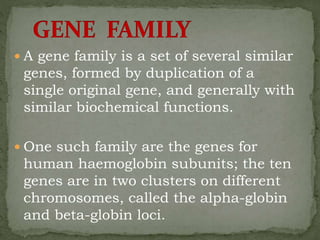
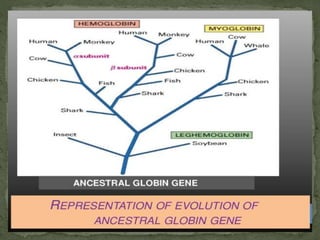
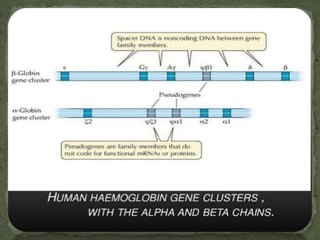
This document discusses several gene families and related concepts. It describes how a gene family is a set of similar genes formed by duplication of a single original gene, often with similar functions. It provides examples like the human hemoglobin gene family. It also discusses histone gene families, which package DNA into nucleosomes and are present in tandem repeats due to high demand during DNA replication.