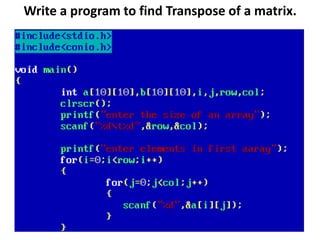
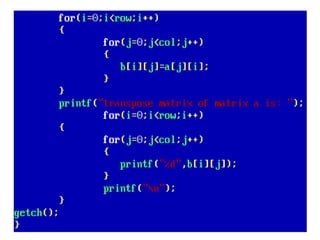
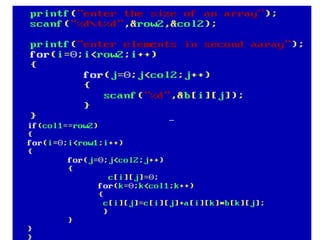
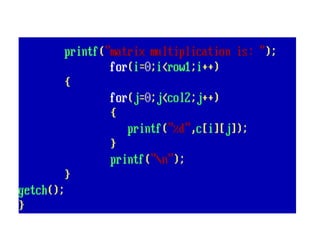
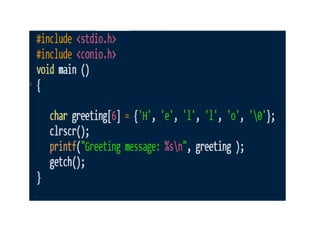
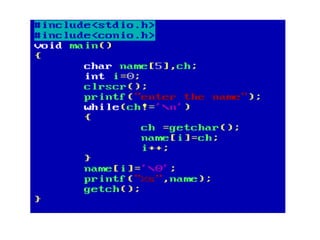
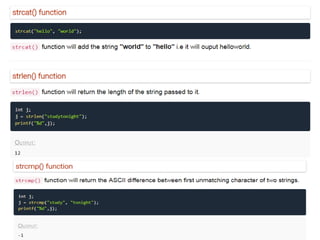
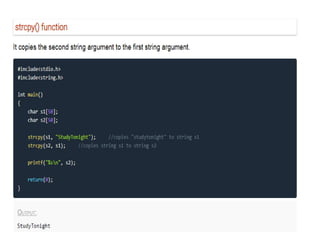
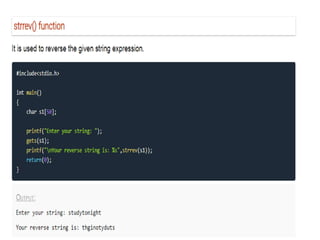
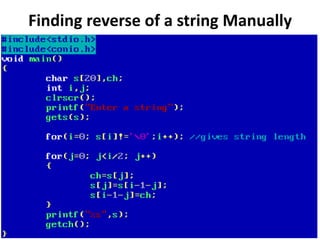
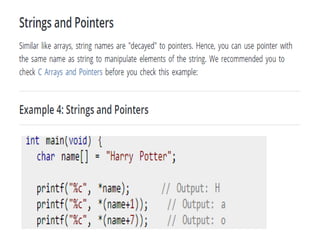
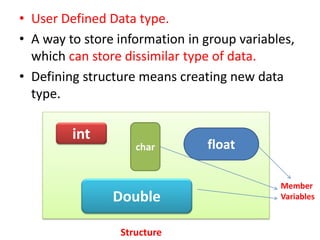
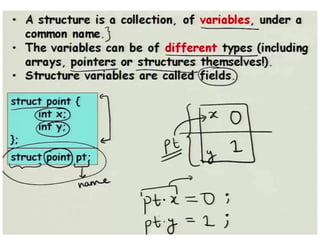
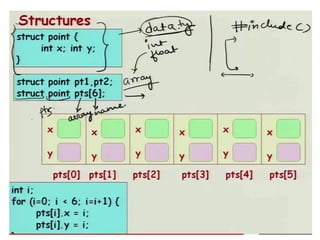
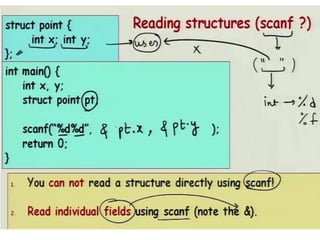
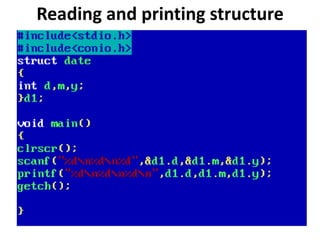
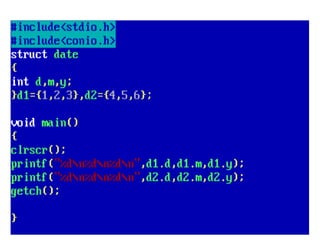
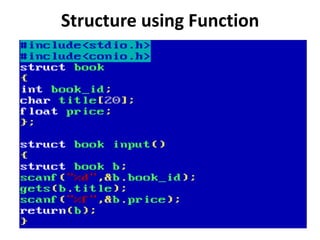
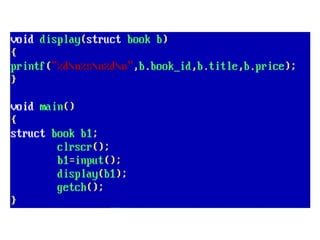
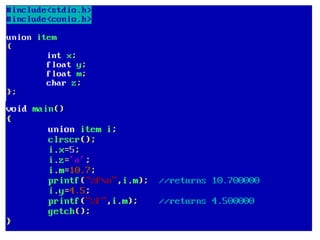
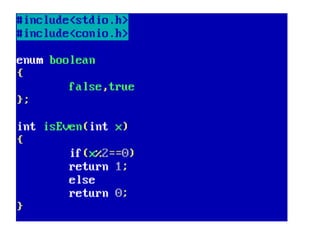
Arrays allow the storage of multiple values of the same type in memory locations next to each other. Arrays must be declared with a size and can then be accessed using indexes. Common array operations include traversal, insertion, deletion, searching and sorting. Two-dimensional arrays, also called matrices, store arrays of data in rows and columns. Strings in C are arrays of characters that end with a null terminator. Structures allow the grouping of different data types under one name. Enumerated types define a list of named integer constants.



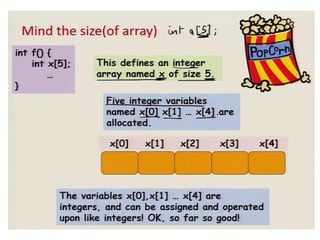
![Declaration of an array
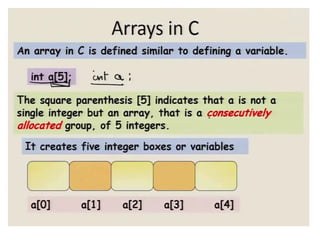
• Array must be declared before use:
data_type array_name [size]
• C does not allow declaring an array whose
number of elements is not known at the time
of compilation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiv-190418111426/85/Unit-4-6-320.jpg)

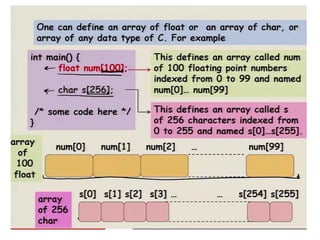

![Initializing an array
• Two ways:
1. int arr[4]={5,0,1,7}
2. int arr[] ={2,8,0,4,7,2}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiv-190418111426/85/Unit-4-13-320.jpg)


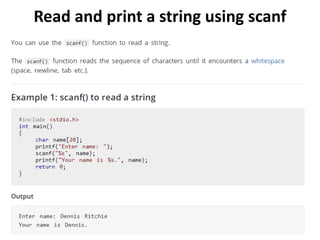
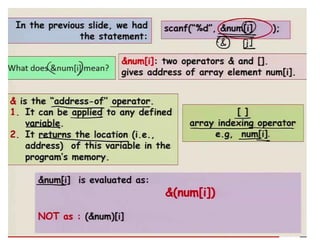
![Reading array elements
• scanf(“%d”, &a*0+);
• scanf(“%d”, &a[1]);
• scanf(“%d”, &a[2]);
• Using loops:
for(i=0; i<=2; i++)
{
scanf(“%d”, &a*i+);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiv-190418111426/85/Unit-4-17-320.jpg)
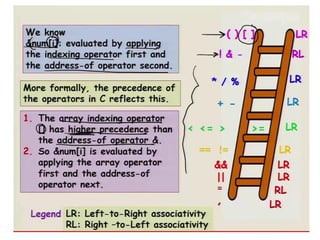
![Printing array elements
• printf(“%d”, a*0+);
• printf(“%d”, a[1]);
• printf(“%d”, a[2]);
• Using loops:
for(i=0; i<=2; i++)
{
printf(“%d”, a*i+);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiv-190418111426/85/Unit-4-20-320.jpg)

![To find the address of a particular
element in an array
• Eg. If base address=2000, each element need
2 bytes, find address of fifth element.
A[5] = 2000+ 2*(5-0) =2010
arr[k] =
Base address (B) + Size of element(W) * (Index of element(K) – Base index)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiv-190418111426/85/Unit-4-22-320.jpg)






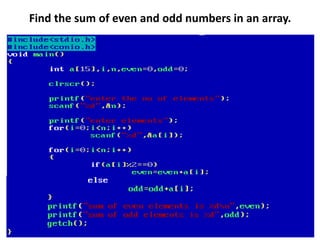


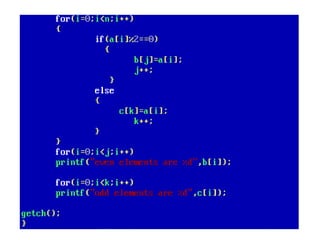

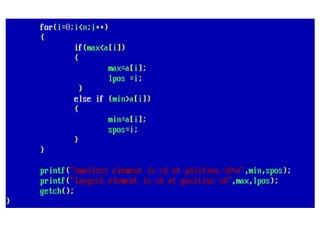

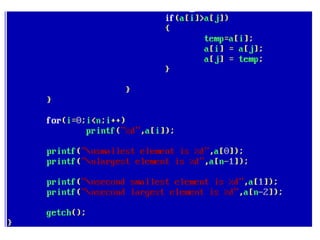

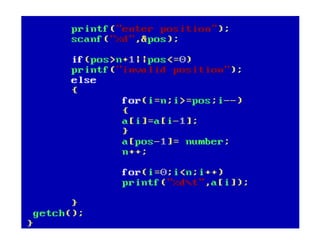

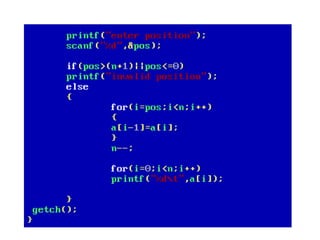


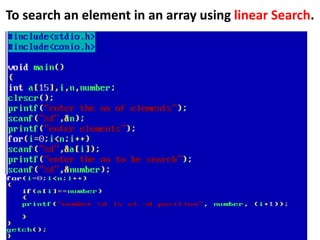

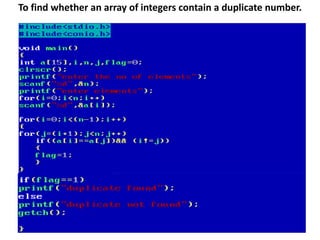
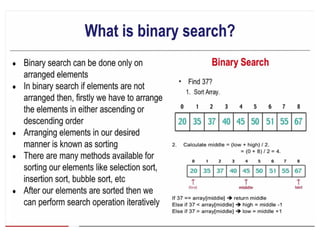
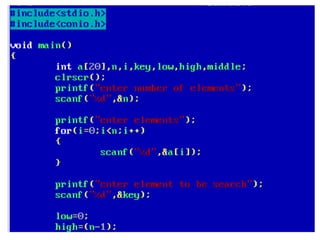
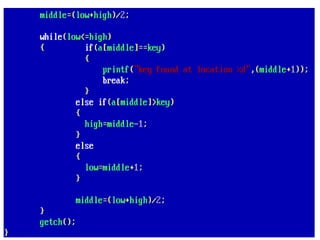


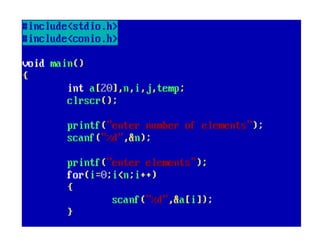
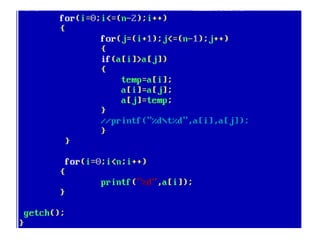

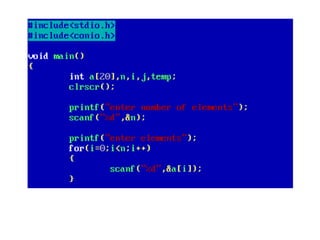
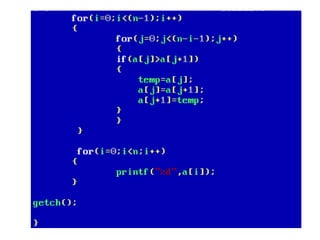

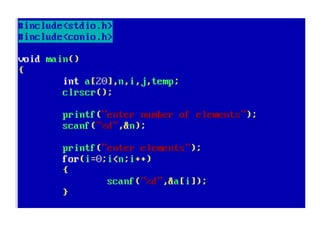
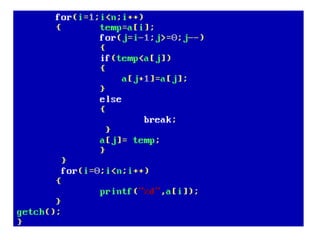

![• An array of arrays is known as 2D array. The two
dimensional (2D) array in C programming is also
known as matrix. A matrix can be represented as
a table of rows and columns.
• A 2D array is stored in the computer's memory
one row following another.
• If each data value of the array requires B bytes
of memory, and if the array has C columns, then
the memory location of an element such as
score[m][n] is (m*c+n)*B from the address of
the first byte.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiv-190418111426/85/Unit-4-62-320.jpg)
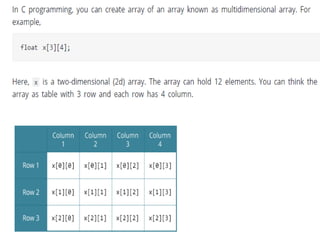
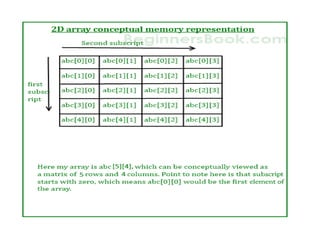
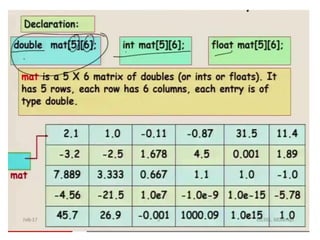
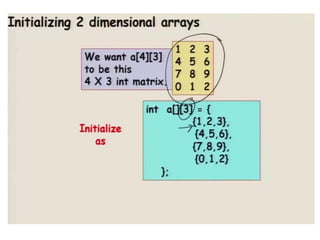
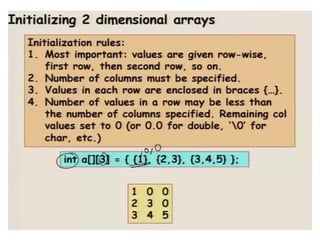
![Initialization of a two dimensional array
• Different ways to initialize two dimensional :
• int c[2][3] = {{1, 3, 0}, {-1, 5, 9}};
• int c[][3] = {{1, 3, 0}, {-1, 5, 9}};
• int c[2][3] = {1, 3, 0, -1, 5, 9};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiv-190418111426/85/Unit-4-66-320.jpg)