This document provides an introduction and outline for a course on computer applications. It covers the following topics:
- The course outline includes introductions to information technology, computer hardware and software, operating systems like Windows and Office applications.
- It defines key computer terms like information, technology, hardware, software and provides a brief history of computers from the dark ages to modern computers.
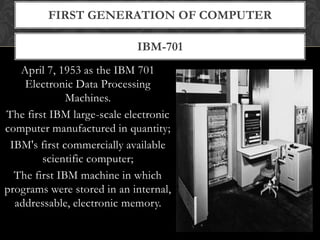
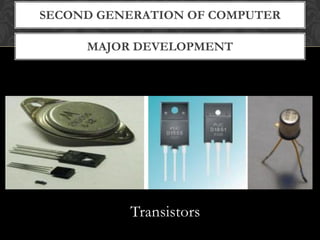
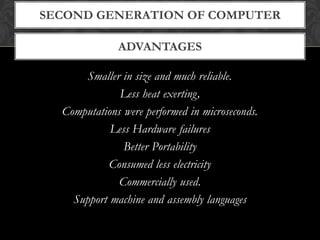
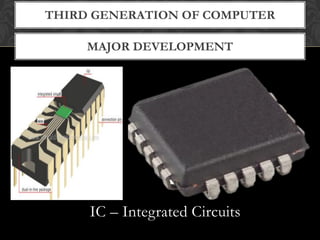
- The document explains the five generations of computers defined by their underlying technologies from vacuum tubes to integrated circuits and microprocessors. Each generation brought improvements in size, cost, reliability and capabilities.
- It provides examples of some representative computers from each generation like ENIAC, IBM 360, personal computers and modern devices. The latest generation