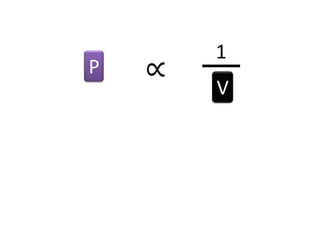
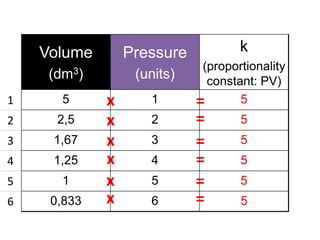
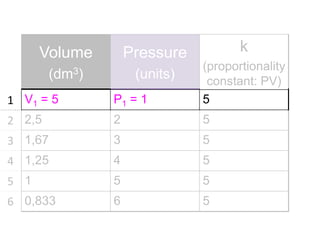
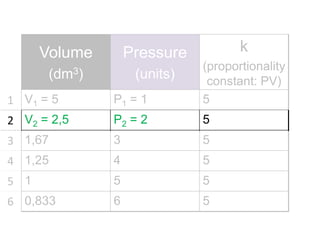
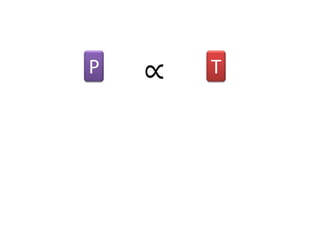
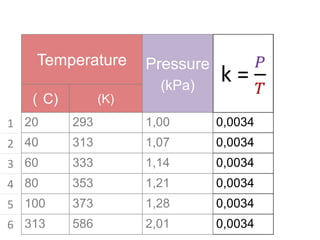
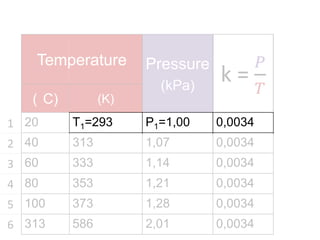
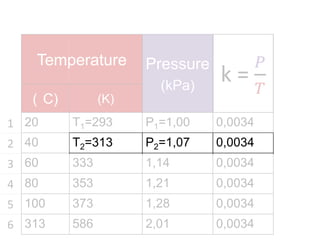
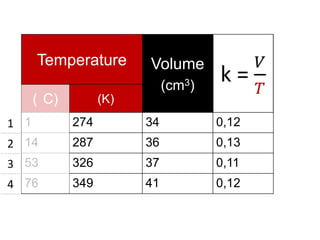
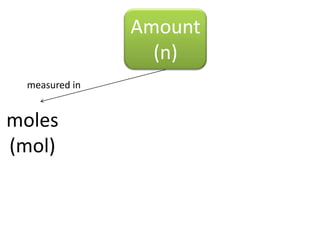
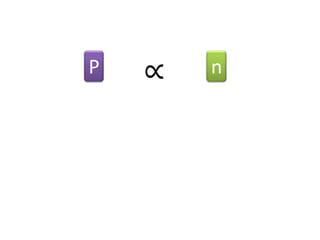
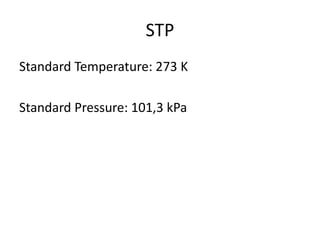
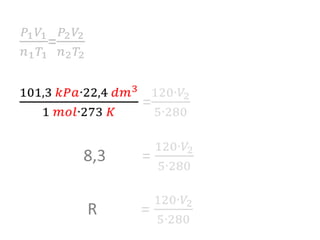
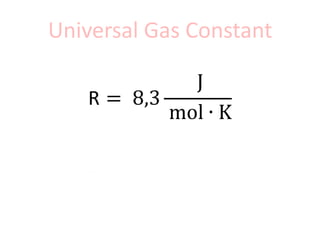
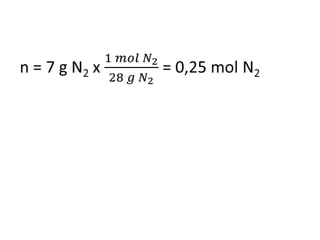
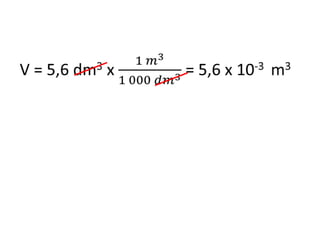
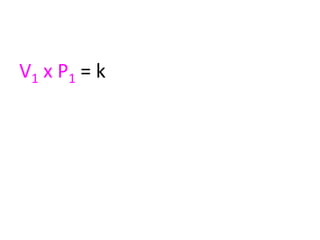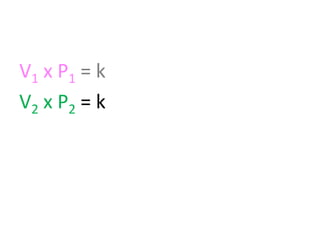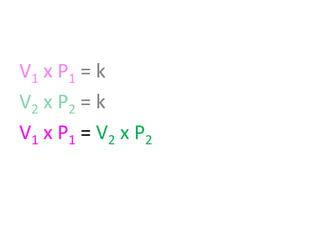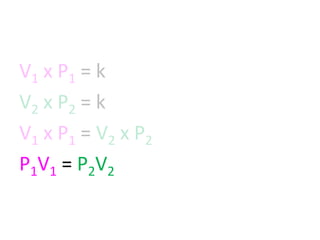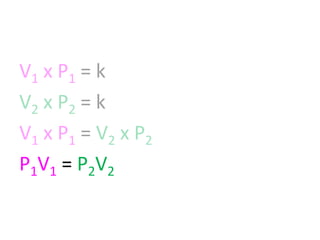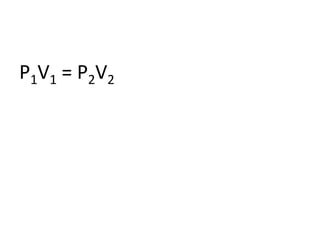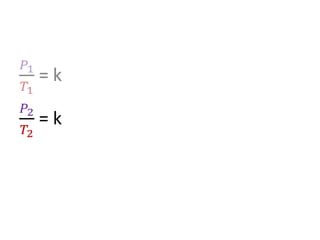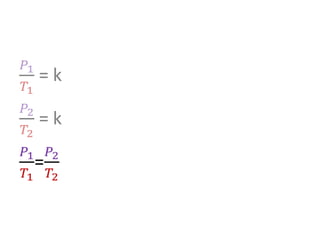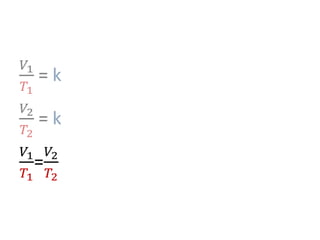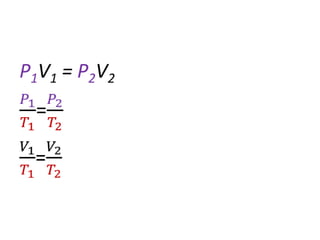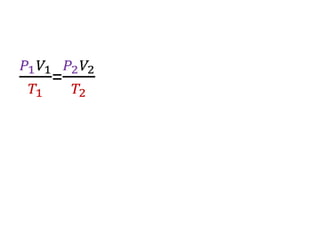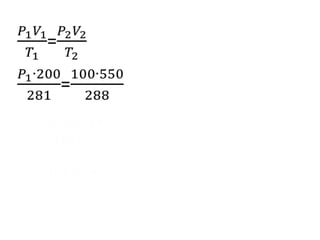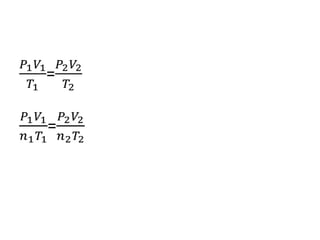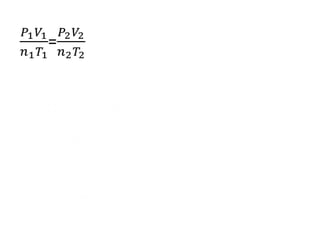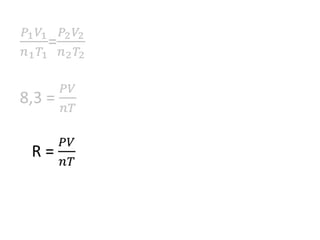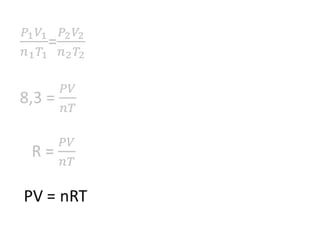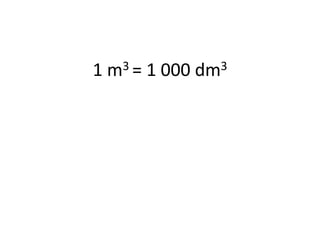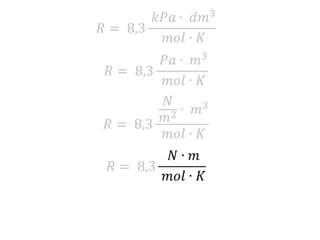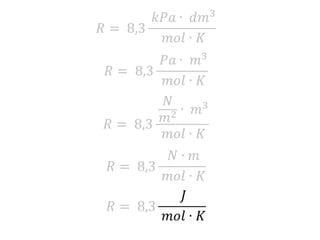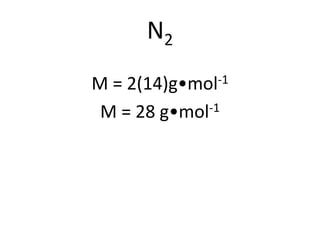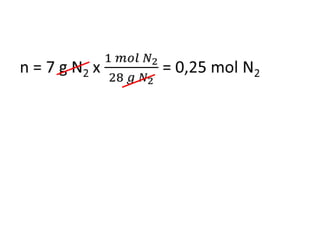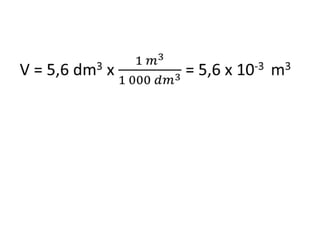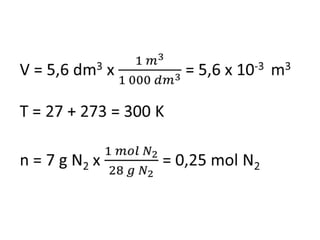The document discusses gas laws including Boyle's law, Charles' law, and the general gas equation. It provides sample data and calculations to illustrate these laws. Specifically, it shows how volume and pressure are inversely proportional based on Boyle's law. It also demonstrates how volume and temperature are directly proportional based on Charles' law. The general gas equation combines these relationships as PV=nRT. Sample questions at the end apply this equation to calculate pressure, volume, temperature or amount of a gas.