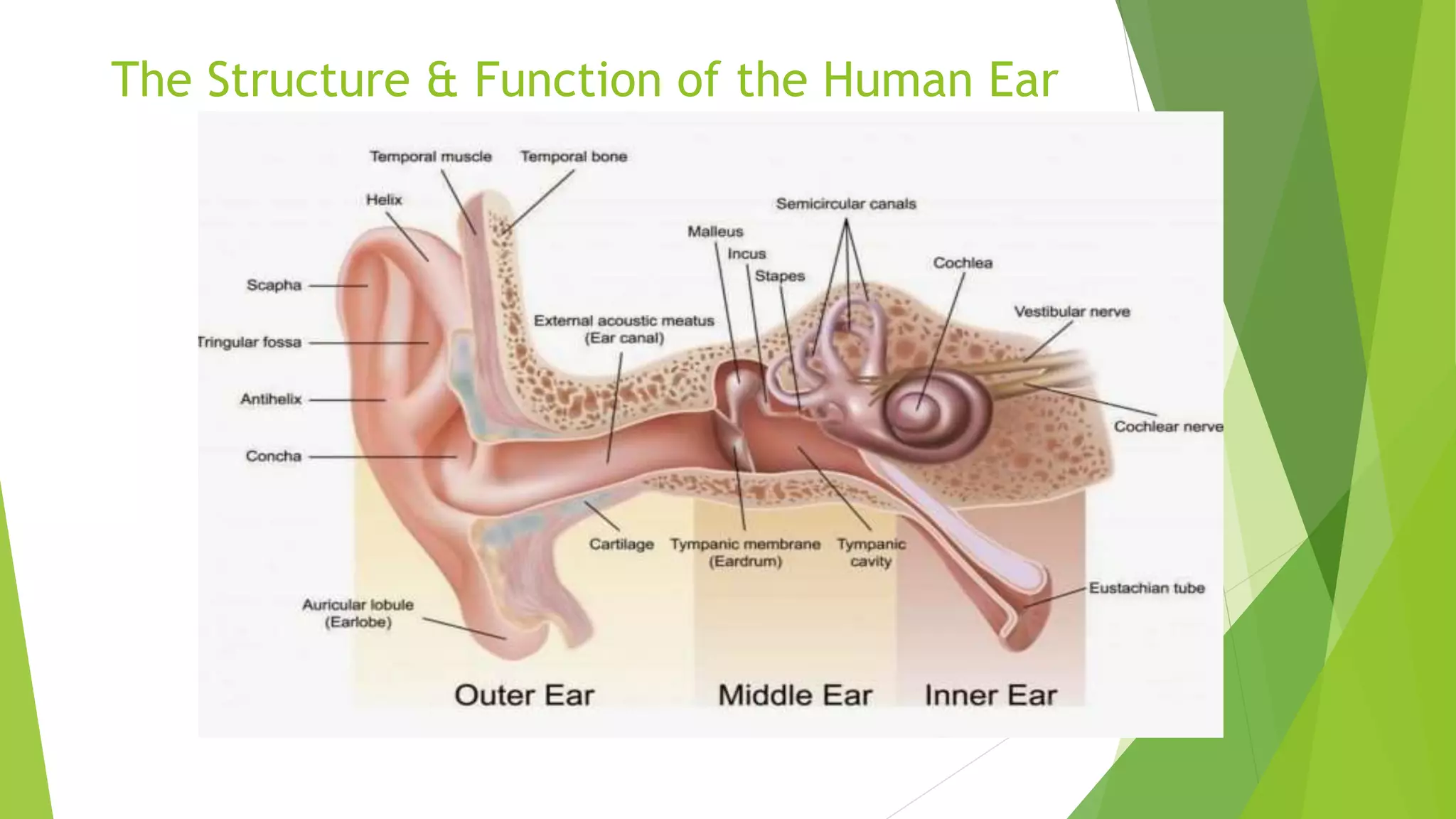
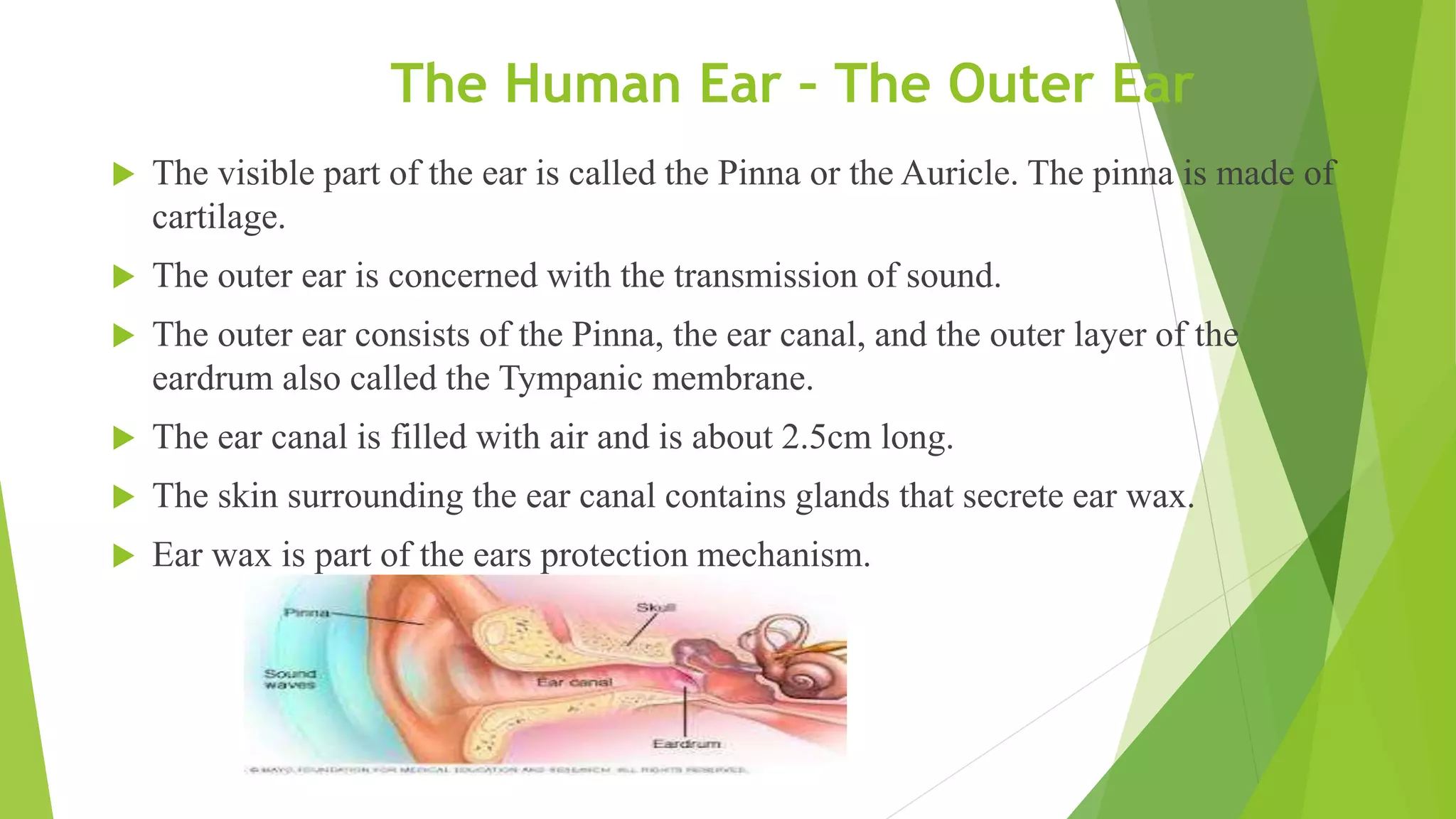
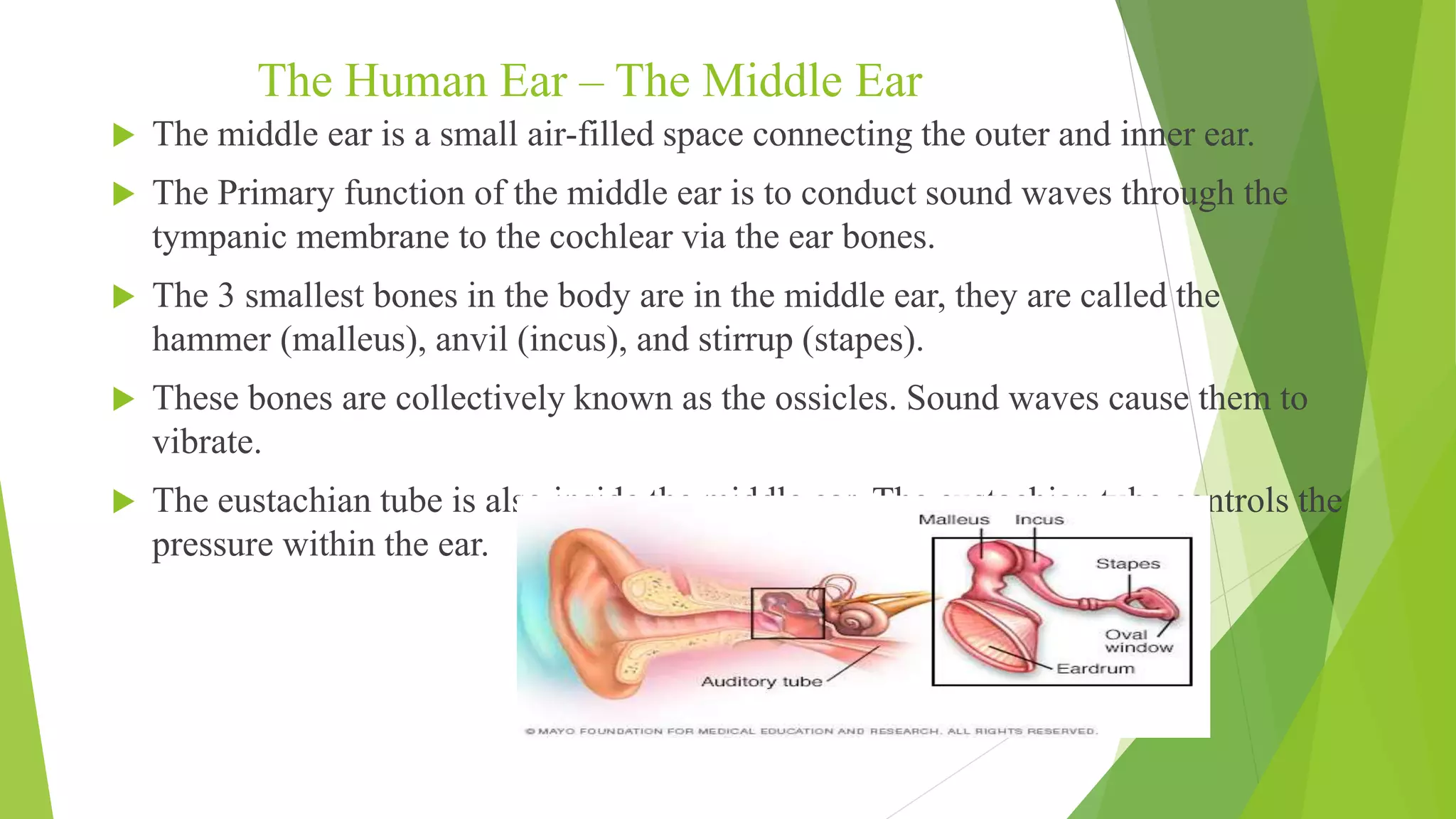
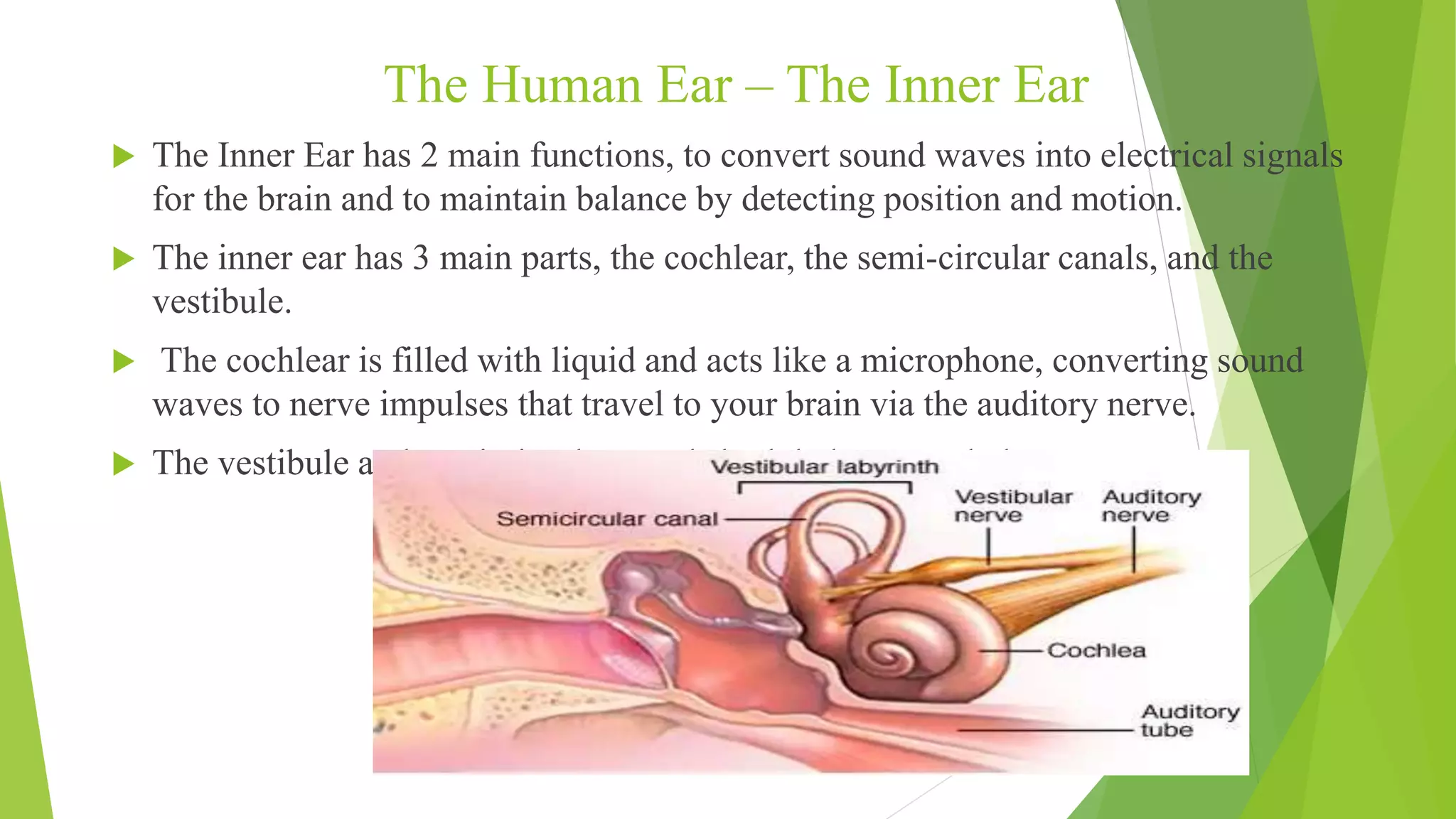
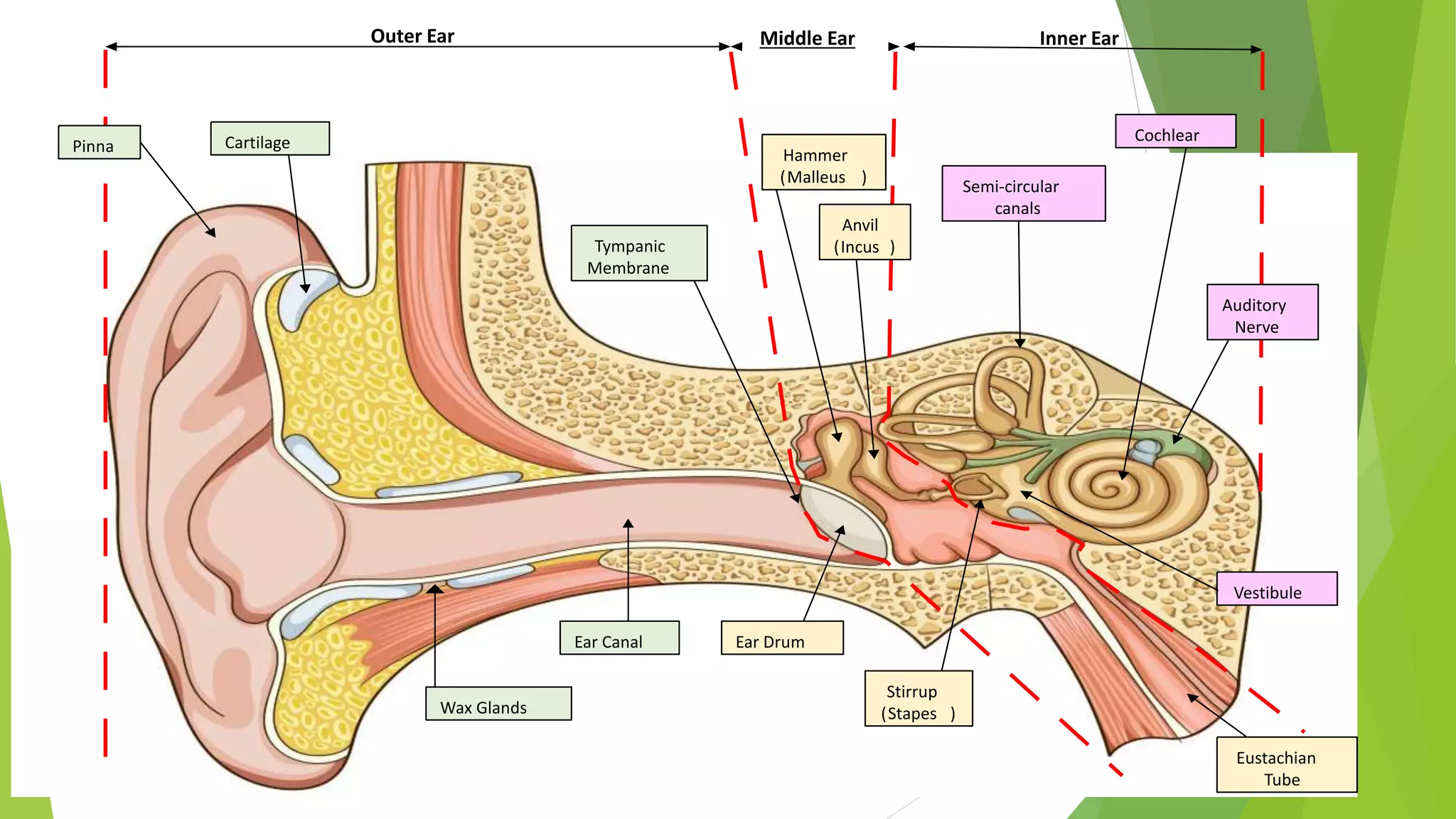
The human ear is divided into three main sections - the outer, middle, and inner ear. The outer ear collects sound waves and directs them through the ear canal to the eardrum. The middle ear contains three small bones called the hammer, anvil, and stirrup that transmit vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear. The inner ear converts the vibrations into neural signals and sends them to the brain, allowing us to perceive sound. It also helps maintain balance through the semi-circular canals and vestibule.