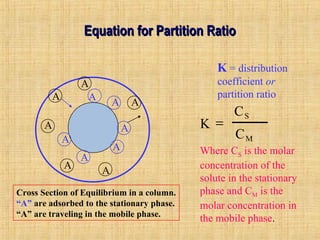
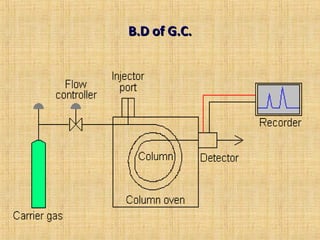
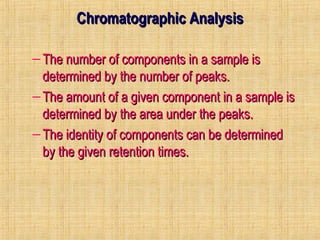
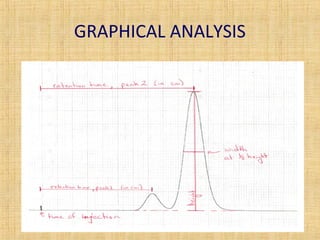
This document provides an overview of gas chromatography. It describes the basic chromatographic process of partitioning between a mobile and stationary phase. Key aspects covered include common types of chromatography, how chromatography works using partition coefficients, criteria for analyzing compounds via gas chromatography, and separation techniques. Applications of gas chromatography such as qualitative and quantitative analysis are also discussed.