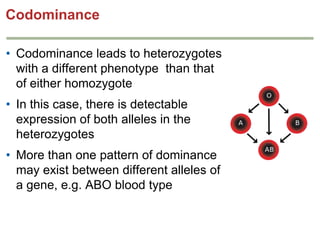
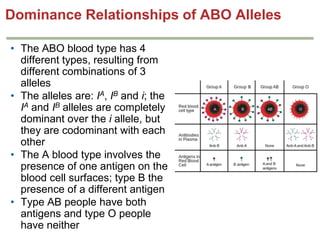
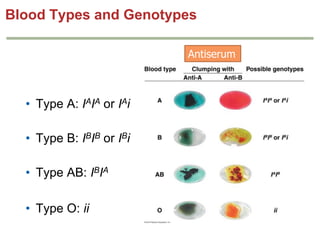
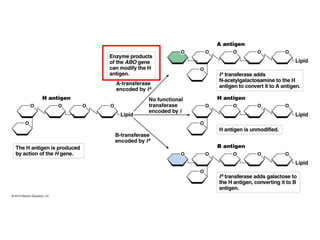
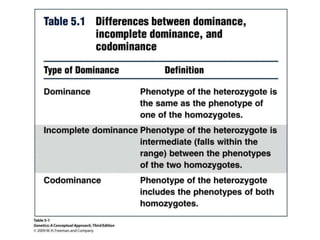
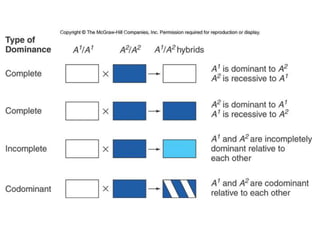
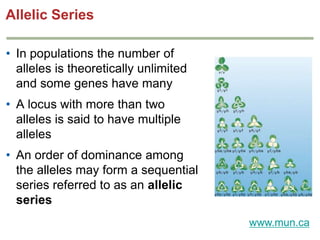
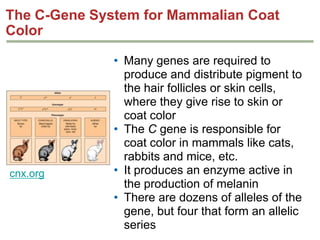
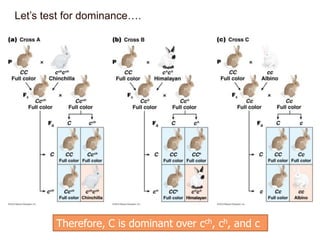
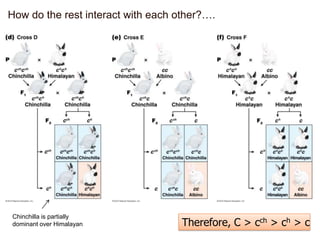
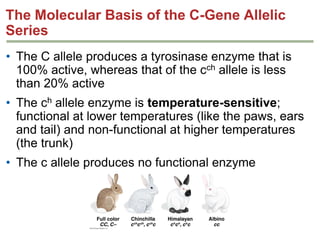
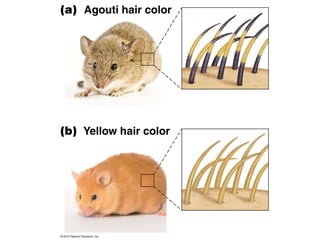
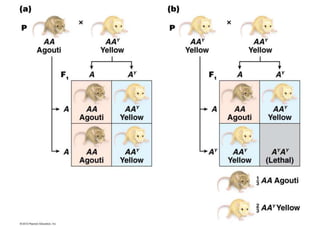
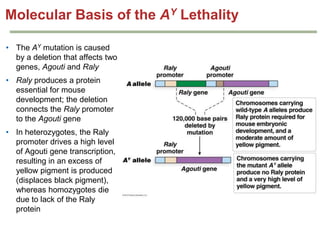
- Dominance relationships can be complete, incomplete, or codominant. Incomplete dominance results in intermediate phenotypes, while codominance allows both alleles to be expressed. Multiple alleles can form allelic series with different dominance hierarchies.
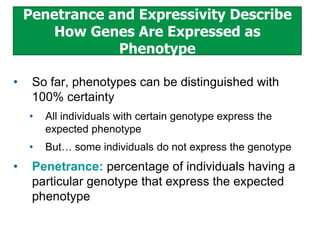
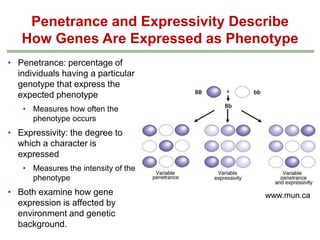
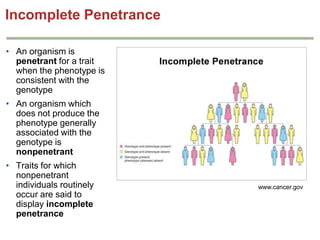
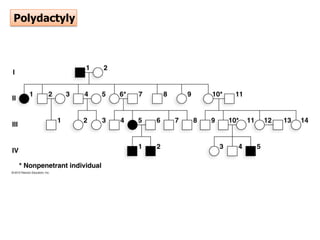
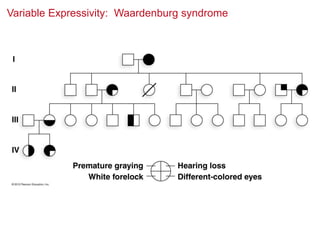
- Penetrance and expressivity describe how consistently and intensely a genotype is expressed as a phenotype, which can be influenced by environment and other genes. Gene-environment interactions are important, as the environment can modify gene expression and phenotypes.