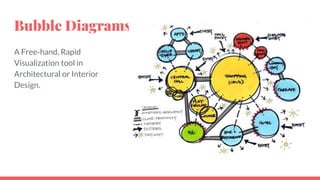
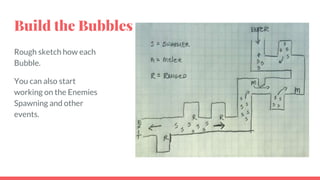
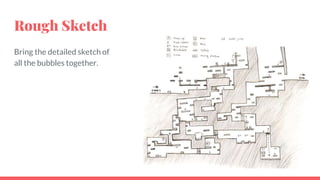
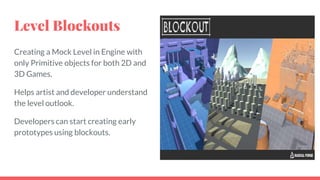
The document outlines the concept and process of level design in game development, emphasizing its importance in creating engaging gameplay environments. It details the steps involved in designing game levels, including brainstorming, sketching, and prototyping, while highlighting the significance of constraints in shaping gameplay experiences. Additionally, the document discusses the roles of level flow, player choices, and aesthetics in achieving successful game design.