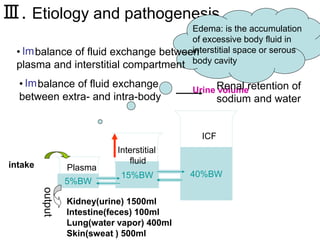
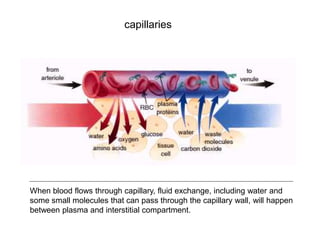
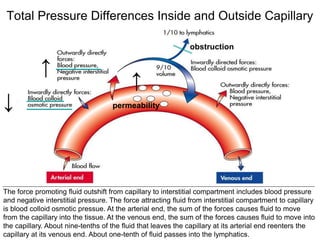
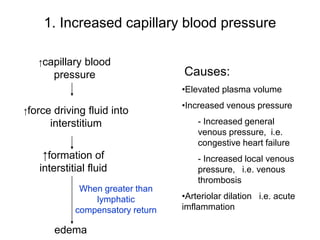
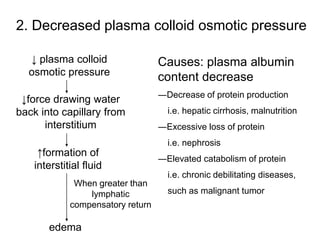
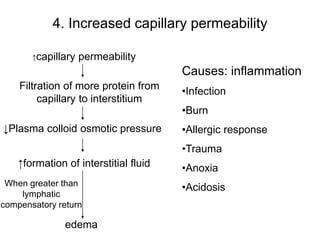
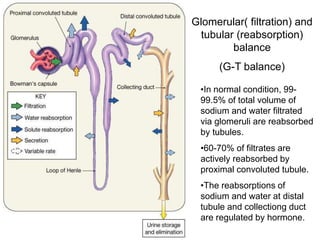
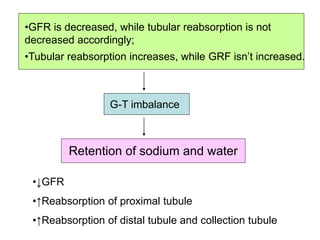
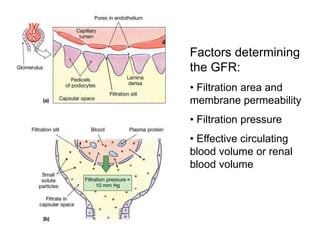
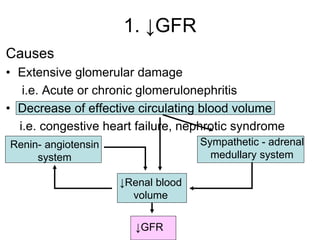
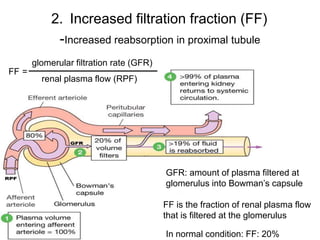
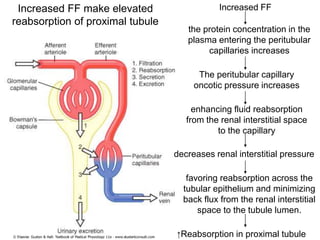
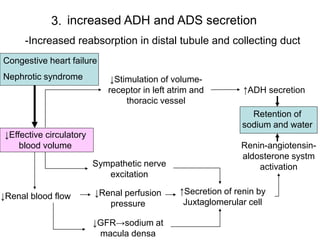
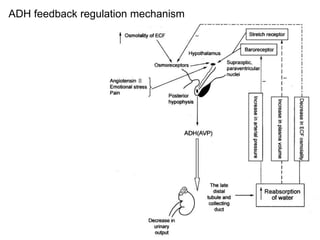
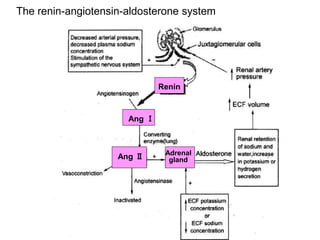
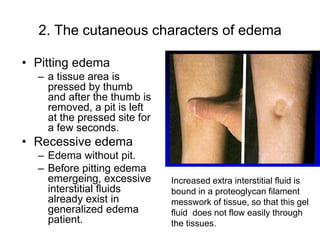
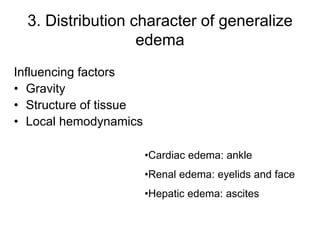
Edema is the accumulation of excessive body fluid in interstitial spaces or serous cavities due to an imbalance in fluid exchange between plasma and tissues. It can be caused by increased capillary permeability, decreased plasma oncotic pressure, renal sodium and water retention, or lymphatic obstruction. Edema fluid characteristics depend on its cause - transudates from normal permeability have low protein while exudates from increased permeability contain cells and protein. Edema affects tissue function and nutrition but can sometimes protect against toxins.