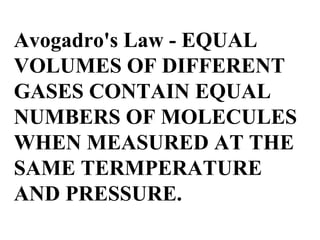I. Gases assume the shape and volume of their container, are highly compressible, and mix evenly when confined together. They have lower densities than liquids or solids.
II. Gases were the first state of matter studied in detail. Their behavior can be described by simple mathematical equations that generally apply over certain temperature and pressure ranges. The study of gases provided evidence that matter is composed of particles rather than being continuous.
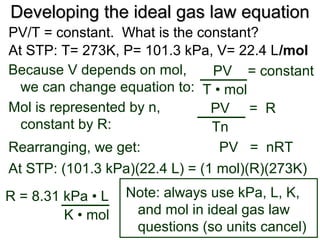
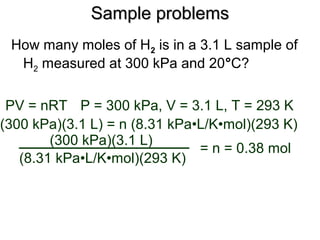
III. The measurable properties of gases are mass (moles), pressure, volume, and temperature (which must be in Kelvin). Various gas laws describe the relationships between these properties, and the ideal gas law combines these individual laws into one equation.