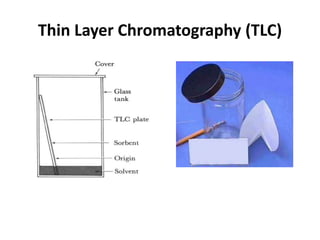
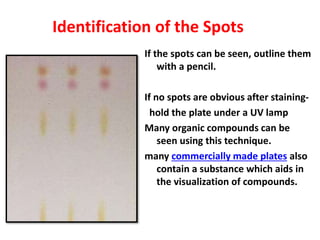
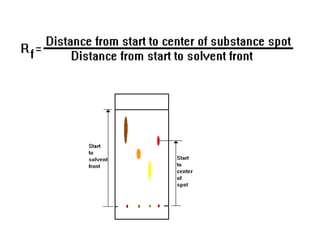
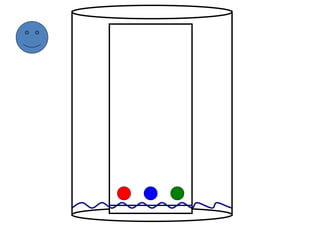
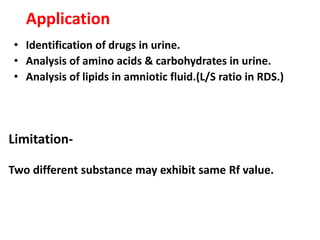
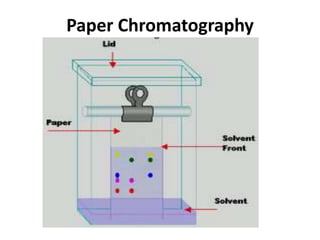
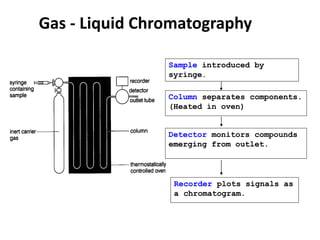
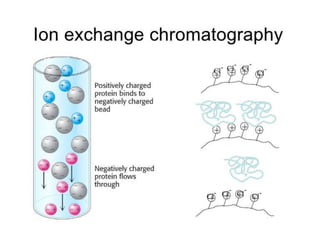
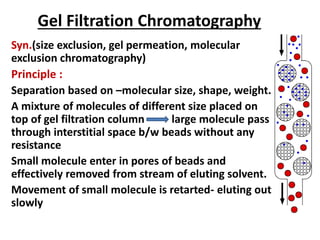
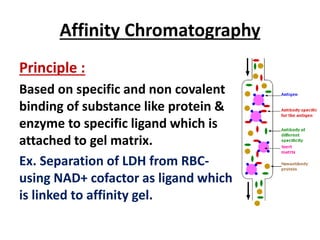
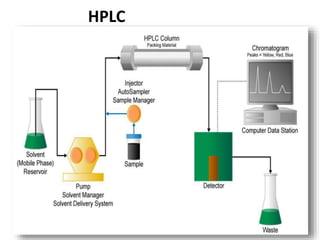
Chromatography is a physical separation technique that separates the components of a mixture based on their interactions with two phases - a stationary phase and a mobile phase. Mikhail Tswett discovered chromatography in 1906 while separating plant pigments. Chromatography has many applications and has contributed to 12 Nobel prizes between 1937-1972. There are several types of chromatography classified by the mobile phase (liquid, gas), stationary phase (thin layer, paper, column), or separation force (adsorption, partition, ion exchange, gel filtration, affinity). High performance liquid chromatography uses high pressure to allow for faster separation over minutes versus hours with other techniques. Chromatography techniques like thin layer chromatography, gas chromatography, and HPLC are used in various