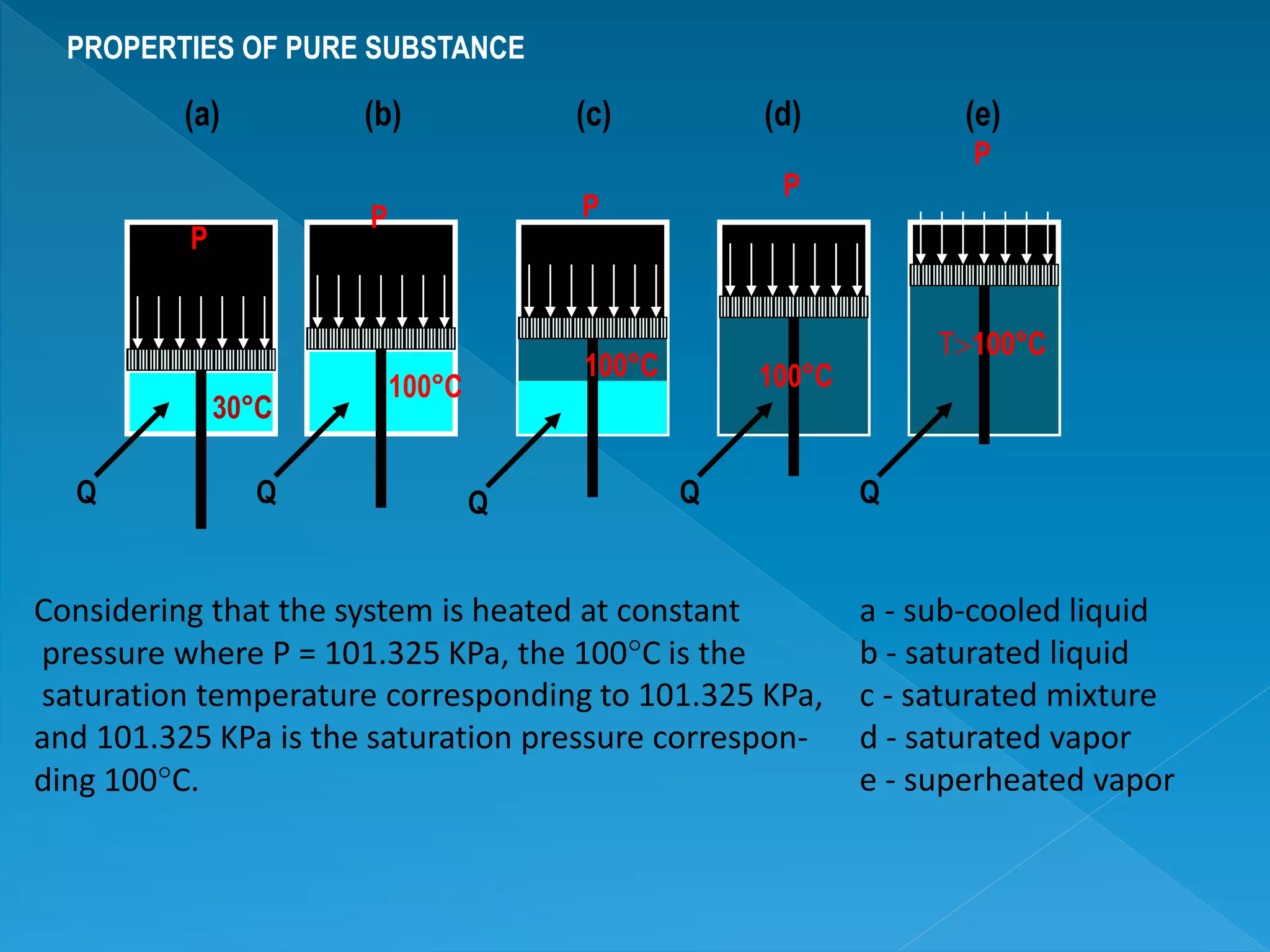
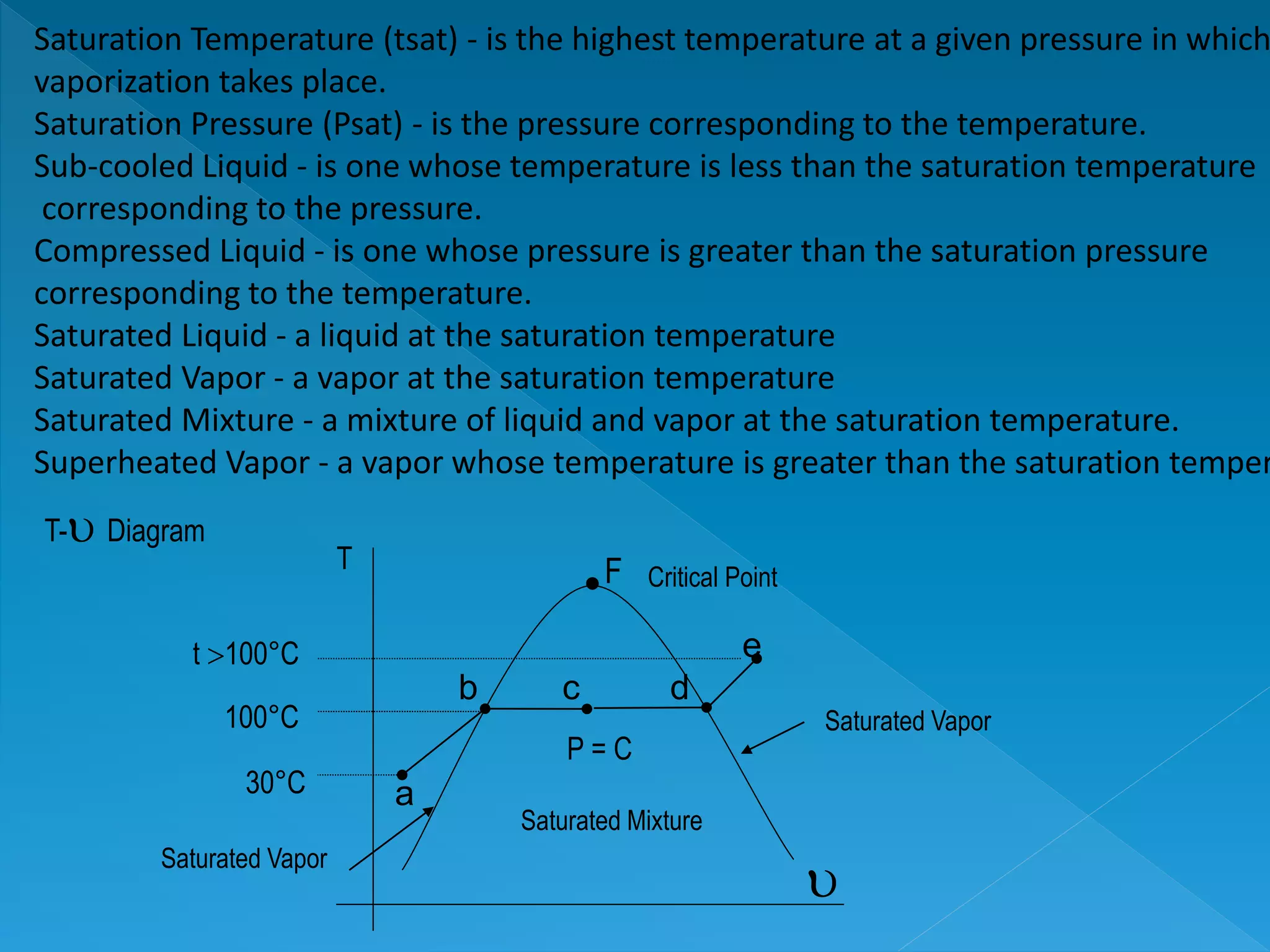
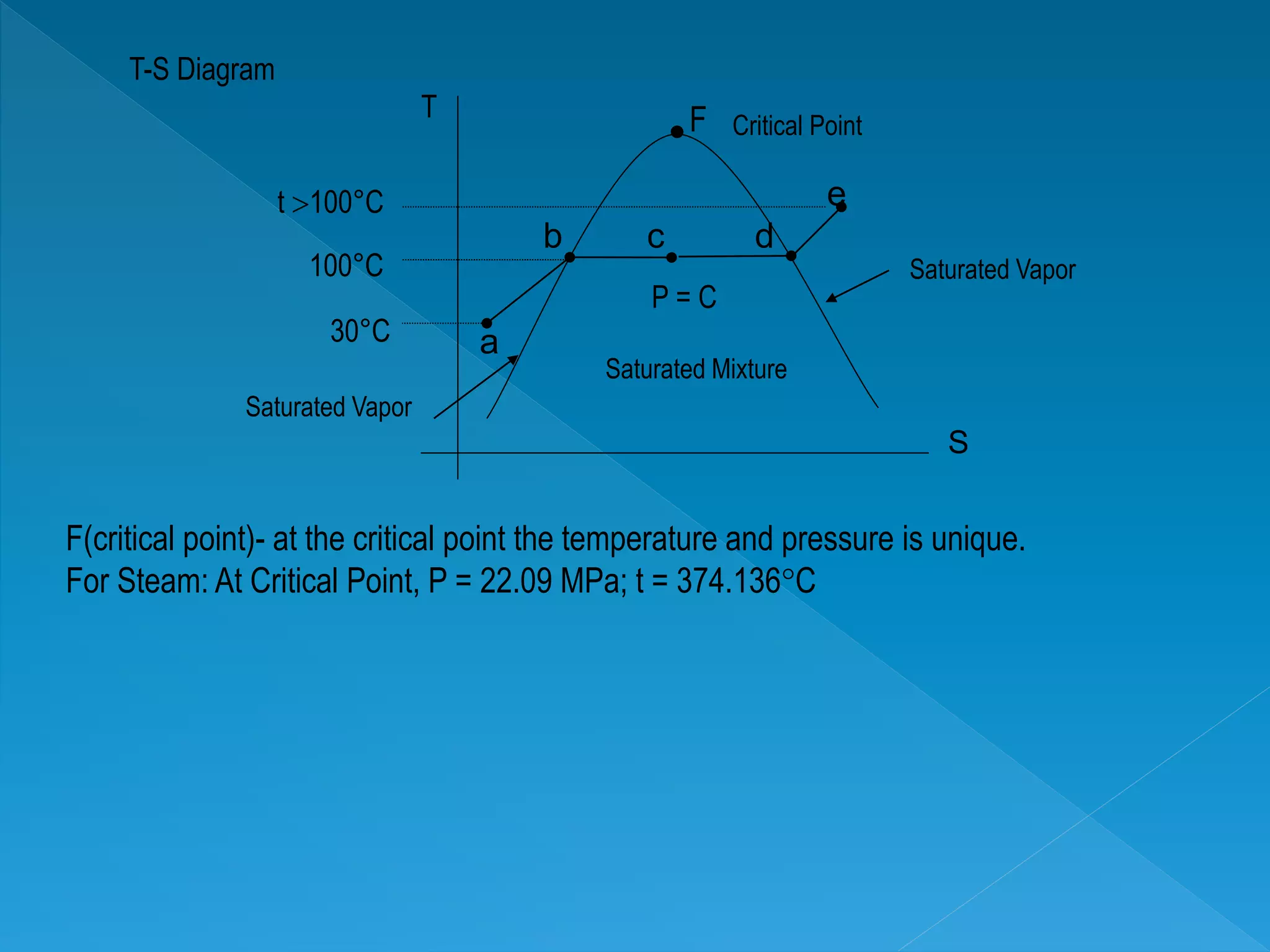
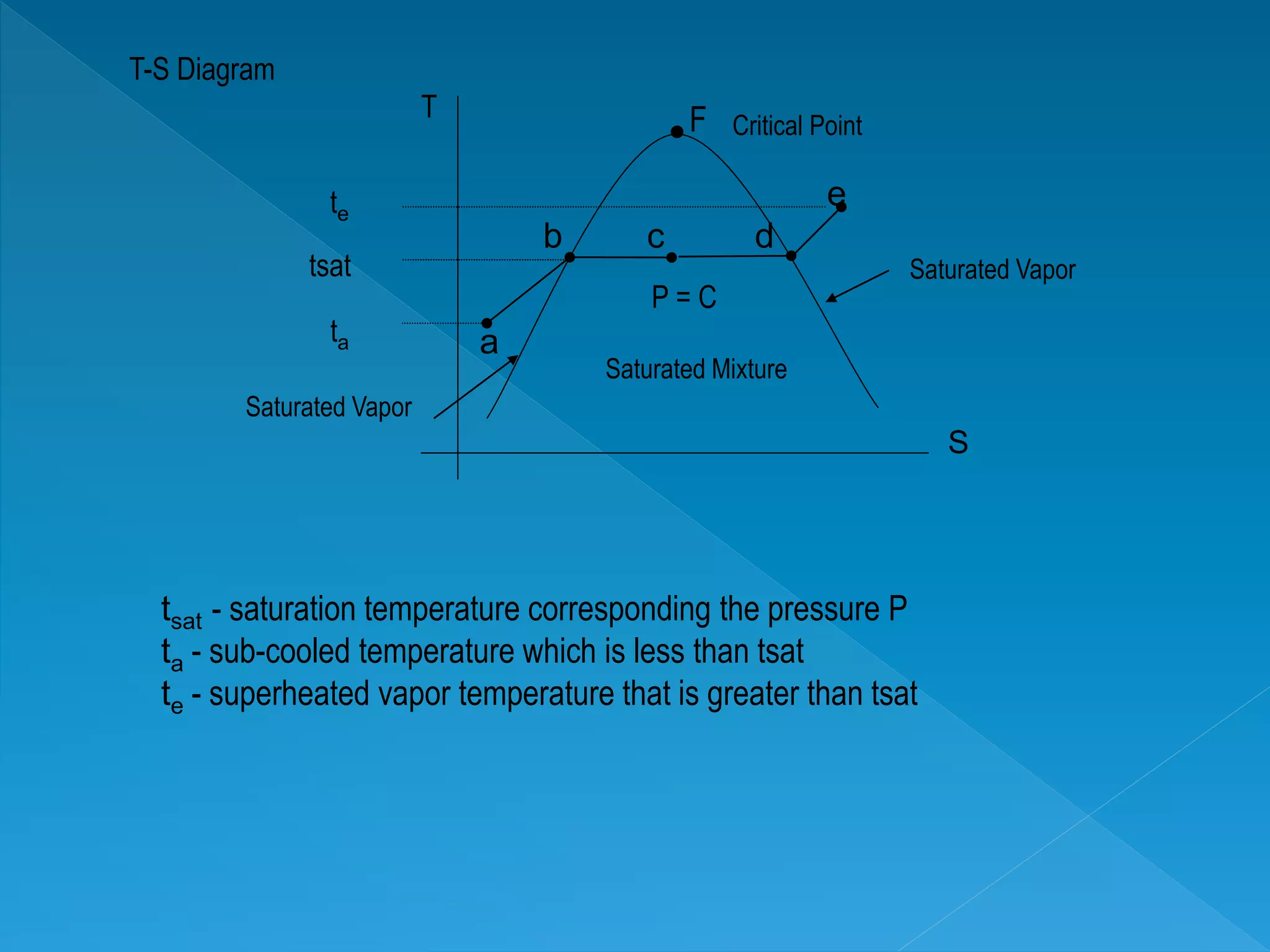
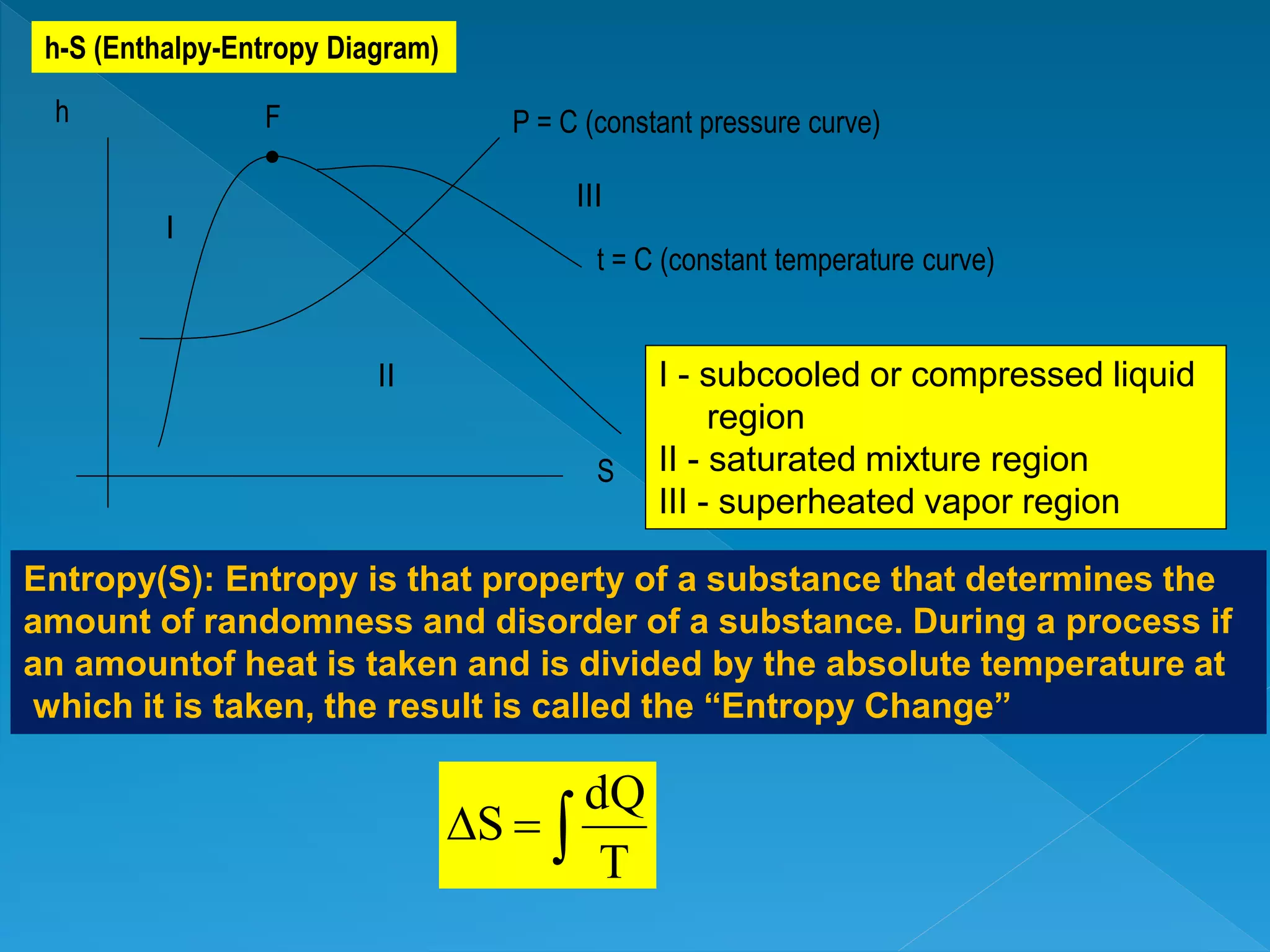
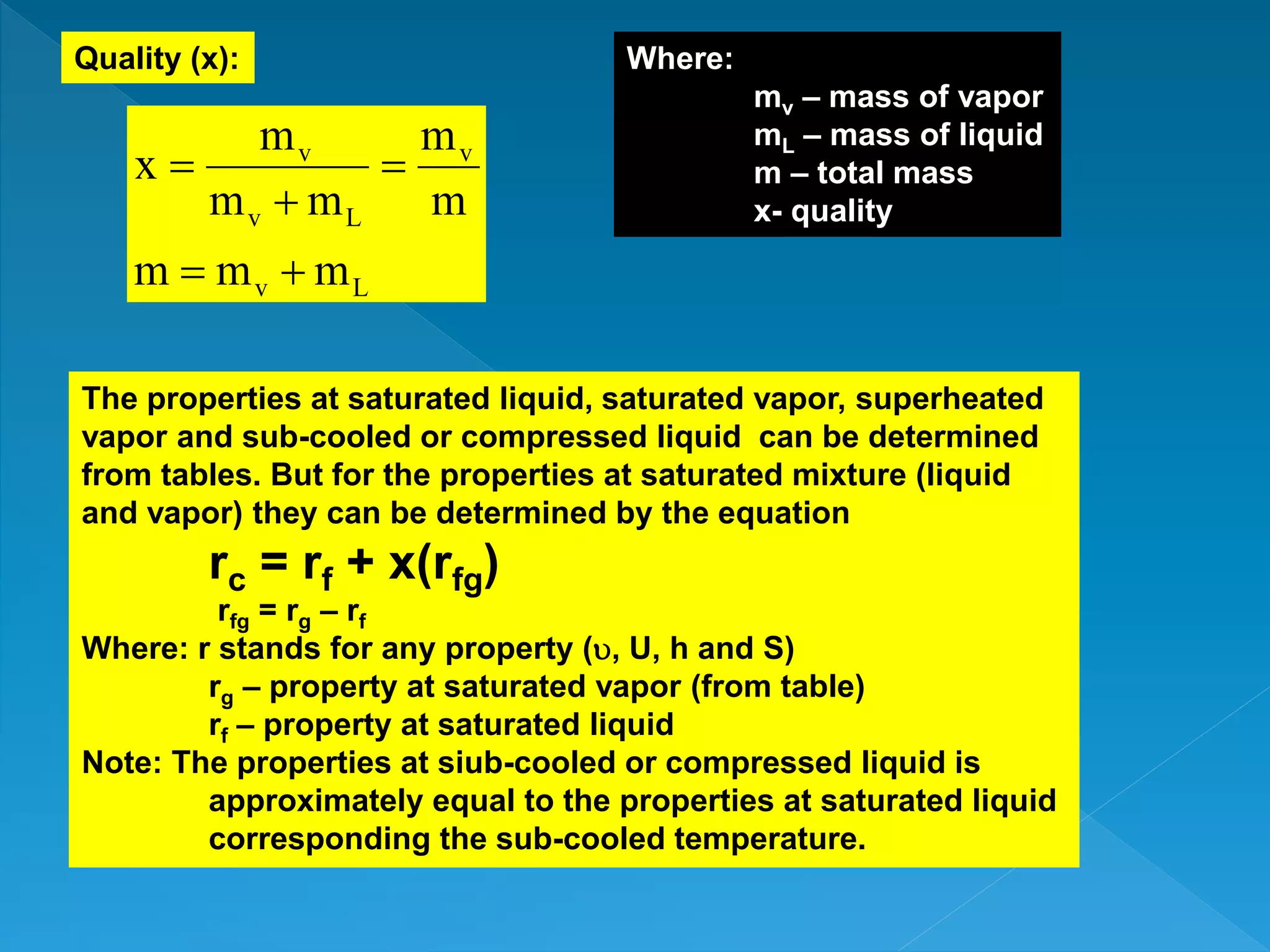
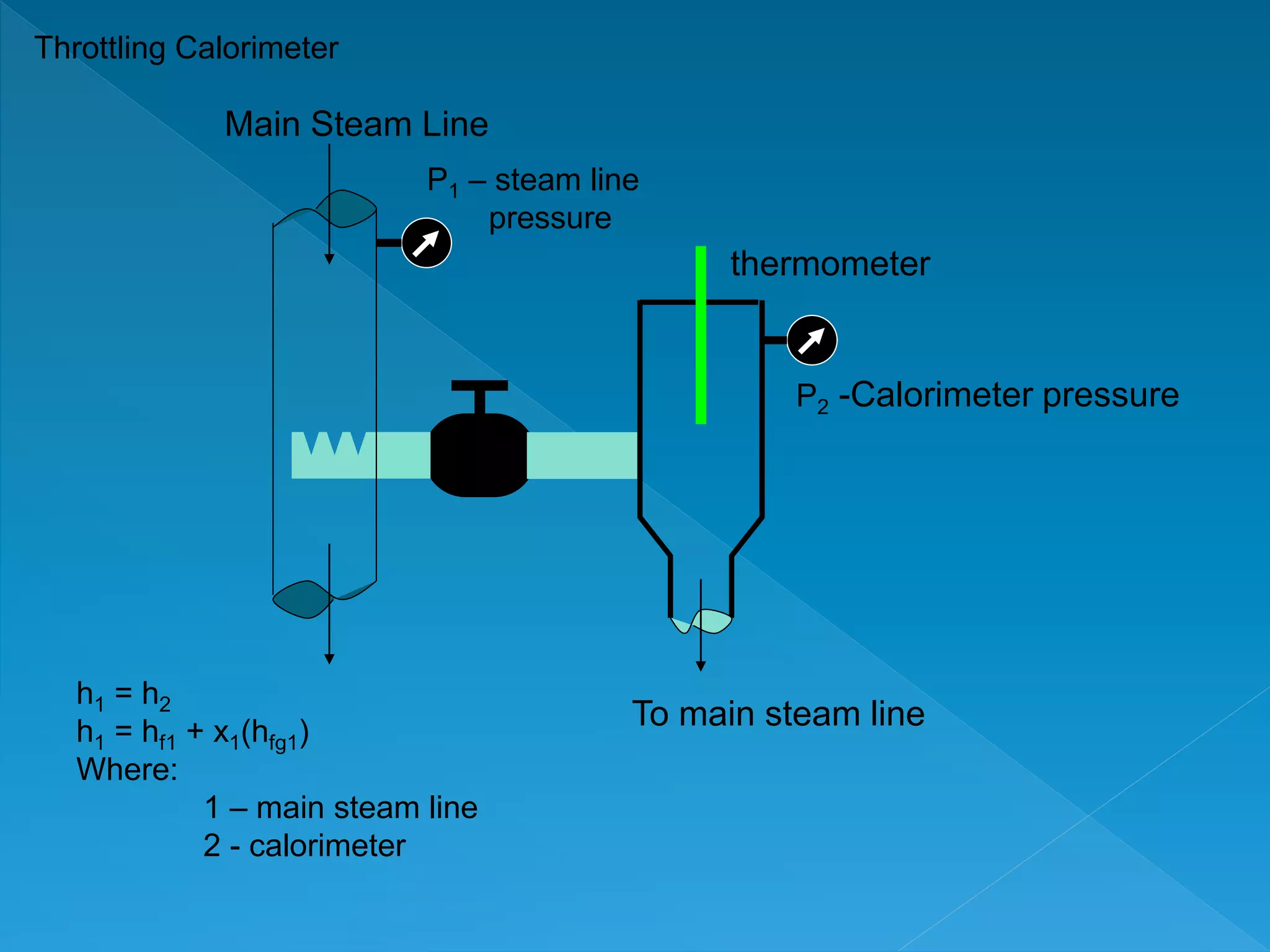
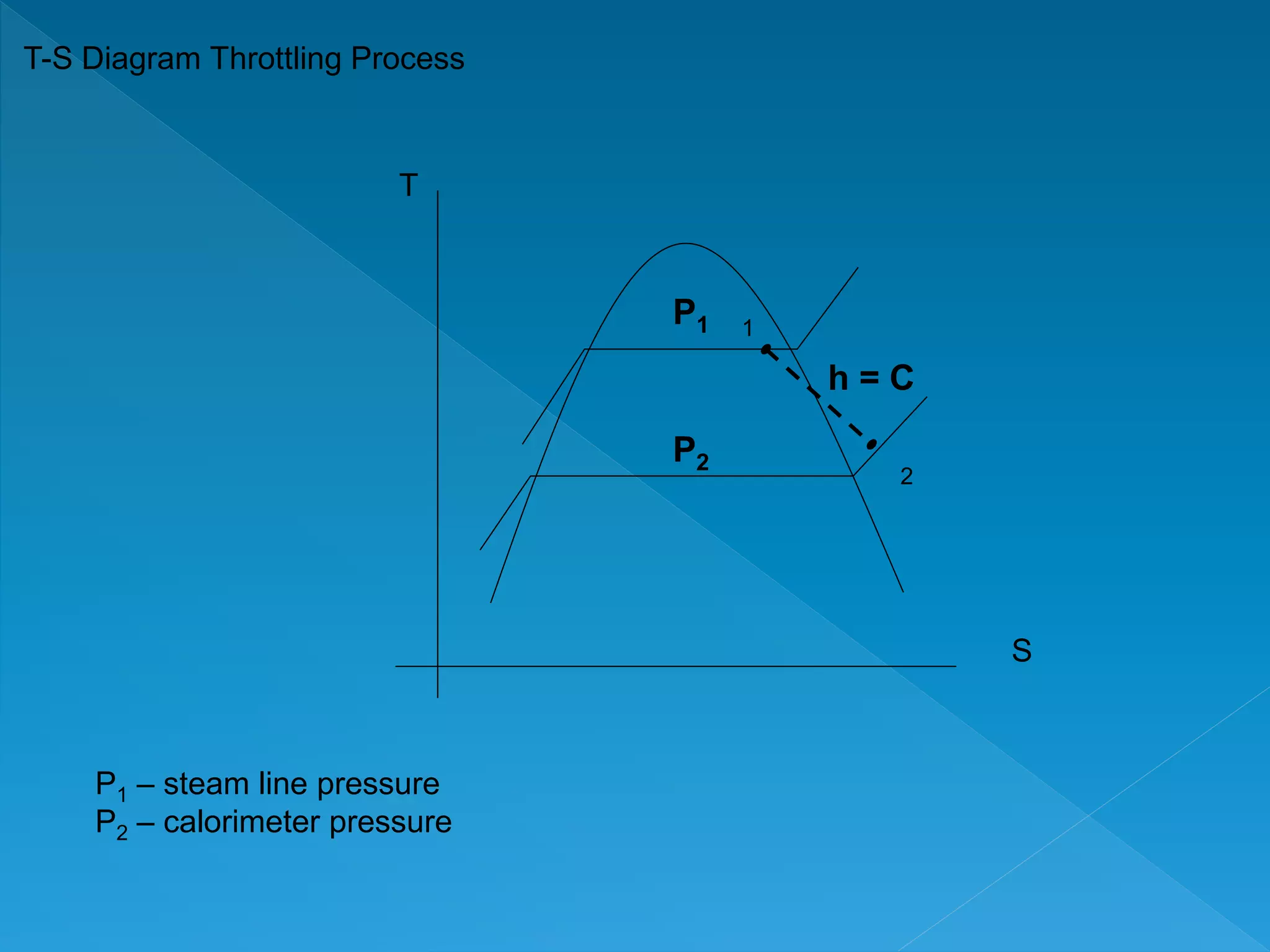
This document discusses the properties of pure substances during phase changes. It defines key terms like saturation temperature, saturation pressure, sub-cooled liquid, saturated liquid, saturated vapor, and superheated vapor. The document explains that 100°C is the saturation temperature corresponding to a pressure of 101.325 kPa. It also provides diagrams to illustrate the different regions on a T-S and h-S chart during phase changes and defines concepts like quality.