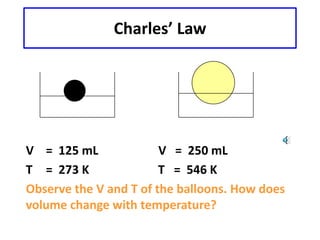
1) This document discusses Charles' Law and how it relates the volume of an ideal gas to its temperature when pressure is held constant. Charles' Law states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature.
2) An example problem demonstrates how to use the Charles' Law equation to calculate the volume of a gas at a different temperature given its initial volume and temperature.
3) Learning checks are included to test understanding of Charles' Law and how the volume and temperature of a gas are related at constant pressure.