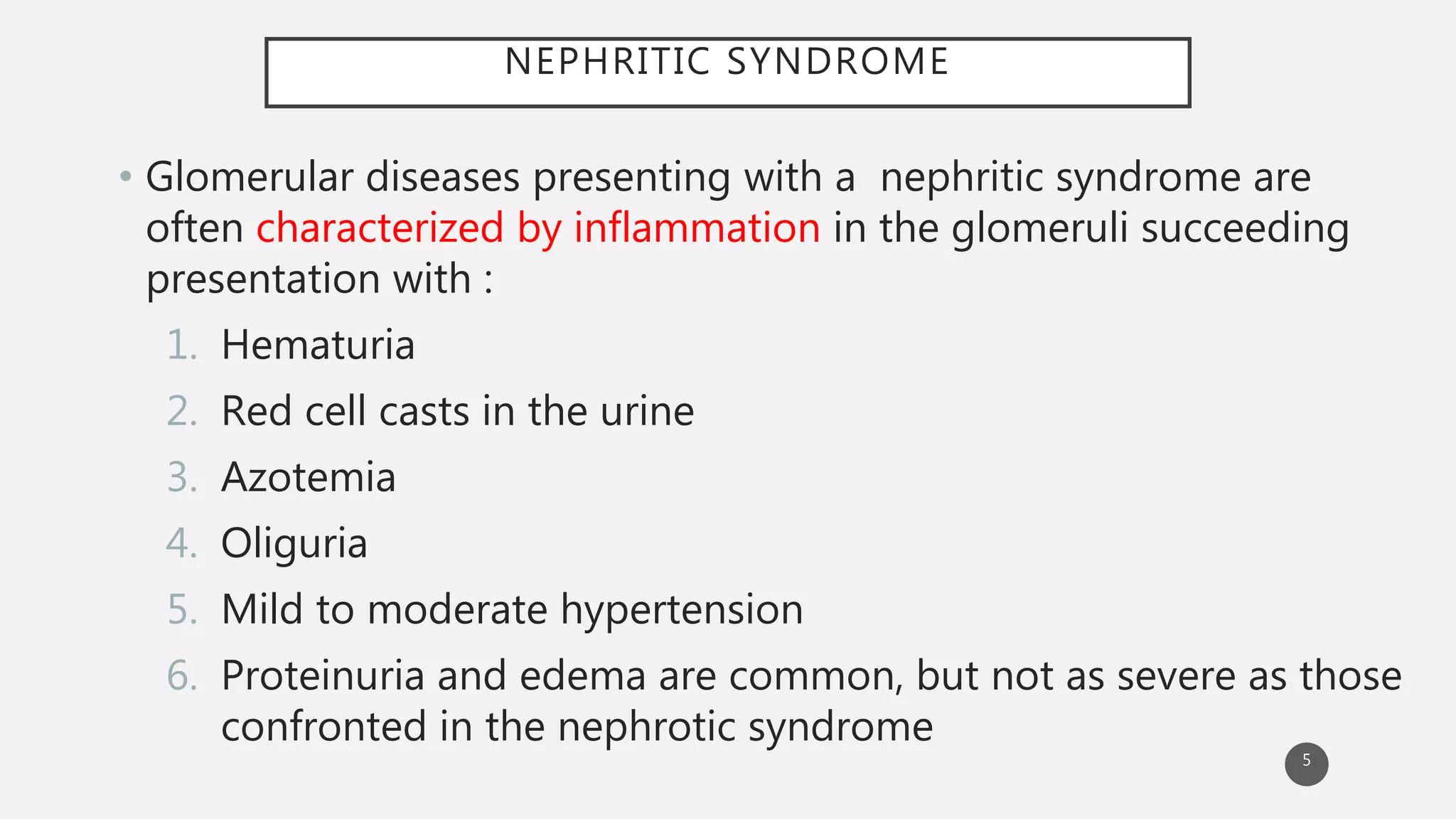
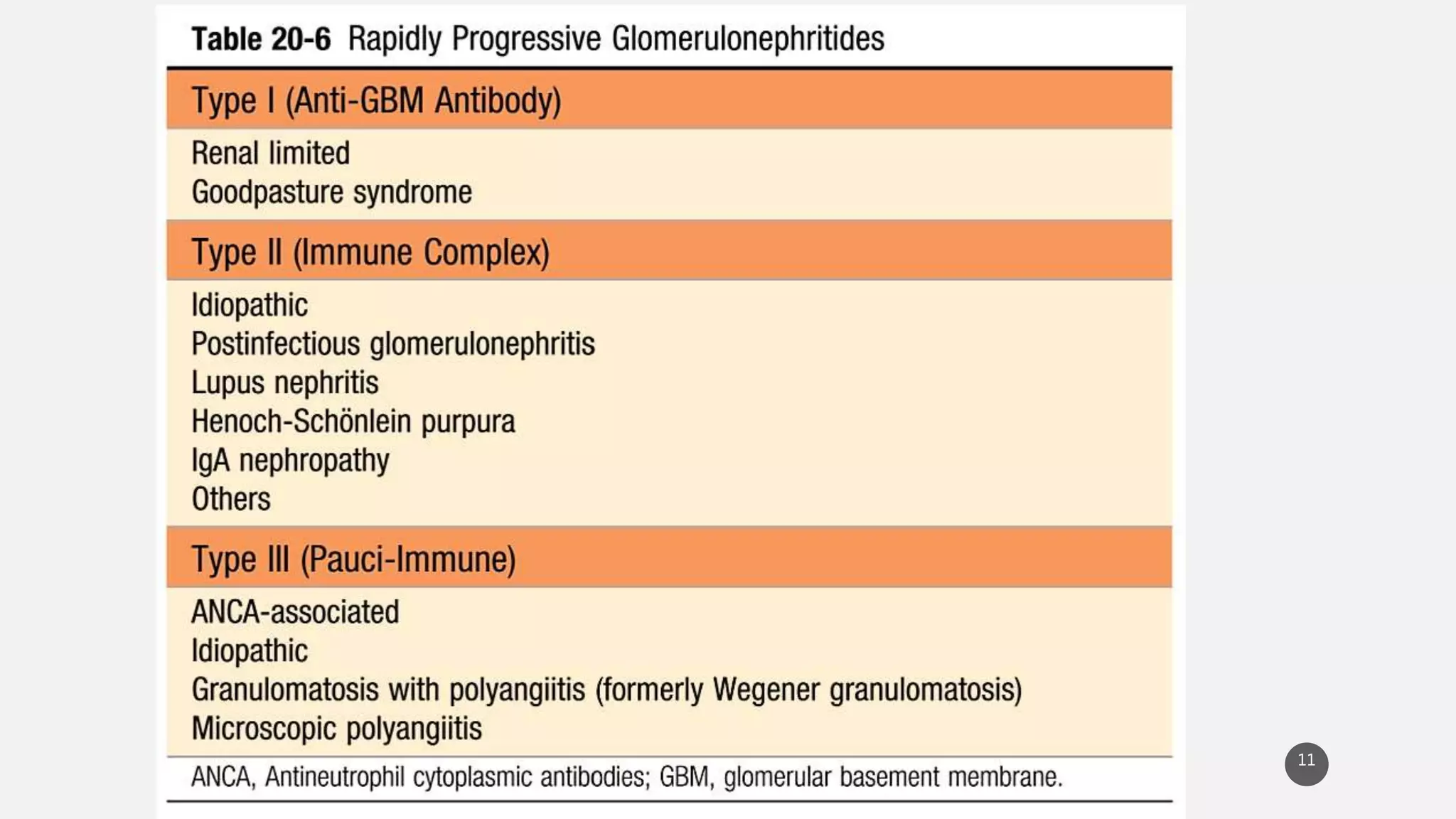
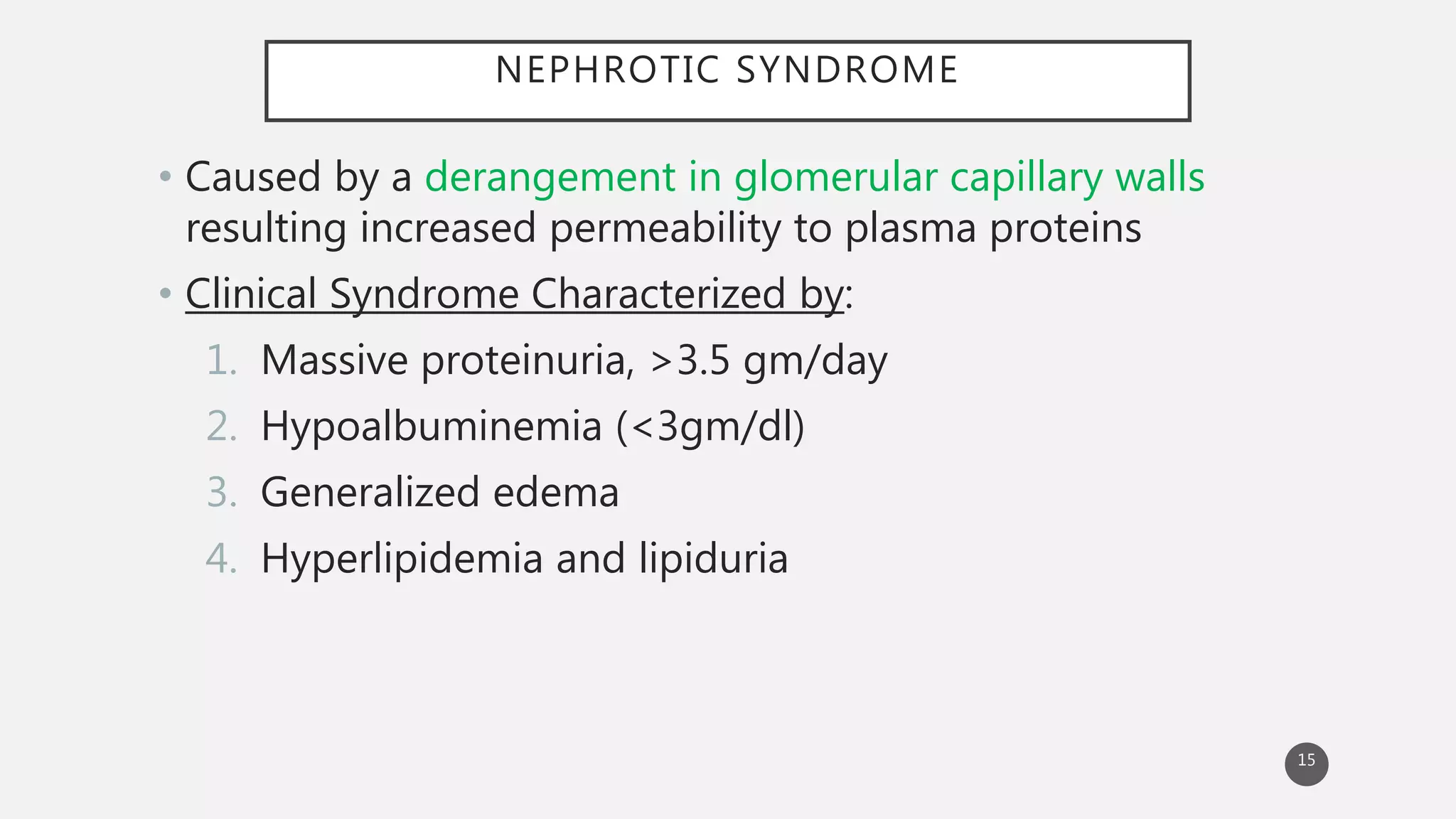
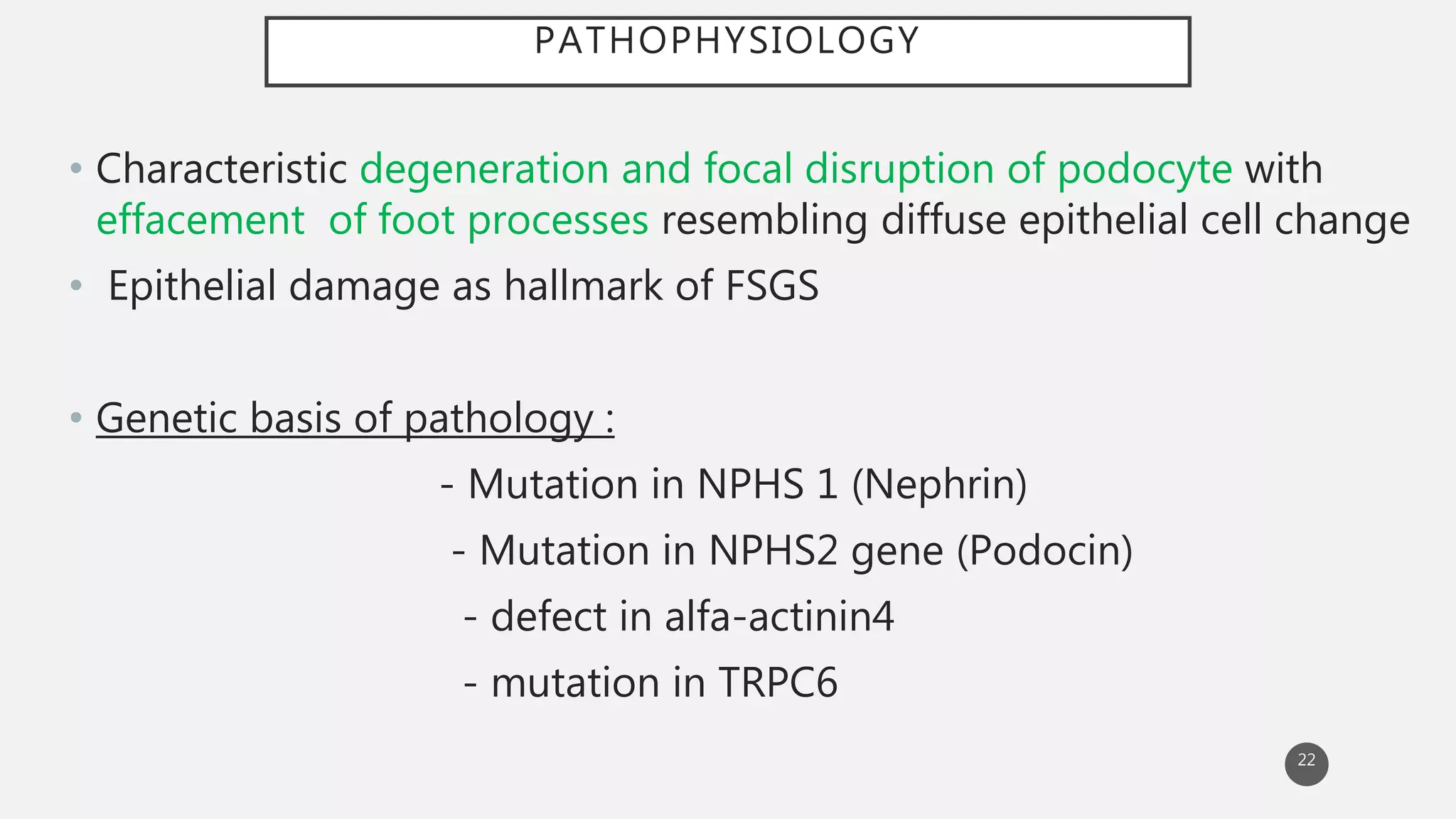
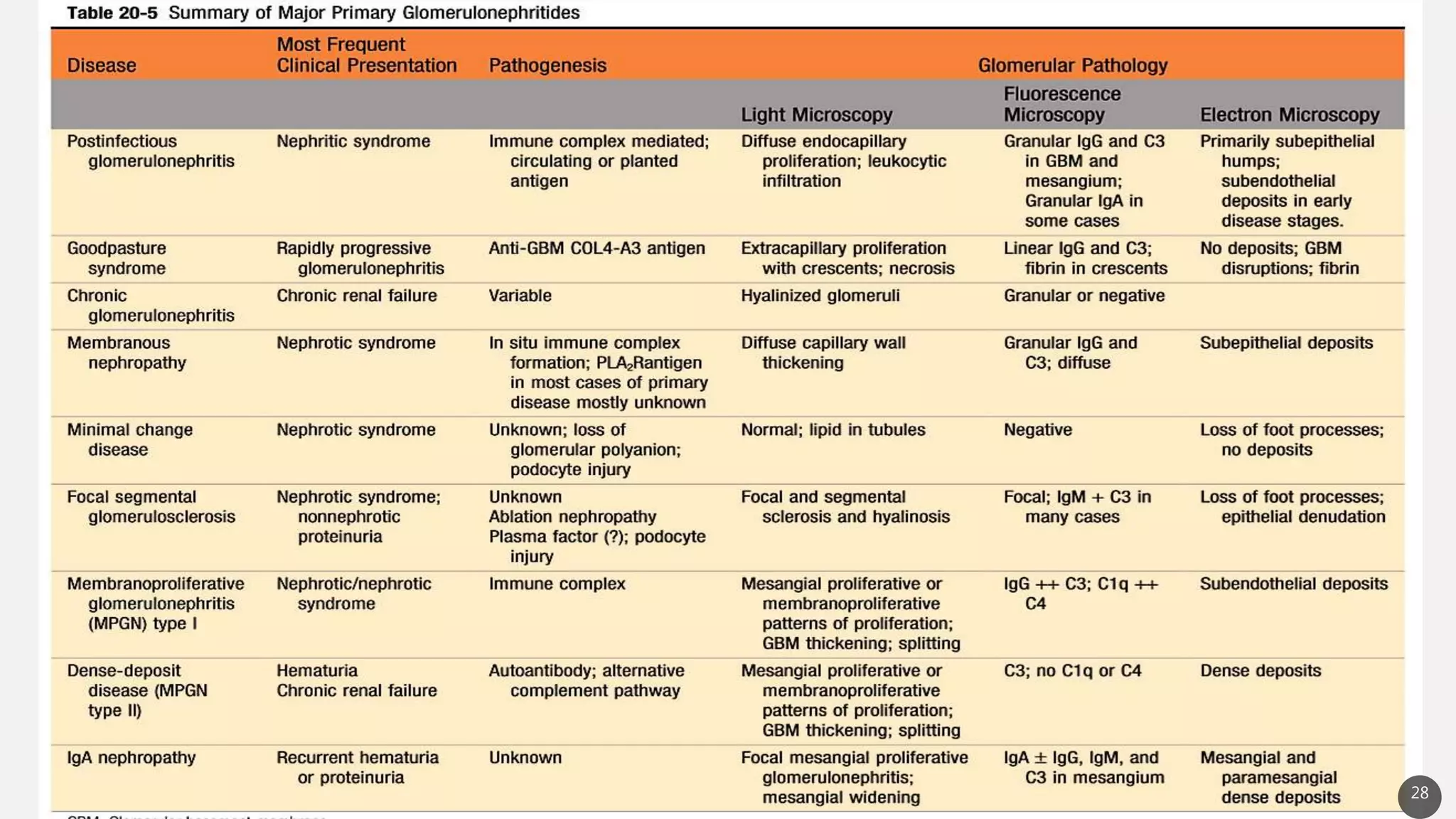
This document provides an overview of nephritic and nephrotic syndrome, describing their pathophysiology and clinical features. Nephritic syndrome is characterized by inflammation of the glomeruli, resulting in hematuria, hypertension, and mild proteinuria. Glomerulonephritis causes include post-streptococcal and rapidly progressive crescentic glomerulonephritis. Nephrotic syndrome is caused by increased glomerular permeability, leading to massive proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, edema, and hyperlipidemia. Specific causes discussed include minimal change disease, membranous nephropathy, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, and membranoproliferative glomerulone