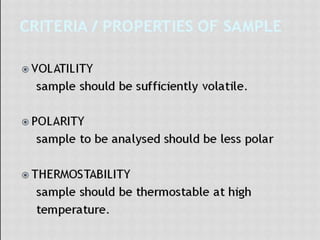
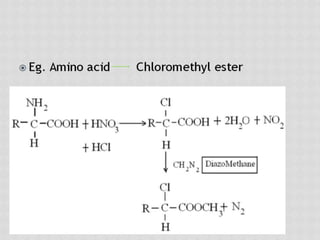
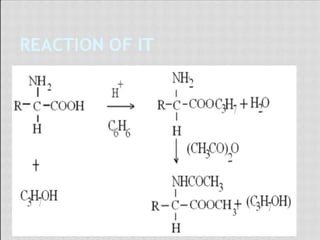
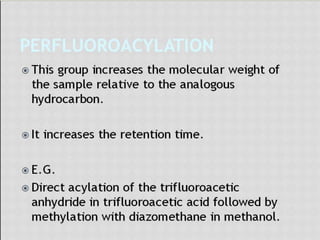
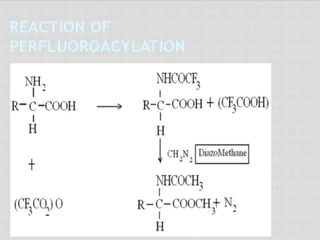
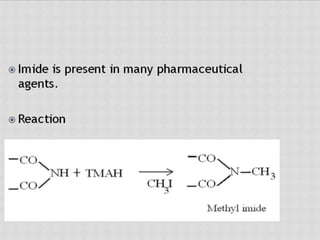
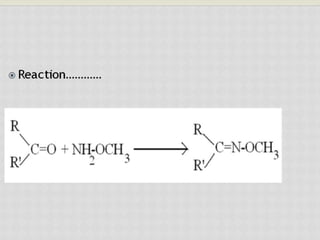
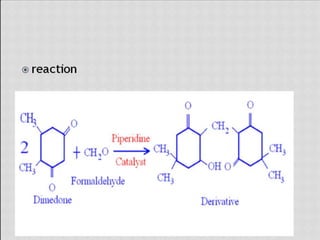
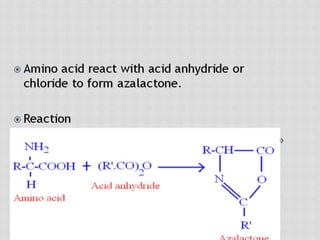
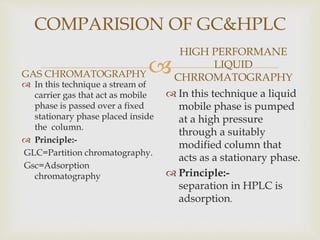
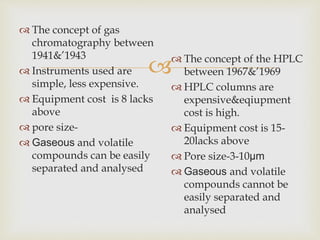
This document compares gas chromatography (GC) and high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). GC uses a gas mobile phase and separates compounds based on volatility, while HPLC uses a liquid mobile phase under high pressure and separates compounds based on interactions with the stationary phase. Some key differences discussed are that GC uses simpler, less expensive equipment than HPLC but can only analyze more volatile compounds, whereas HPLC can analyze a wider range of compounds including thermolabile ones. Both techniques have different instrumentation requirements and a variety of detectors can be used for analysis.