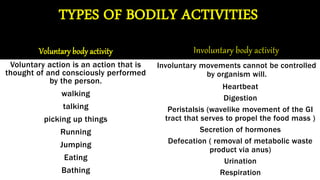
The nervous system has four major functions:
1. Somatic function allows for voluntary movement through electrical signals that cause muscle contraction.
2. Sensory function involves sense organs picking up external and internal stimuli which the brain interprets.
3. Autonomic function involuntarily controls internal organs like the heart and lungs without conscious thought.
4. Cognitive function enables problem-solving and learning through mental processing, distinguishing humans from animals.
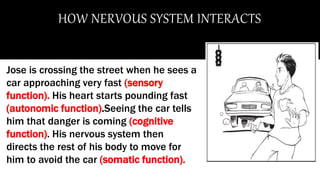
The document provides examples of how these functions interact in the nervous system to allow Jose to avoid an oncoming car through sensory perception, involuntary heart rate increase, cognitive processing, and voluntary movement.