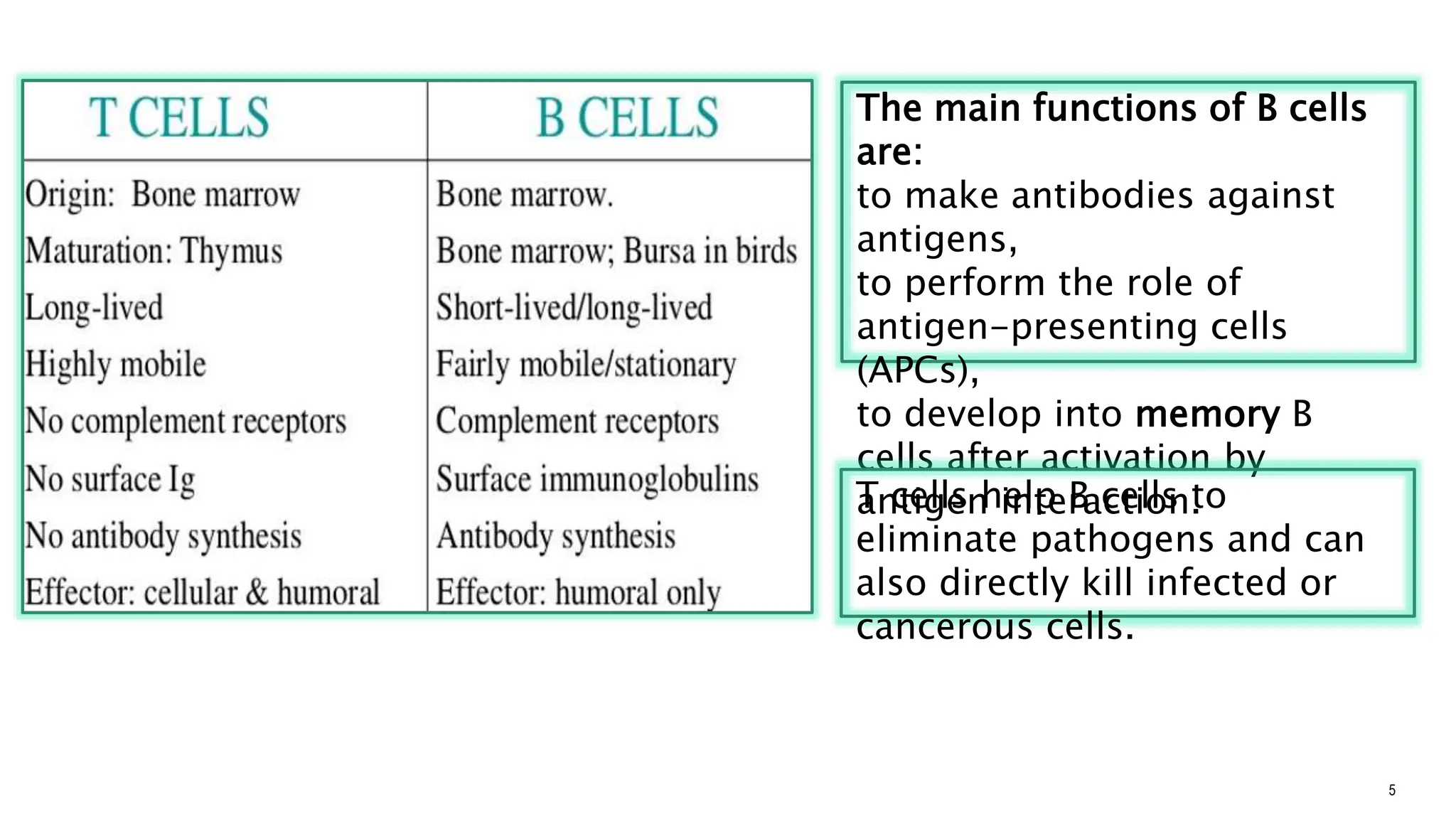
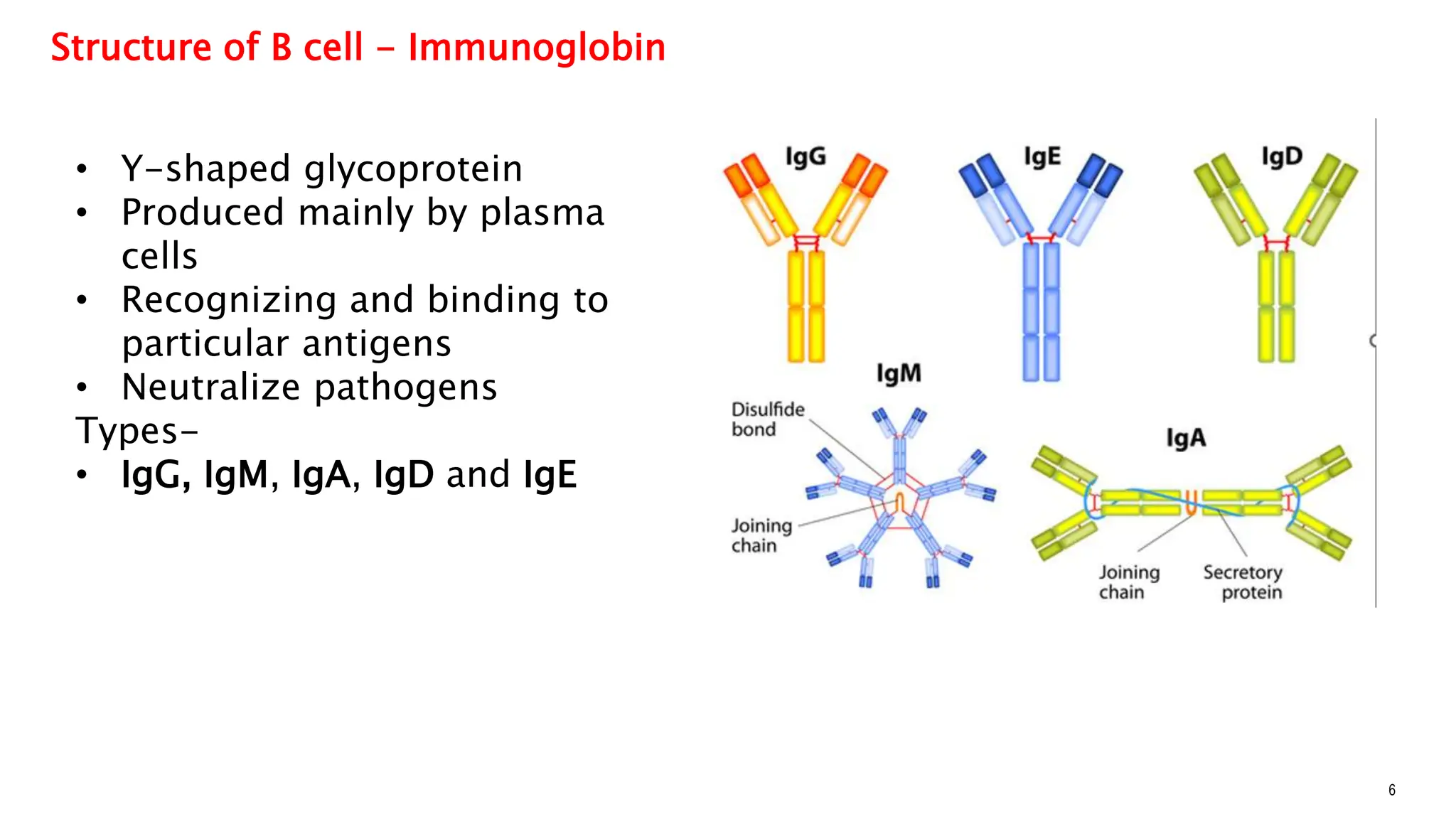
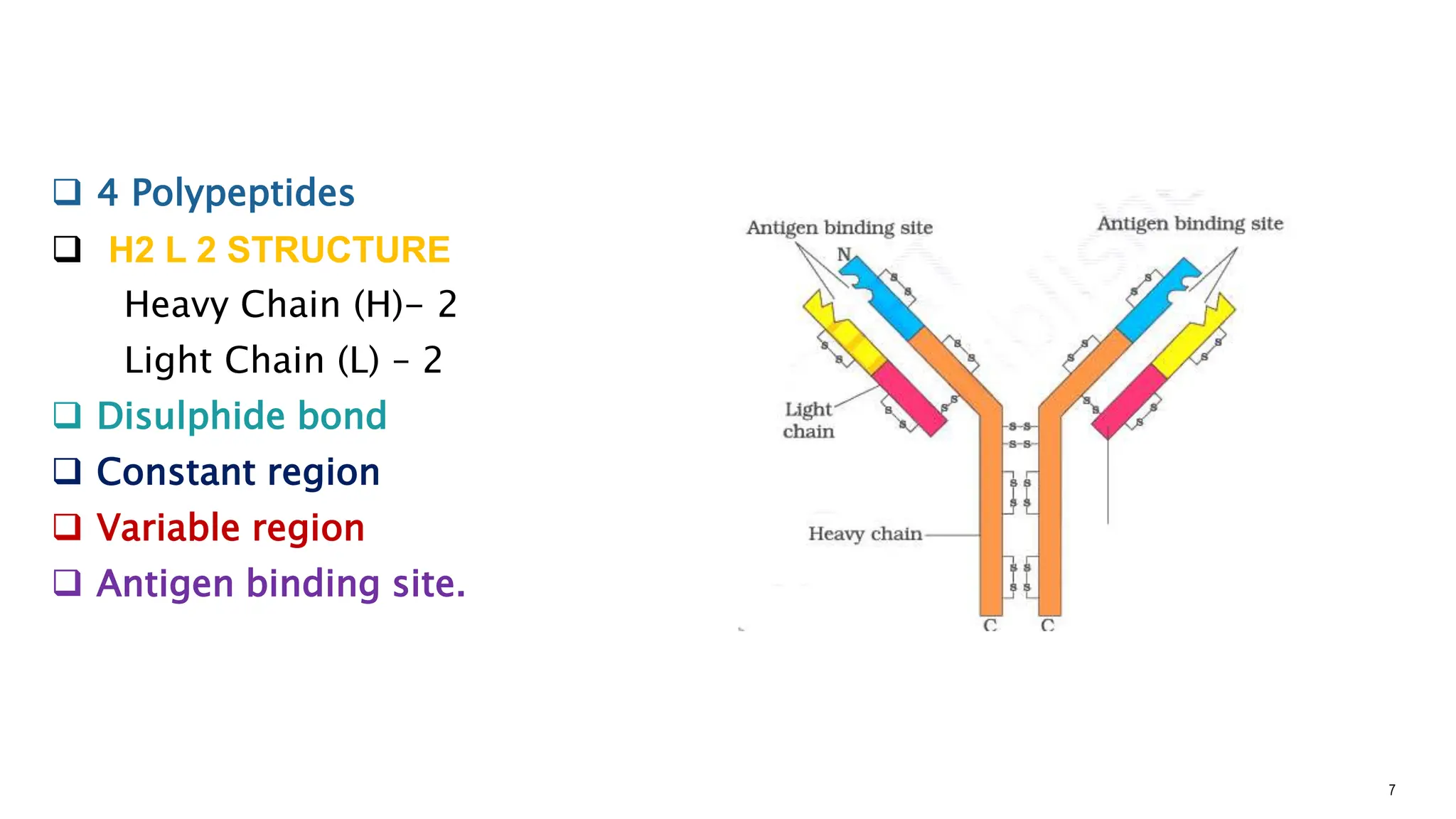
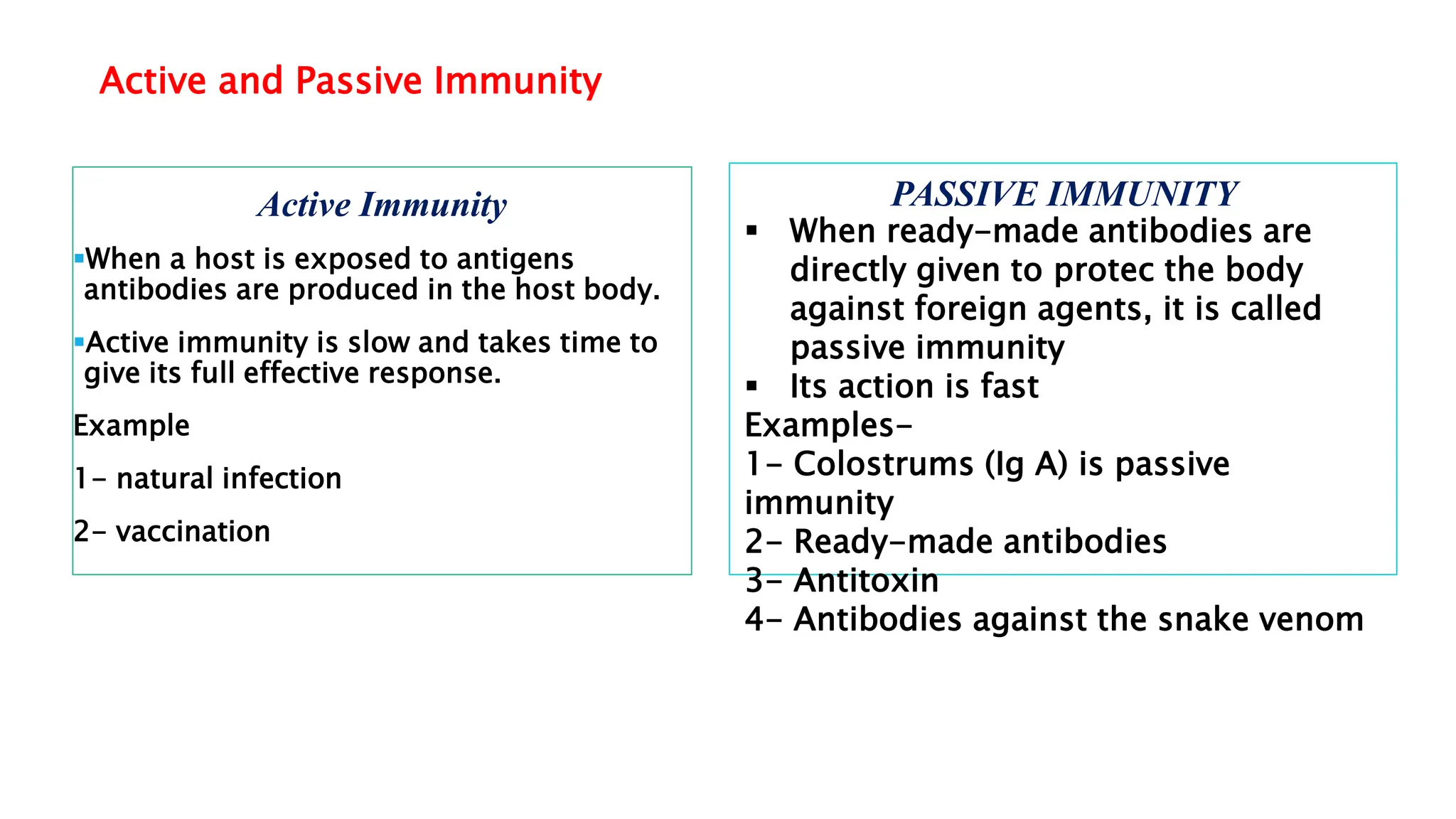
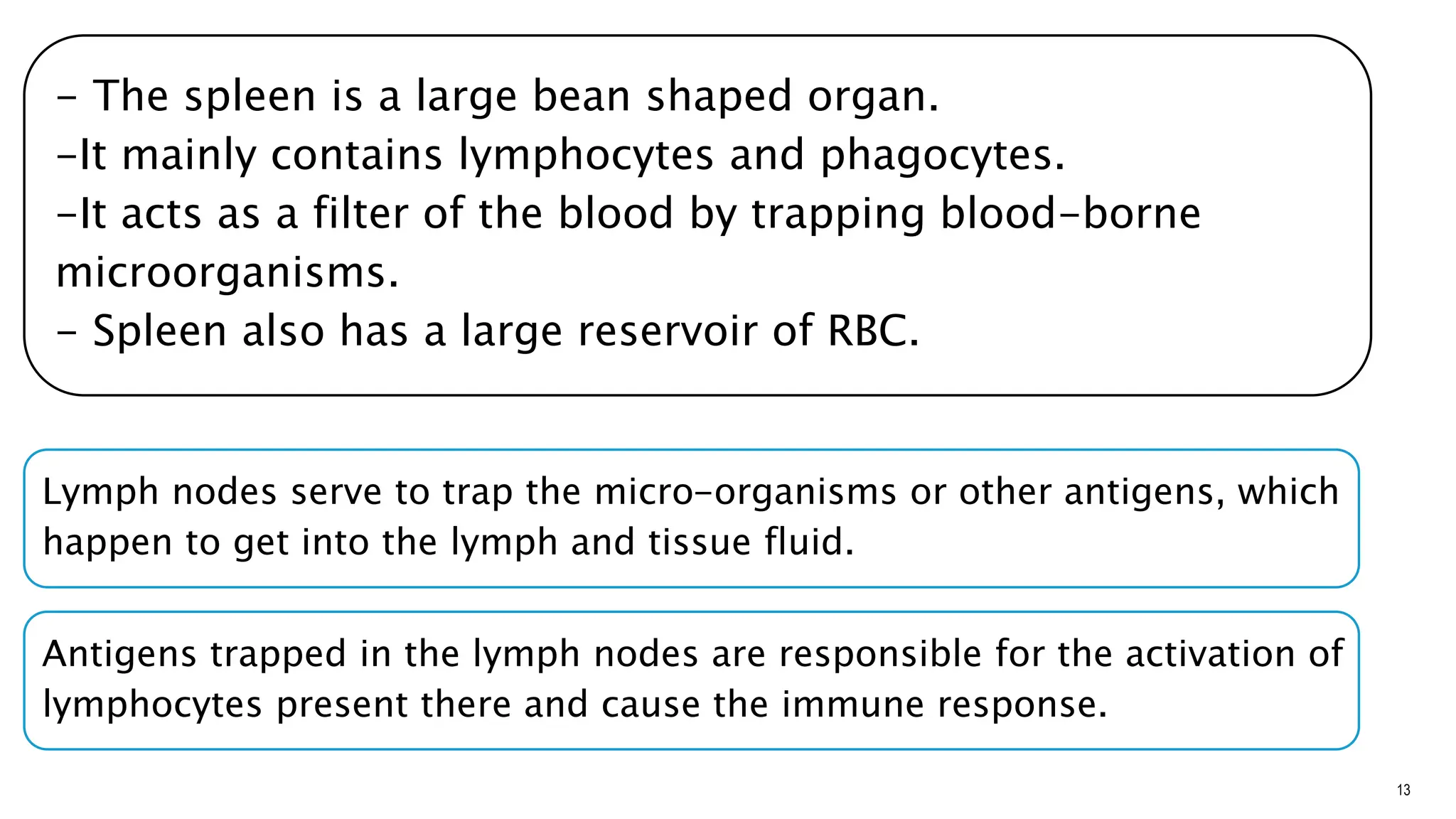
The document explains the immune system's function, detailing innate and acquired immunity, as well as humoral and cell-mediated immunity. It describes the roles of lymphocytes, including B cells and T cells, their structure, and how they produce antibodies. Additionally, it covers active and passive immunity, the significance of vaccination, and the functions of lymphoid organs in immune responses.