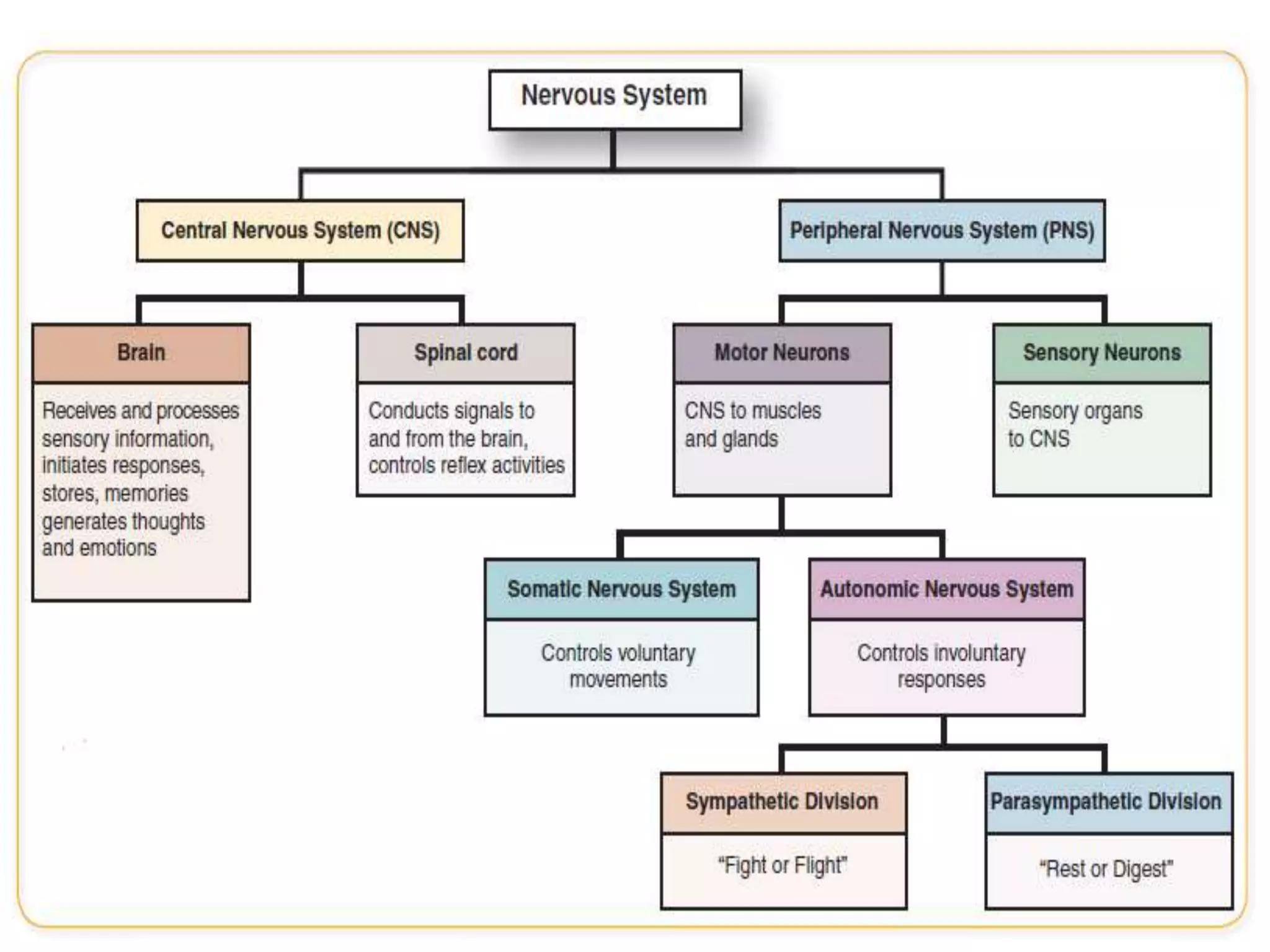
The document summarizes the structure and function of the nervous system. It describes that the nervous system is comprised of two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord, which act as the control center. The PNS includes nerves that connect the CNS to other parts of the body. Neurons are the basic working units that transmit signals through the nervous system. Communication occurs at synapses between neurons. The brain and spinal cord work together with the peripheral nerves to coordinate sensory input, integration of information, and motor output to control bodily functions.