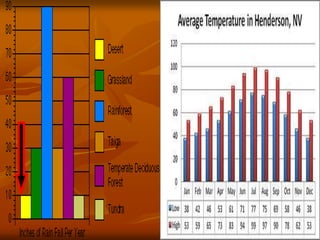
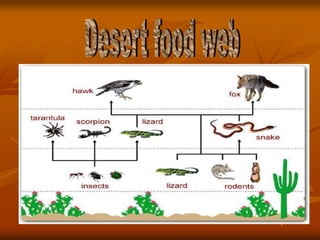
The document discusses the characteristics of desert ecosystems, including their climate, plants, animals, seasons, and human impacts. Deserts have hot or cold climates, with hot deserts receiving less than 10 inches of rain annually. Many desert plants and animals have adaptations like water storage or nocturnal behavior to survive the dry, hot conditions. Seasons are warm year-round with little rainfall. Humans threaten desert ecosystems through activities like poaching, road building, and desertification.