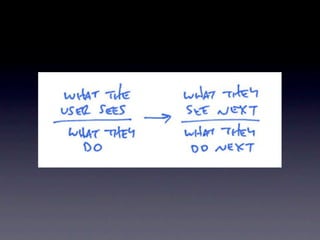
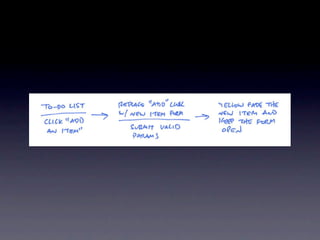
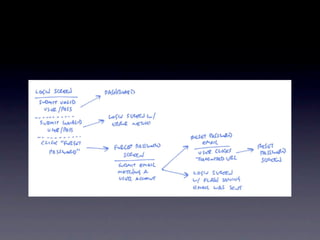
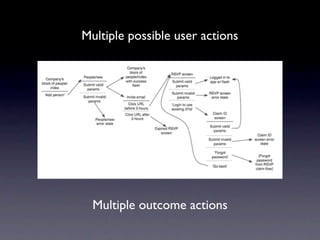
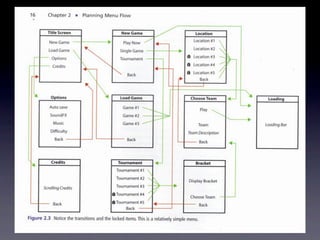
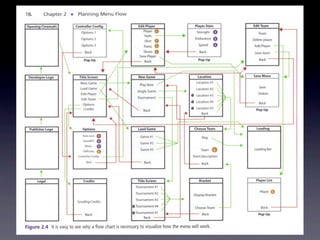
The document discusses planning menu flow in game interfaces. It recommends creating flowcharts to identify how users will navigate between screens, which helps clarify design needs, distribute work, and get approval. Flowcharts should be based on user testing and priority design goals like simplicity versus customization. The document describes flowchart software and techniques like 37signals' approach using simple sketches for use case modeling before finalizing menu designs. It emphasizes planning navigation from a user-centric perspective to avoid missed screens.