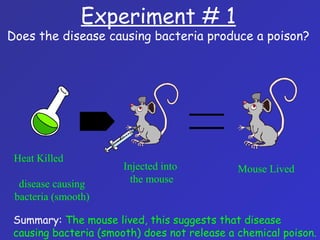
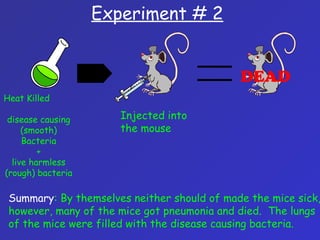
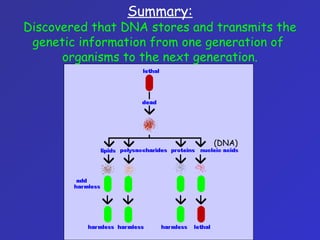
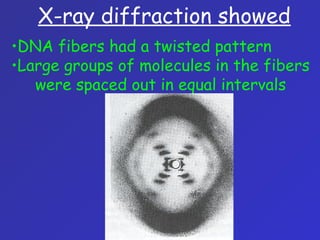
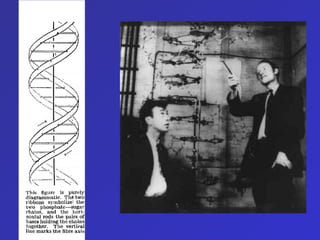
The document summarizes the history of discoveries leading to the understanding that DNA is the molecule of heredity. It describes early experiments in the 1900s and 1920s by scientists like Griffith who found that traits could be transferred between bacteria. Further work by Avery in 1944 found that DNA was responsible for this transformation. Chargaff discovered proportional relationships between DNA bases within species. Experiments in the 1950s by Hershey and Chase and the work of Franklin, Wilkins, Watson and Crick ultimately revealed DNA's double helix structure and its role in storing and transmitting genetic information from parents to offspring.