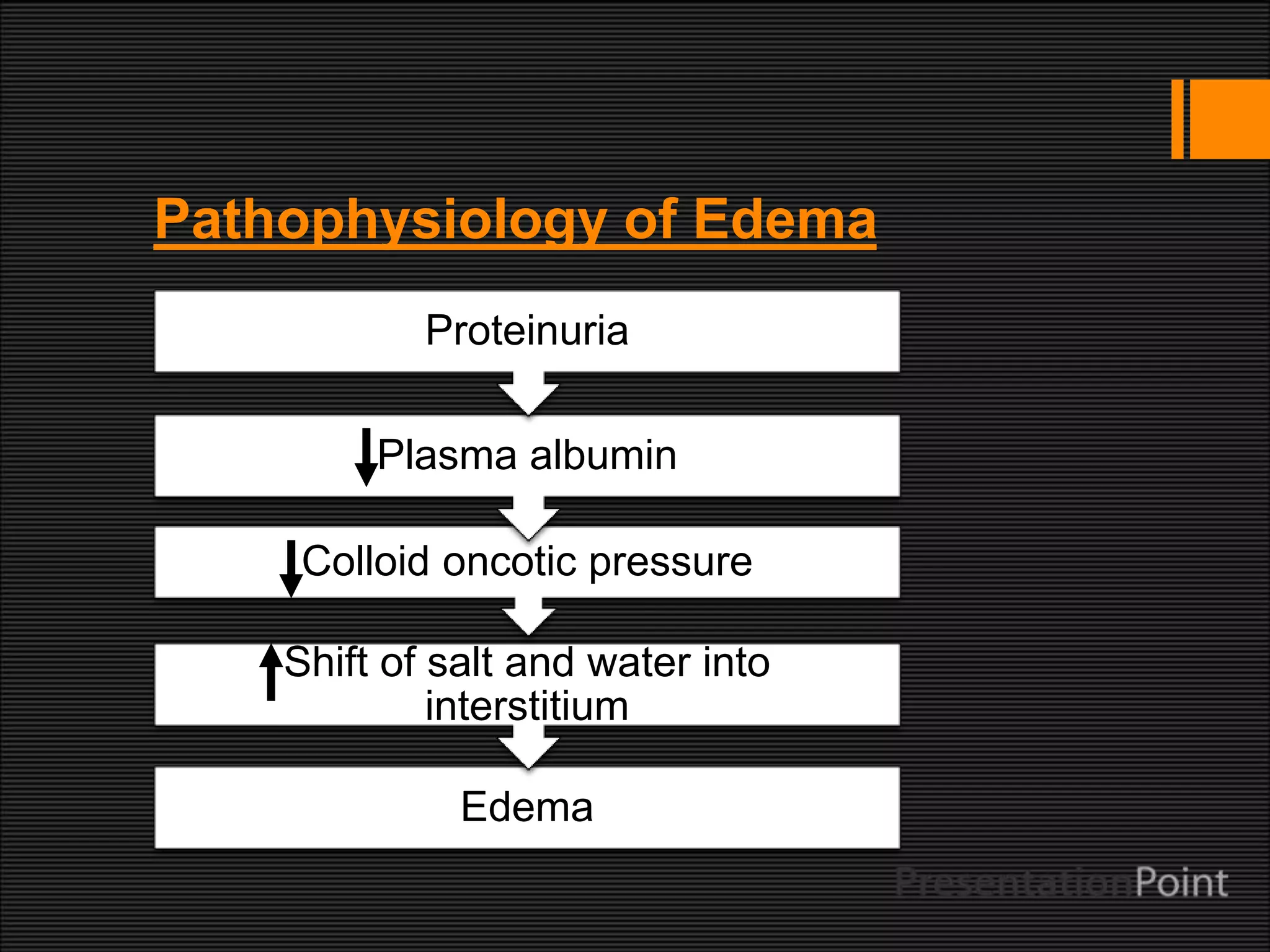
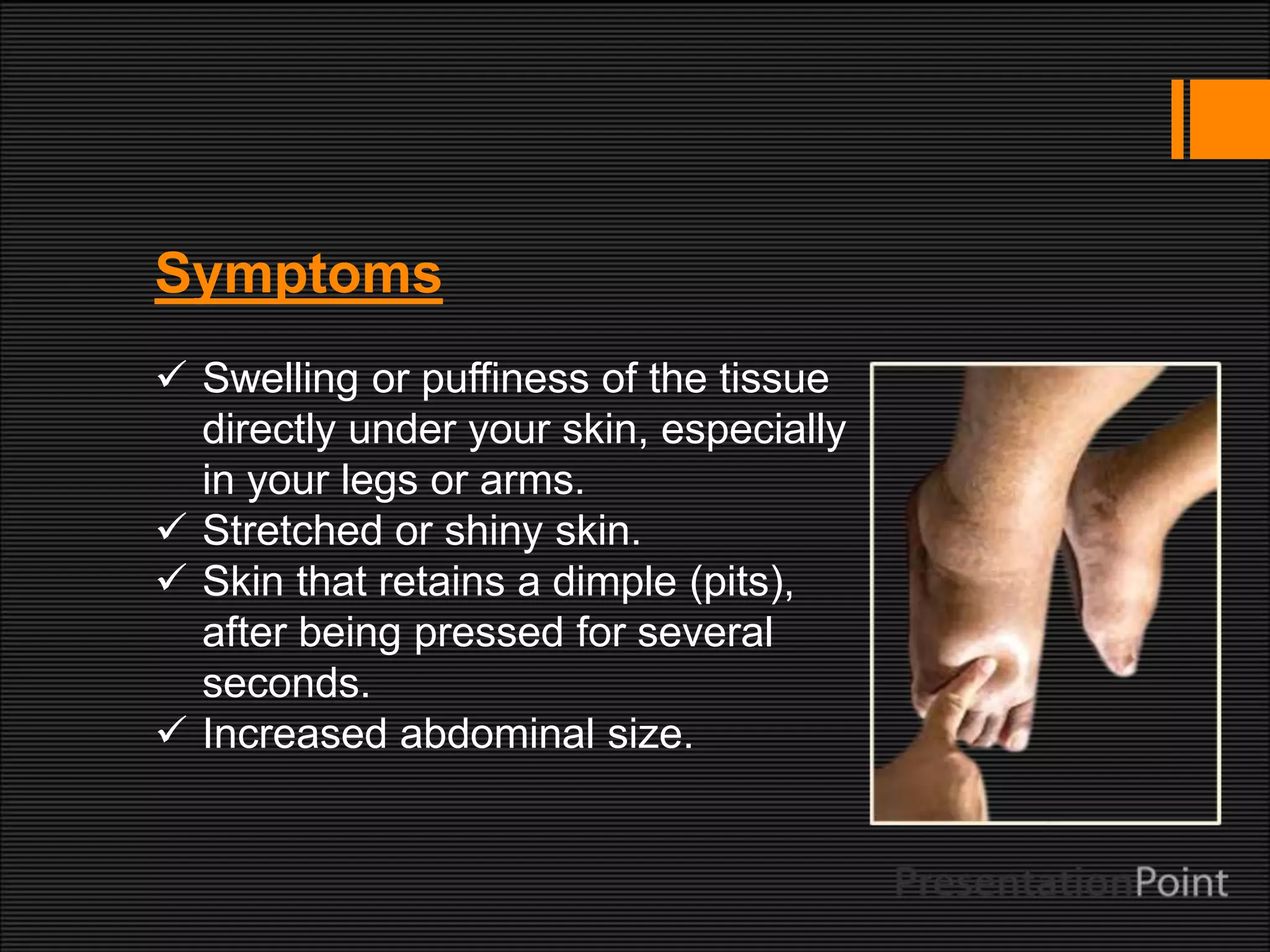
The presentation on edema discusses its definition, types, and underlying causes, which include increased hydrostatic pressure and lymphatic obstruction. It outlines symptoms such as swelling, pitting, and increased abdominal size, as well as complications like respiratory arrest. Treatment options focus on minimizing fluid buildup through various methods, managing pain, and making lifestyle adjustments.