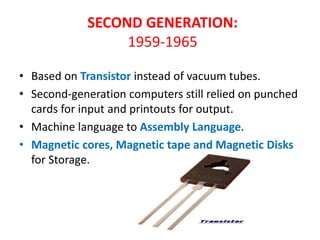
A computer is an electronic device that can store, retrieve, and process data. Charles Babbage conceptualized the first mechanical computer called the Difference Engine in 1822 and later proposed the Analytical Engine, considered the first general mechanical computer. The ENIAC, completed in 1946, was the first fully electronic, general-purpose computer and is considered the first digital computer. Generations of computers progressed from vacuum tubes to transistors to integrated circuits, decreasing in size and power needs while increasing in speed and capabilities over time.