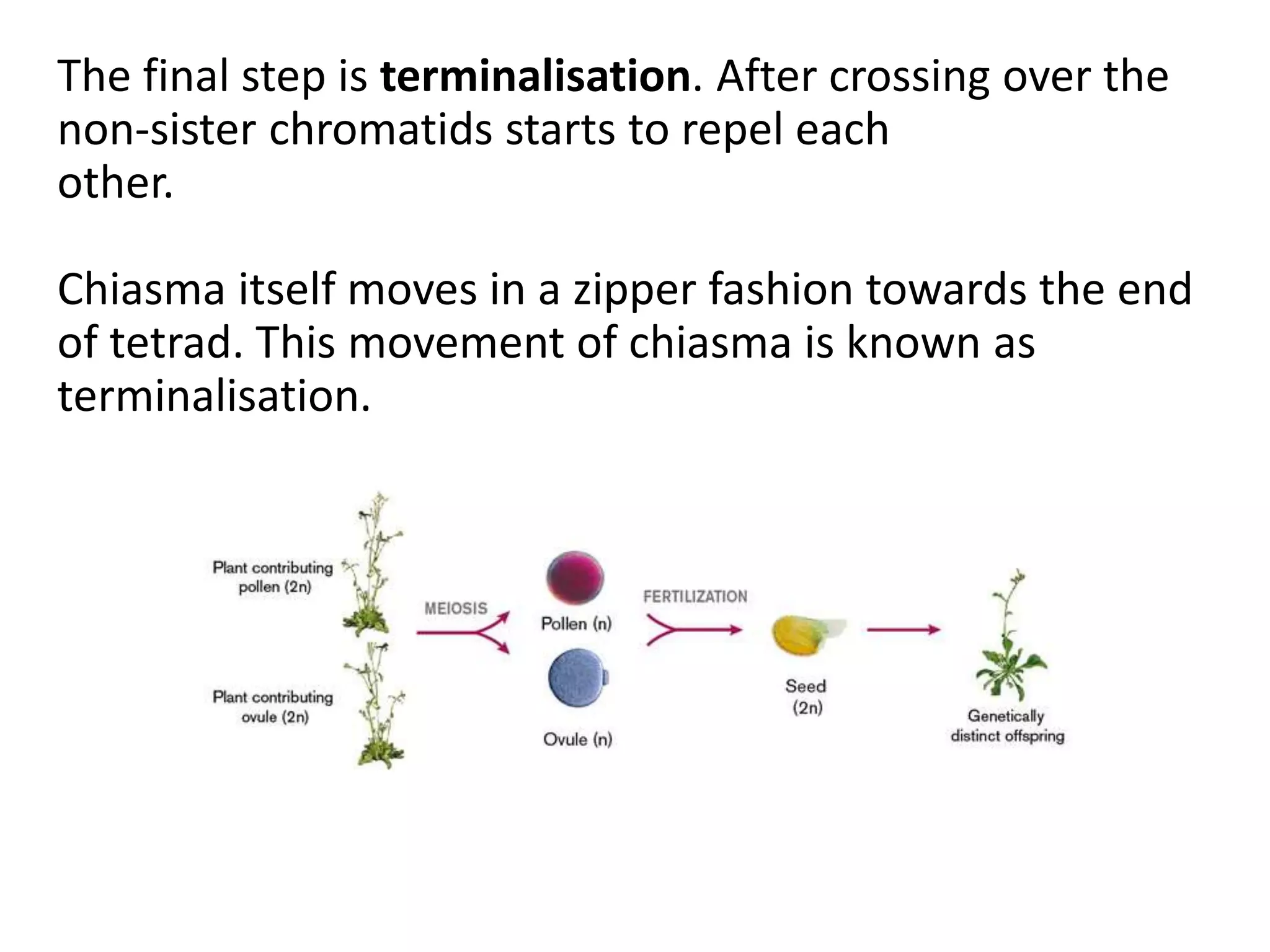
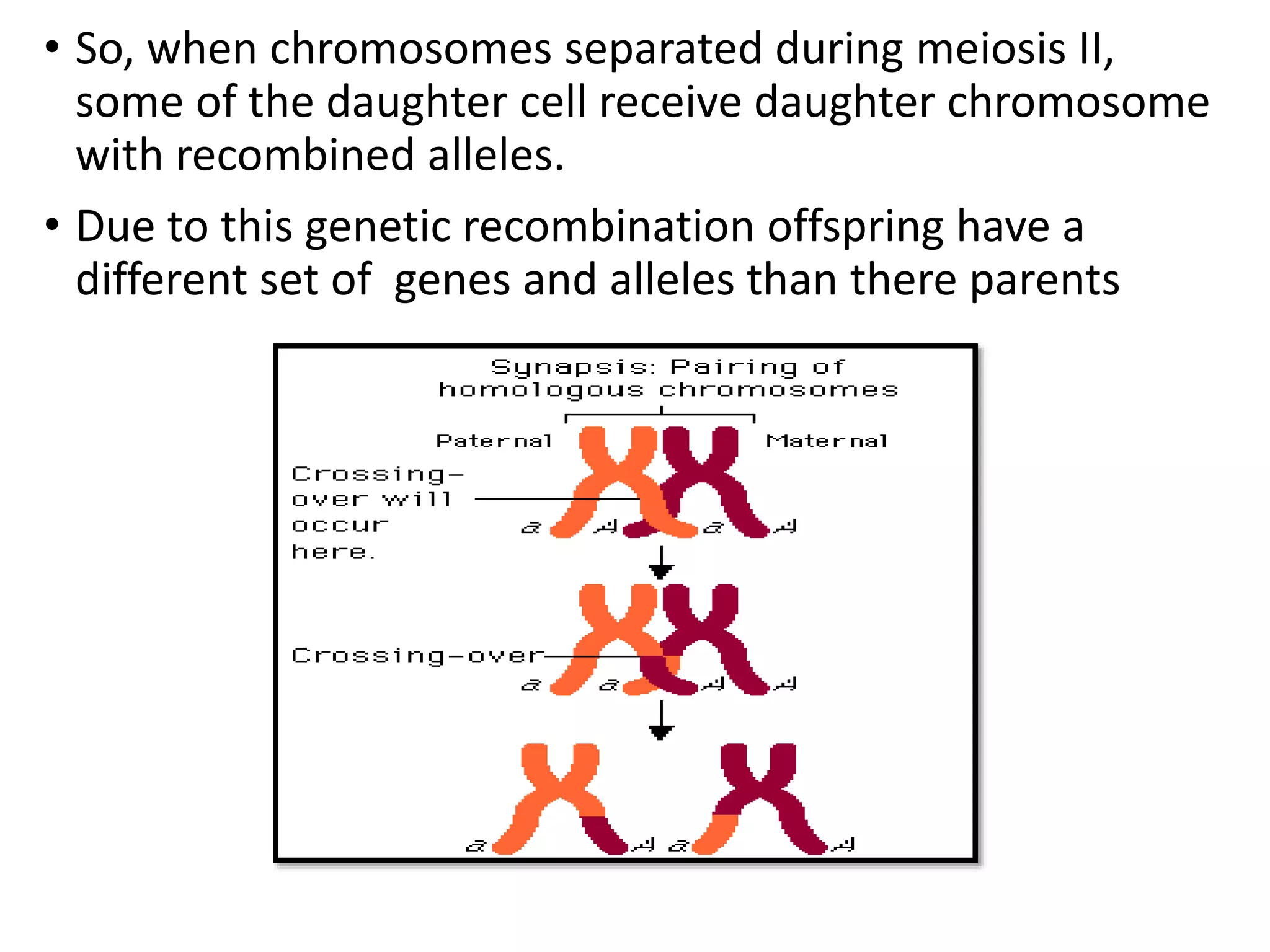
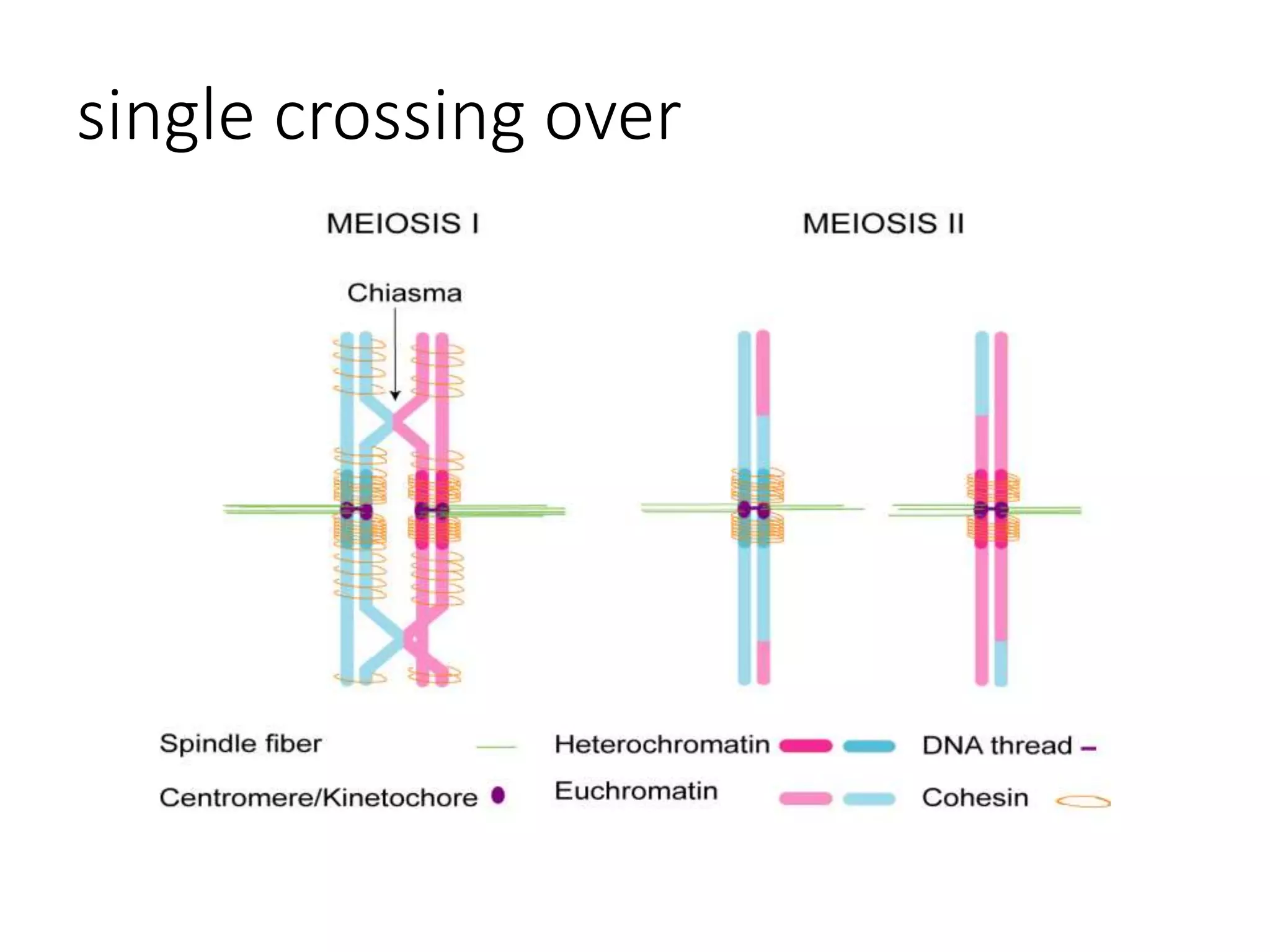
Meiosis is a cell division process that produces gametes (sex cells) with half the number of chromosomes. During meiosis, homologous chromosomes pair up and may exchange DNA segments through a process called crossing over. Crossing over increases genetic diversity and helps ensure balanced distribution of chromosomes in gametes. It occurs during prophase I through the formation of chiasmata between nonsister chromatids. Crossing over plays an important role in evolution by allowing independent assortment of genetic variants on chromosomes.