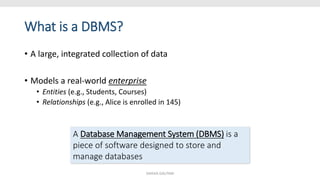
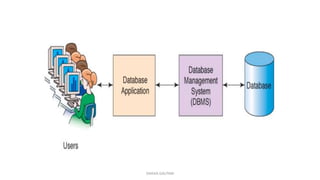
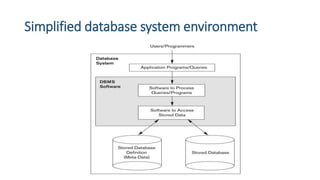
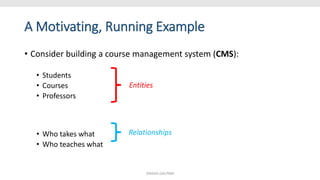
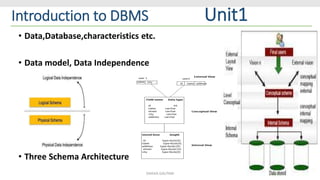
This document provides an overview and introduction to a lecture on database management systems (DBMS). It discusses how companies are increasingly data-driven and how this class will teach the basics of using and managing data. The lecture will cover the motivation for studying DBMS, an overview of the subject, and course logistics. The goal is for students to understand fundamental database concepts and be able to design, query, and build applications with databases.