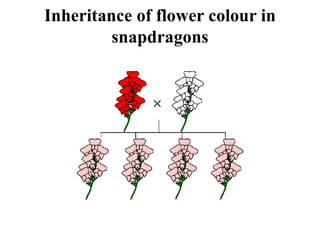
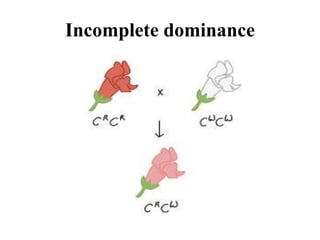
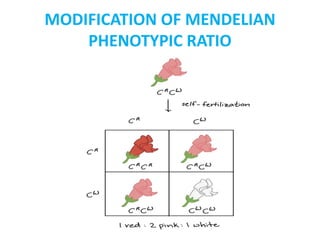
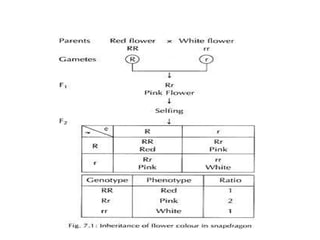
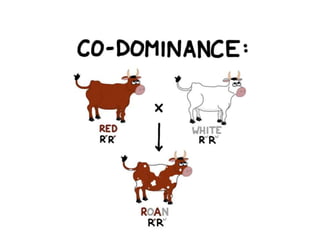
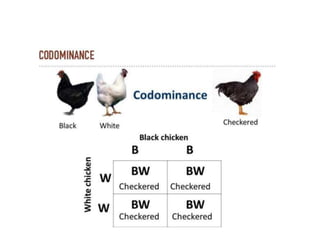
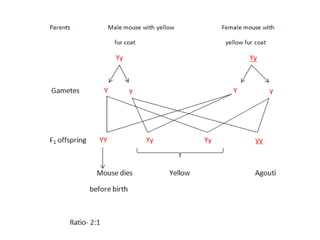
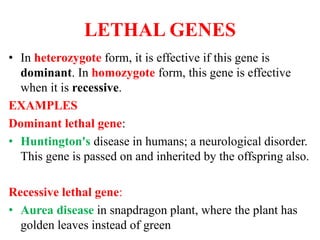
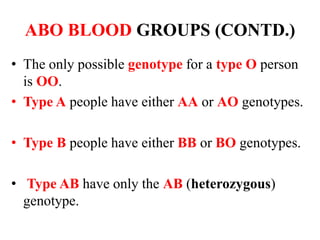
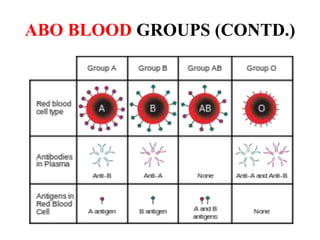
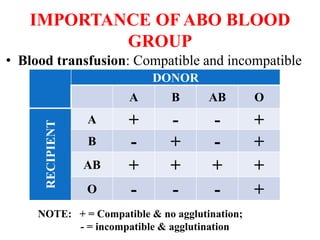
This document discusses different types of gene interactions including inter-allelic, intra-allelic, incomplete dominance, codominance, lethal genes, and multiple alleles. It provides examples of each type of interaction such as incomplete dominance in snapdragons resulting in pink flowers from white and red parents. Codominance is explained using ABO blood types where types A, B, and AB express both alleles. Lethal genes can be dominant or recessive and cause death in homozygous or heterozygous individuals. Multiple alleles are discussed in examples like the three alleles that determine ABO blood groups.