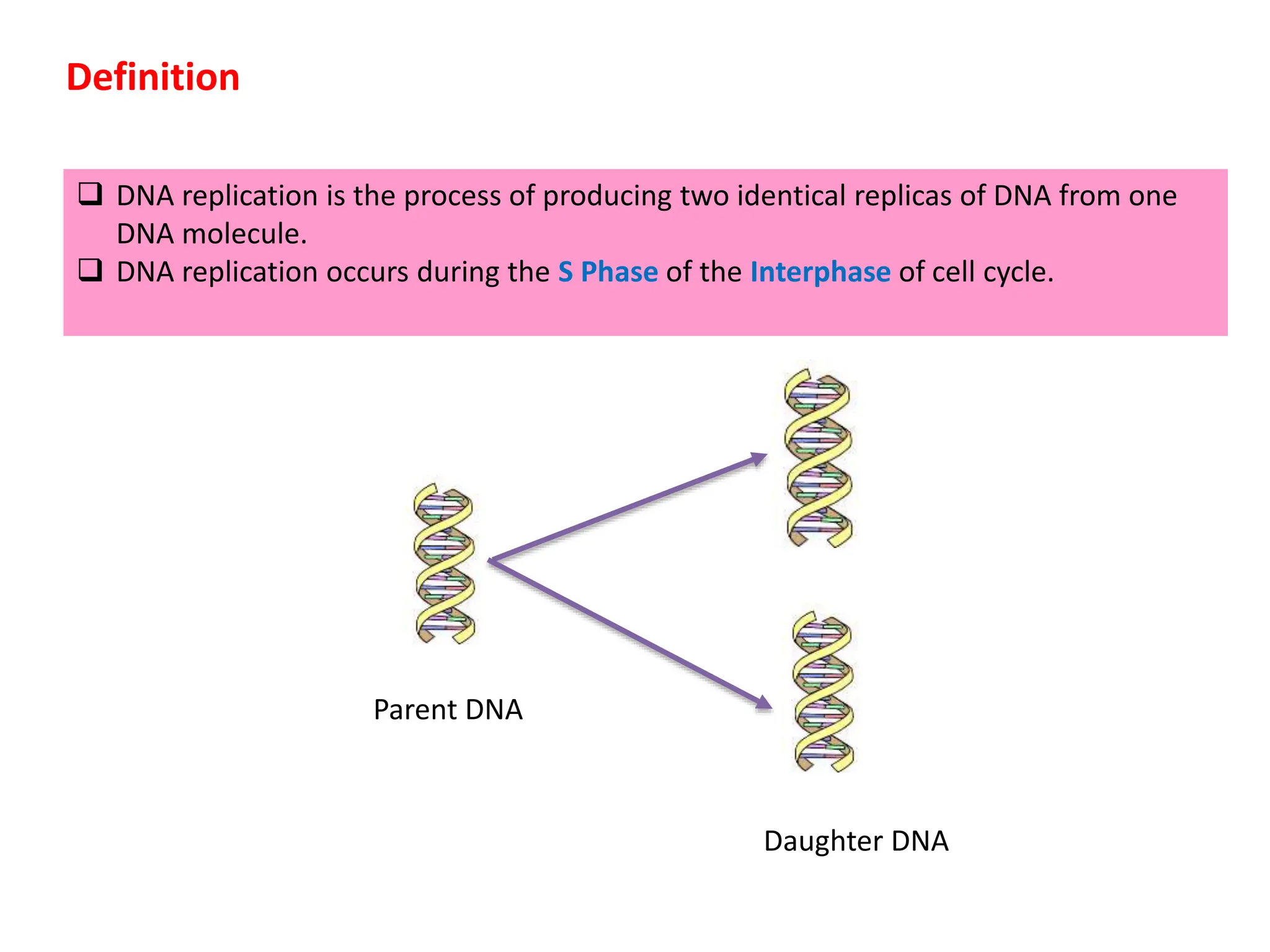
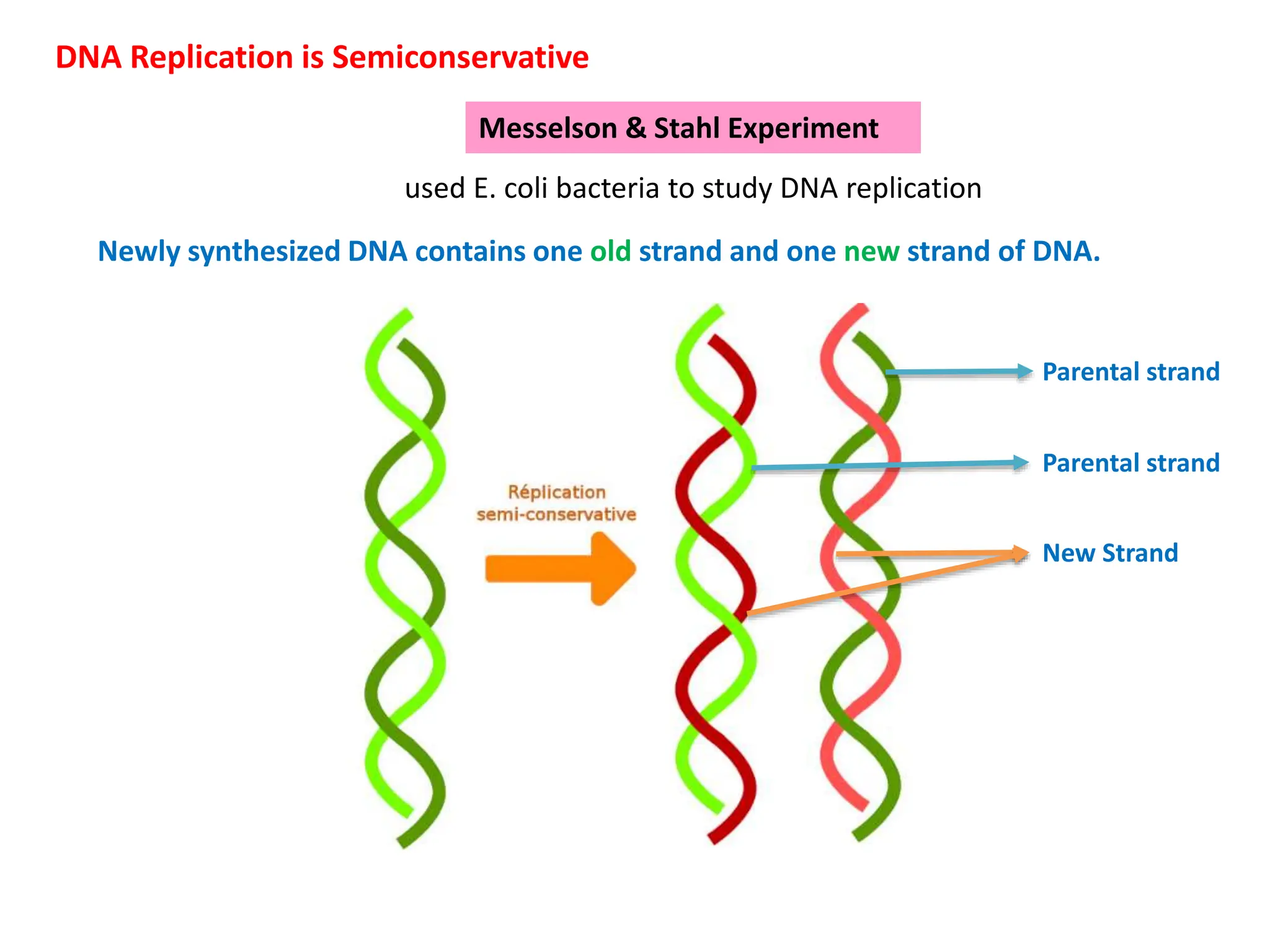
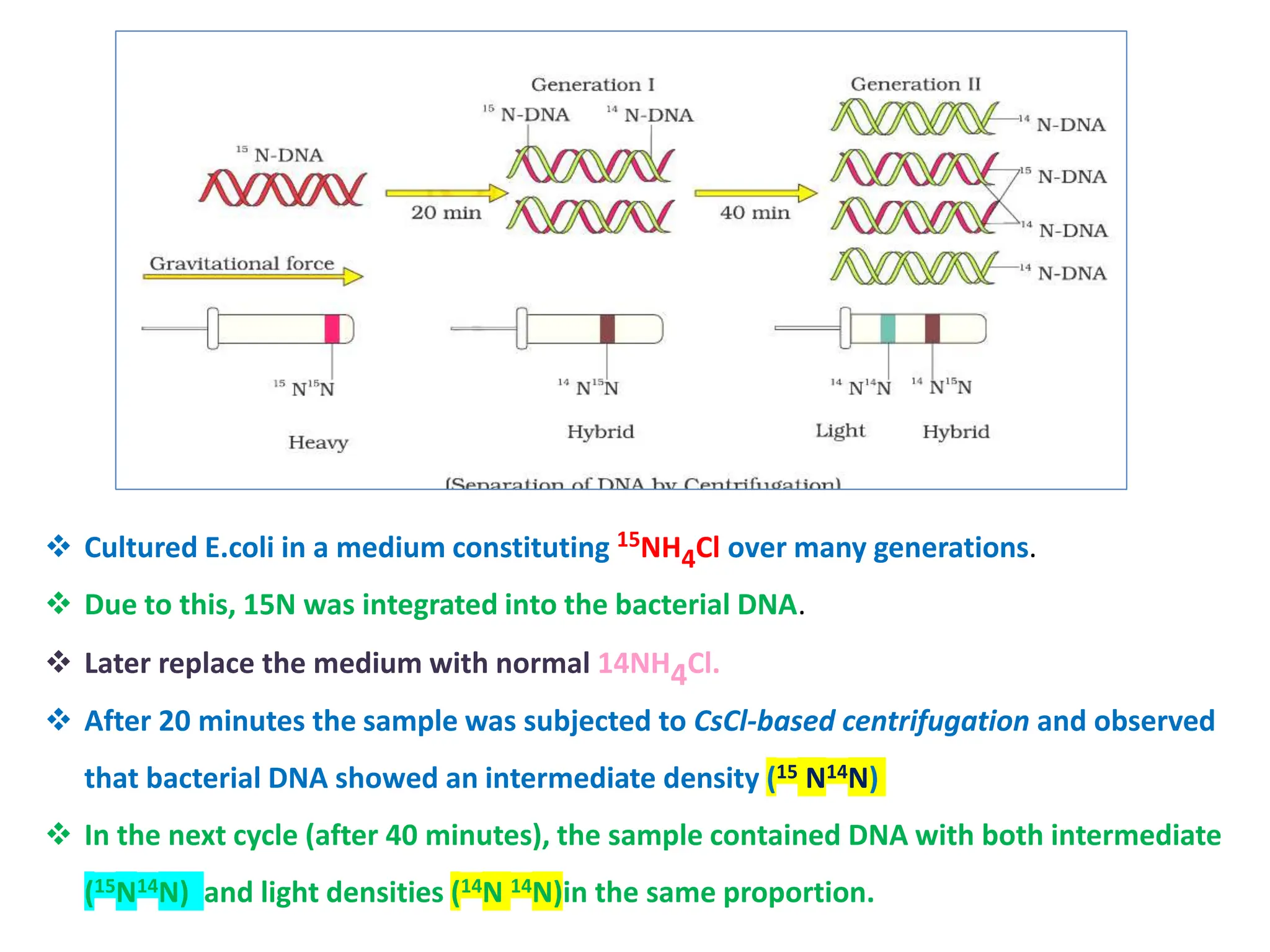
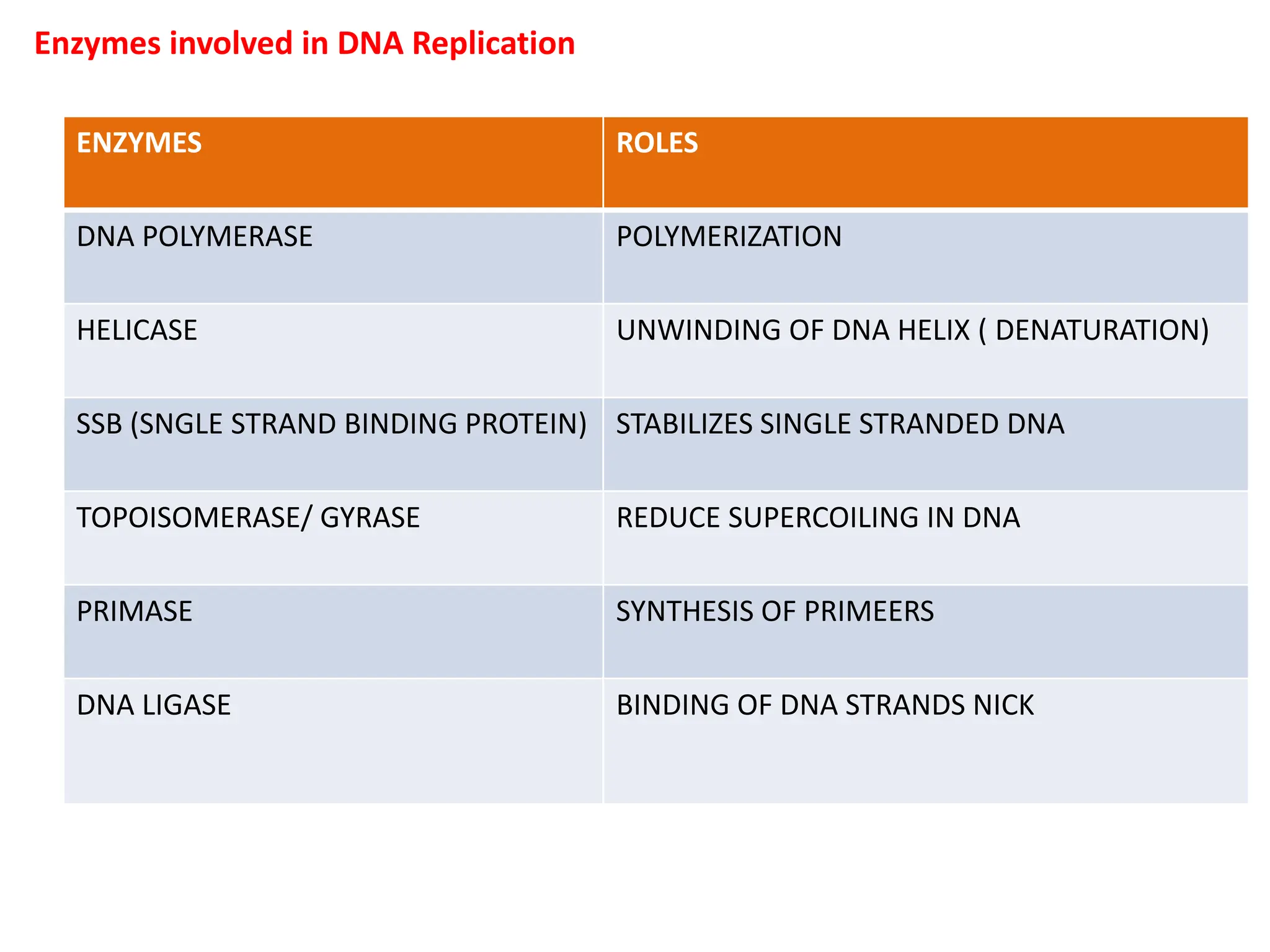
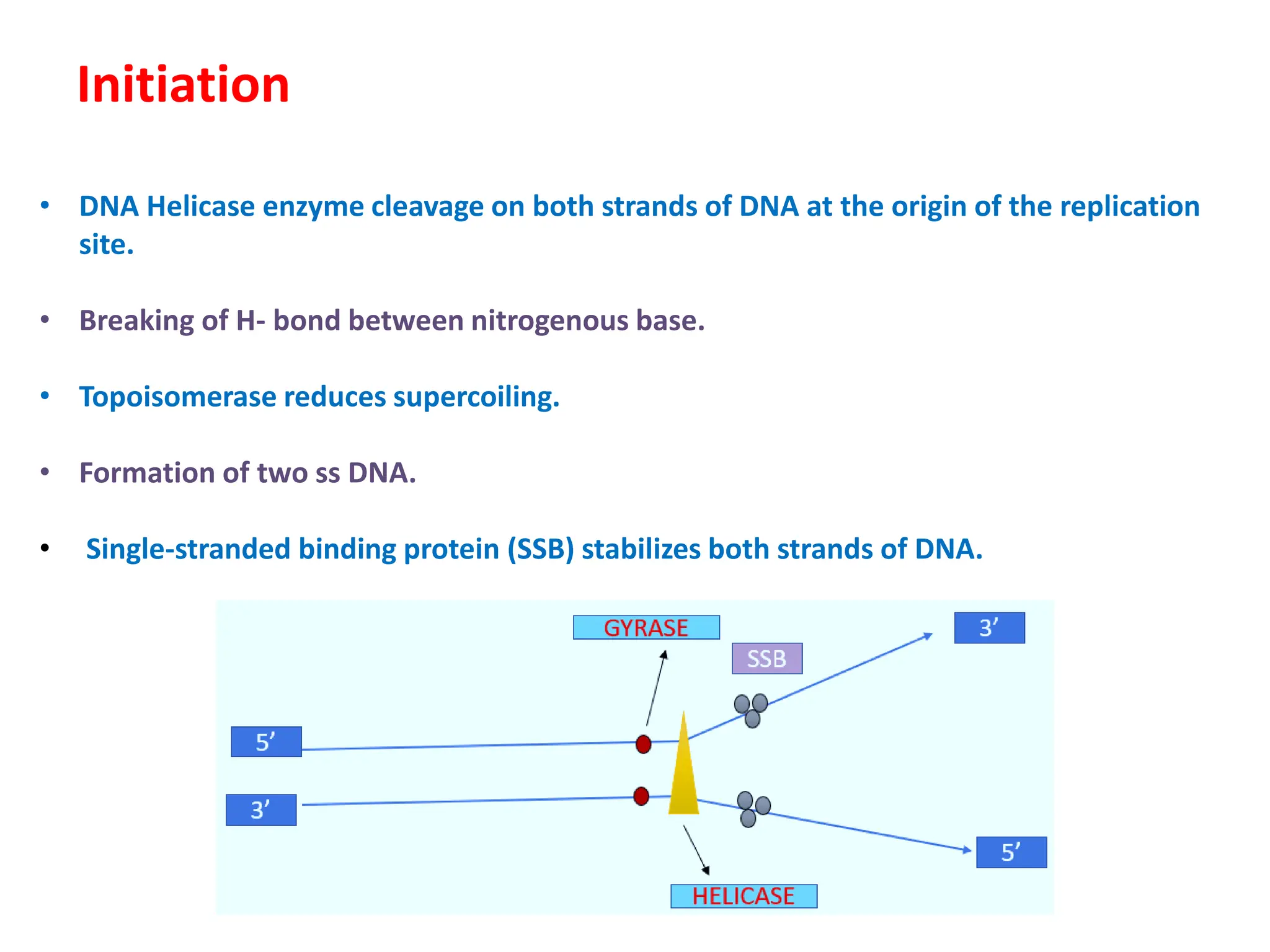
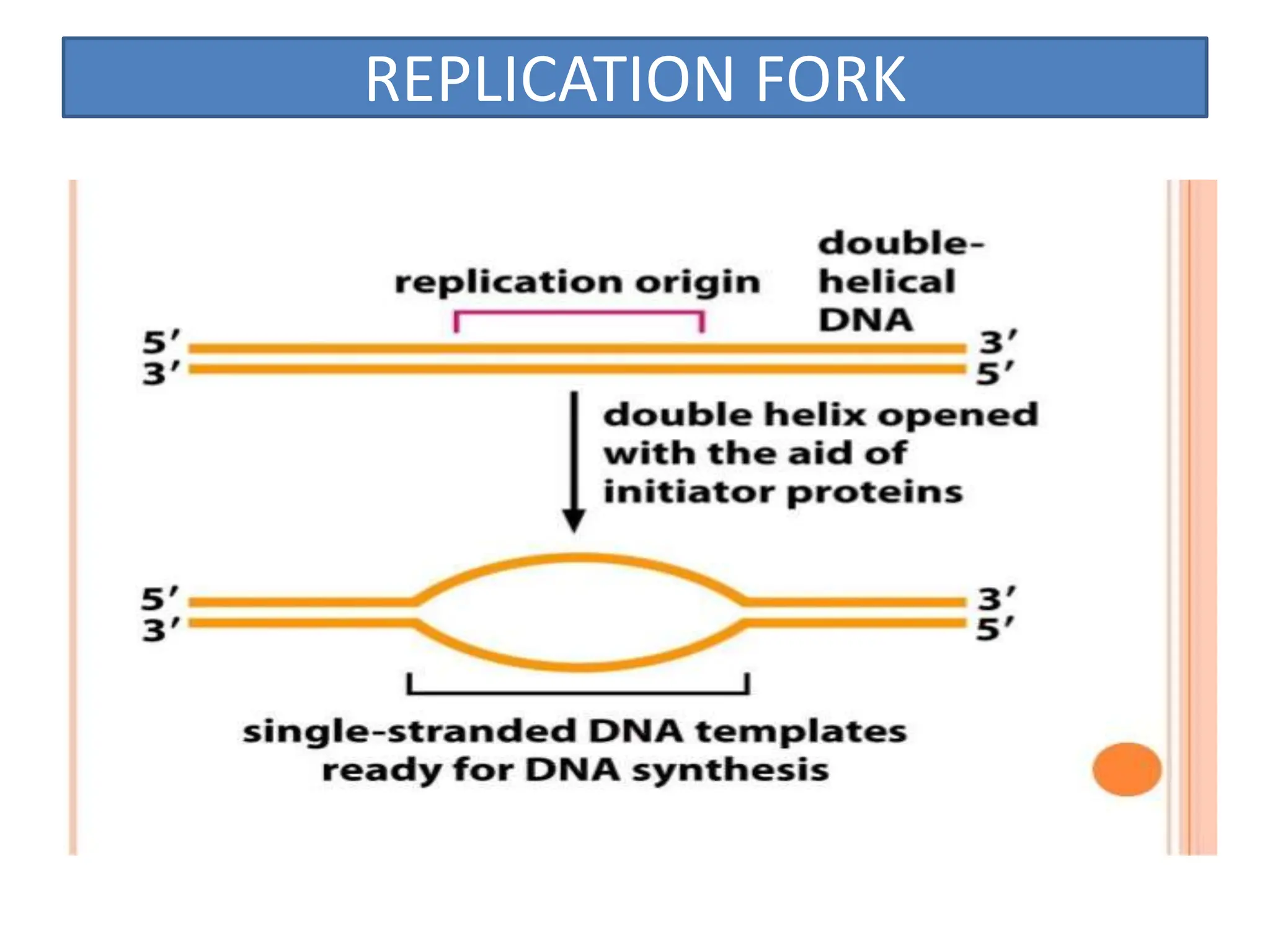
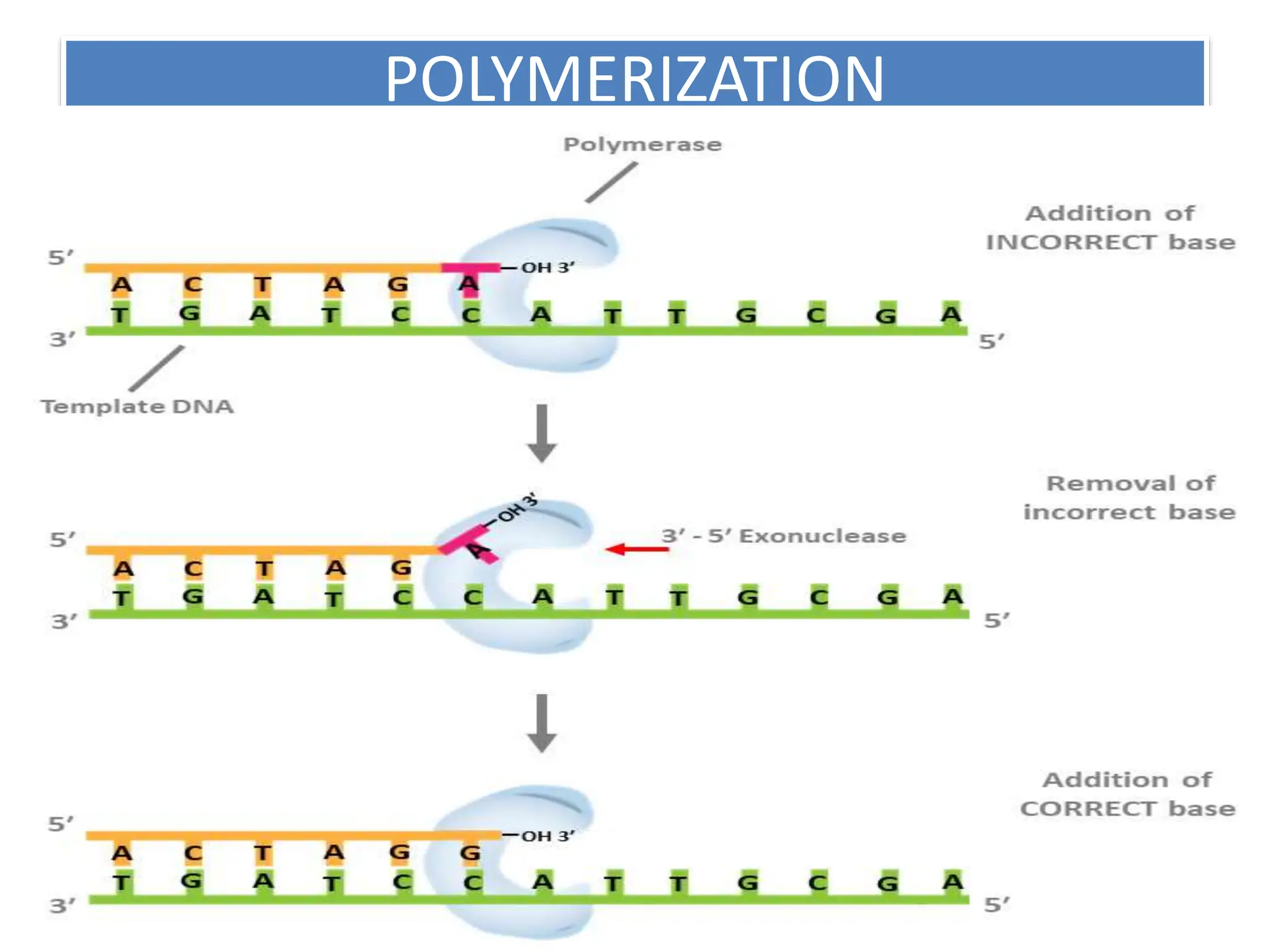
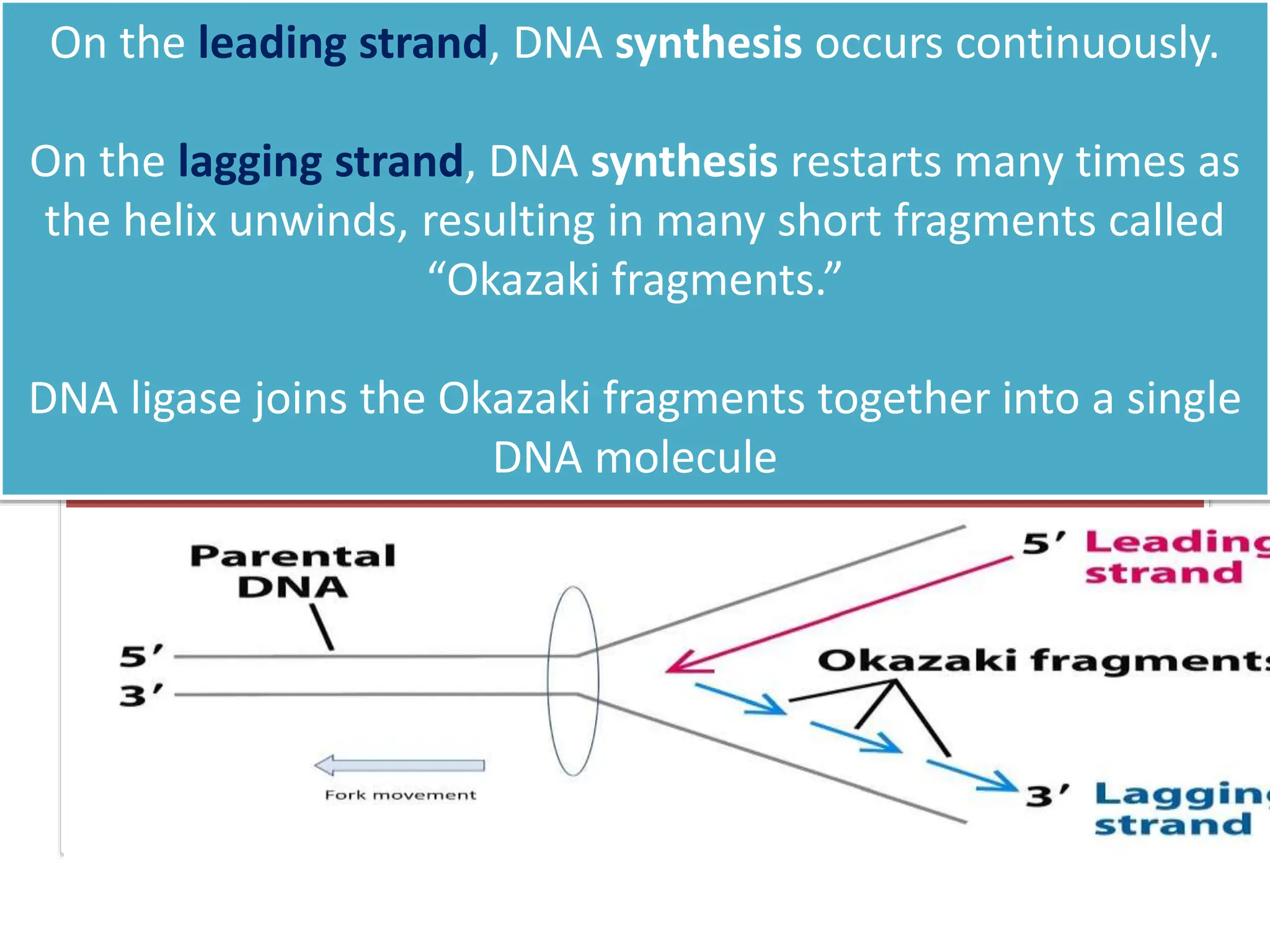
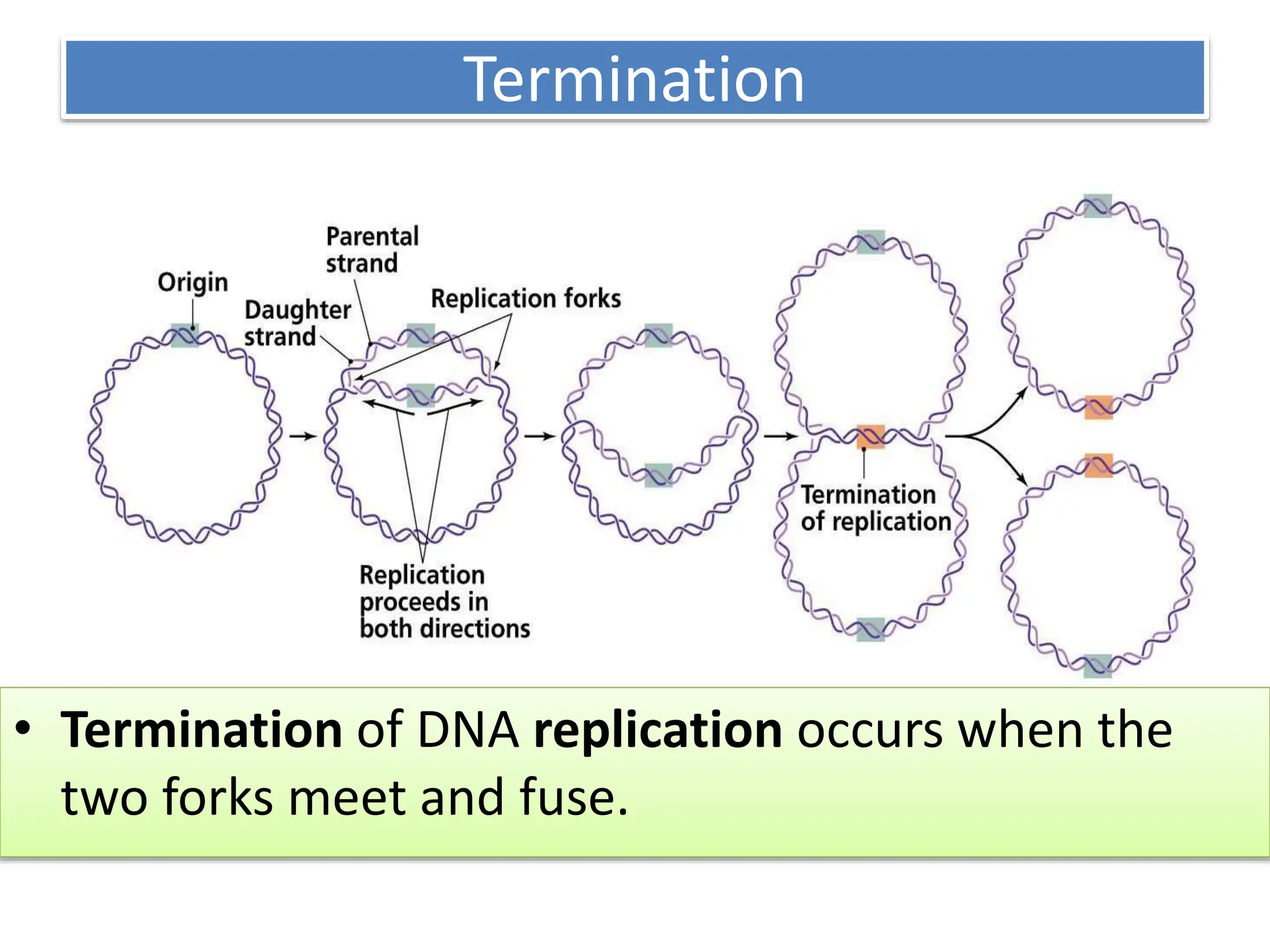
DNA replication is the process of creating two identical DNA replicas from one original strand, occurring during the S phase of interphase. The process is semiconservative, involving parental and newly synthesized strands, and requires various enzymes such as DNA polymerase, helicase, and ligase. Replication begins at origins of replication and includes initiation, elongation with leading and lagging strands, and termination when replication forks meet.