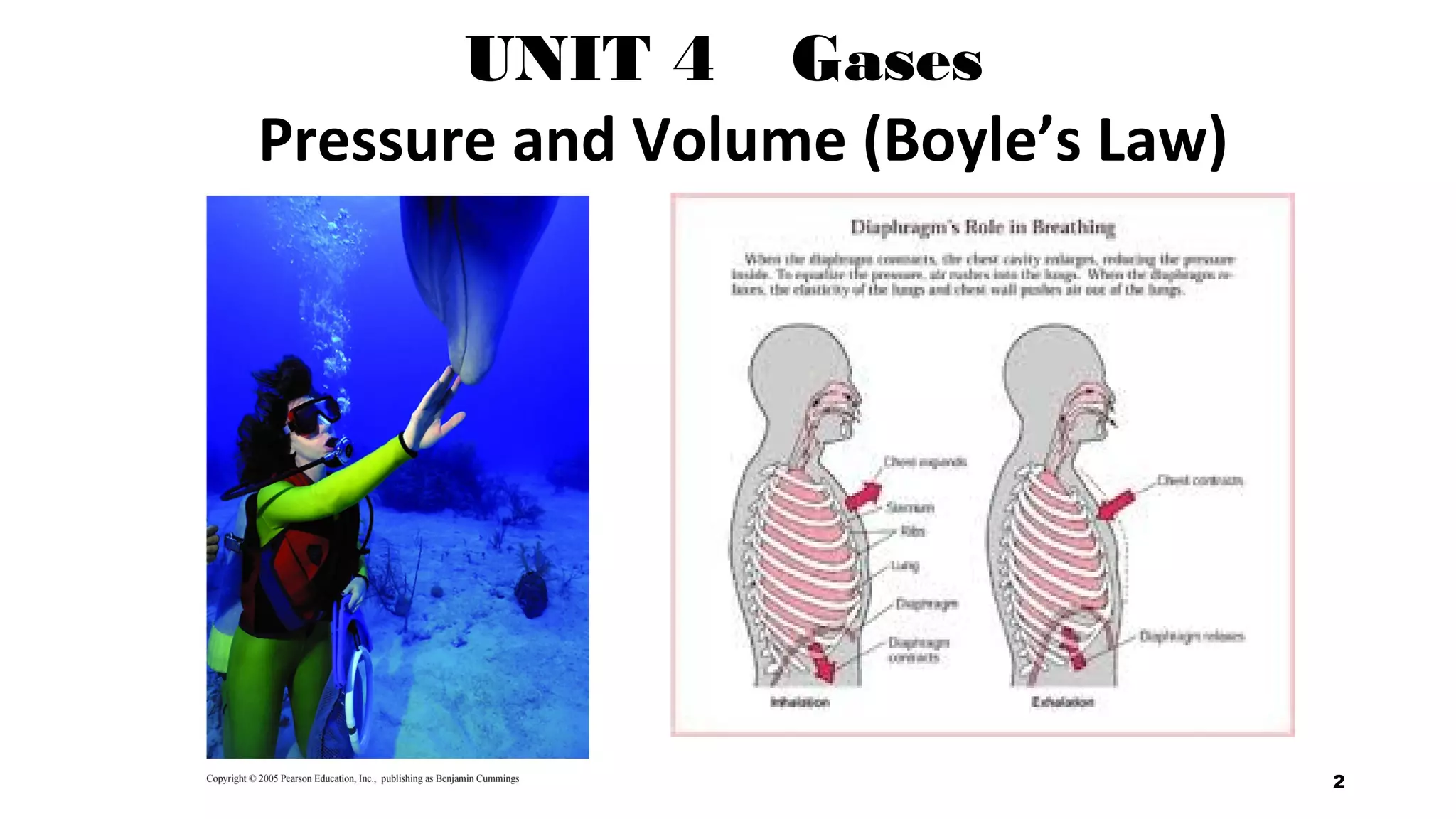
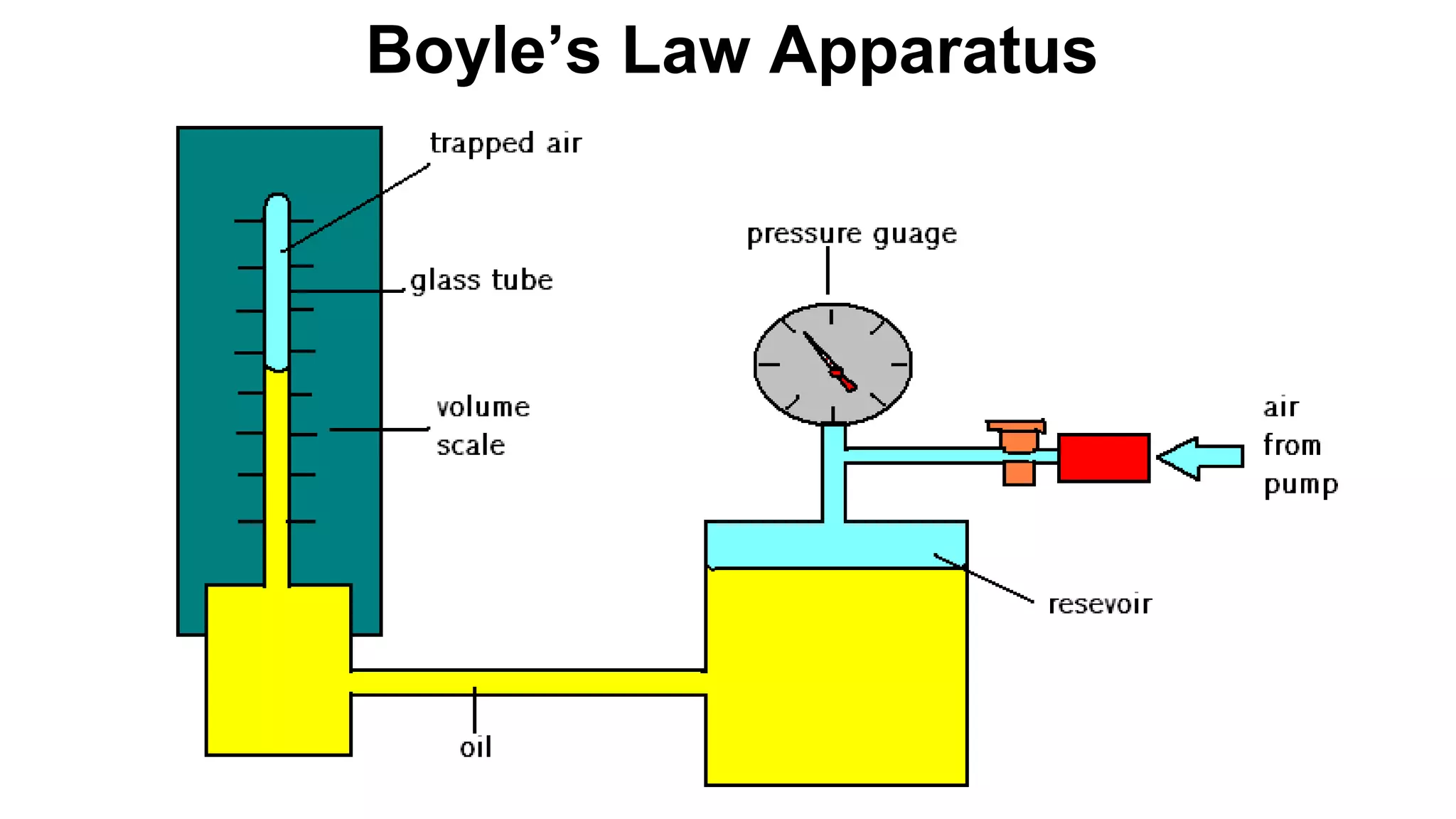
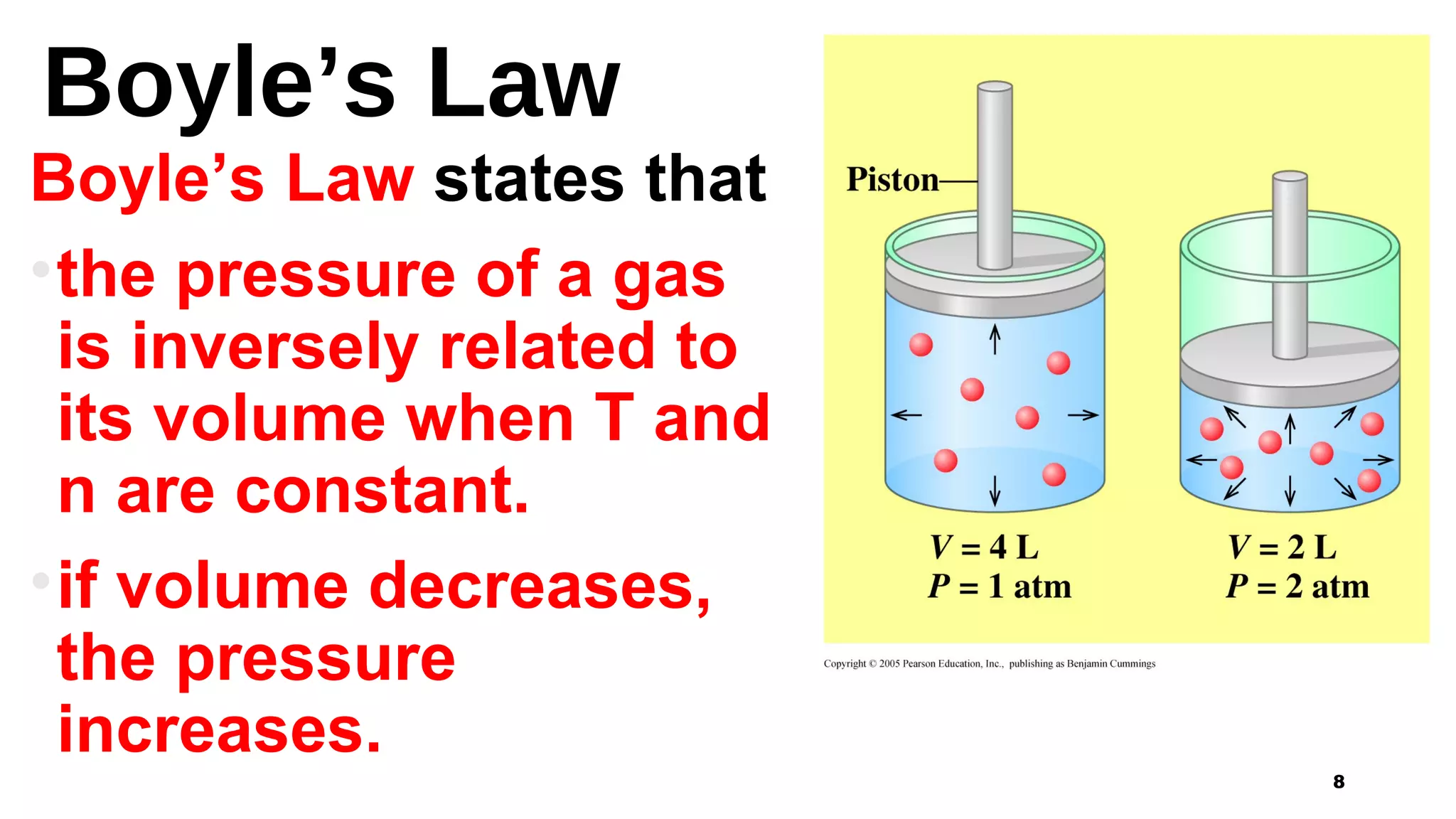
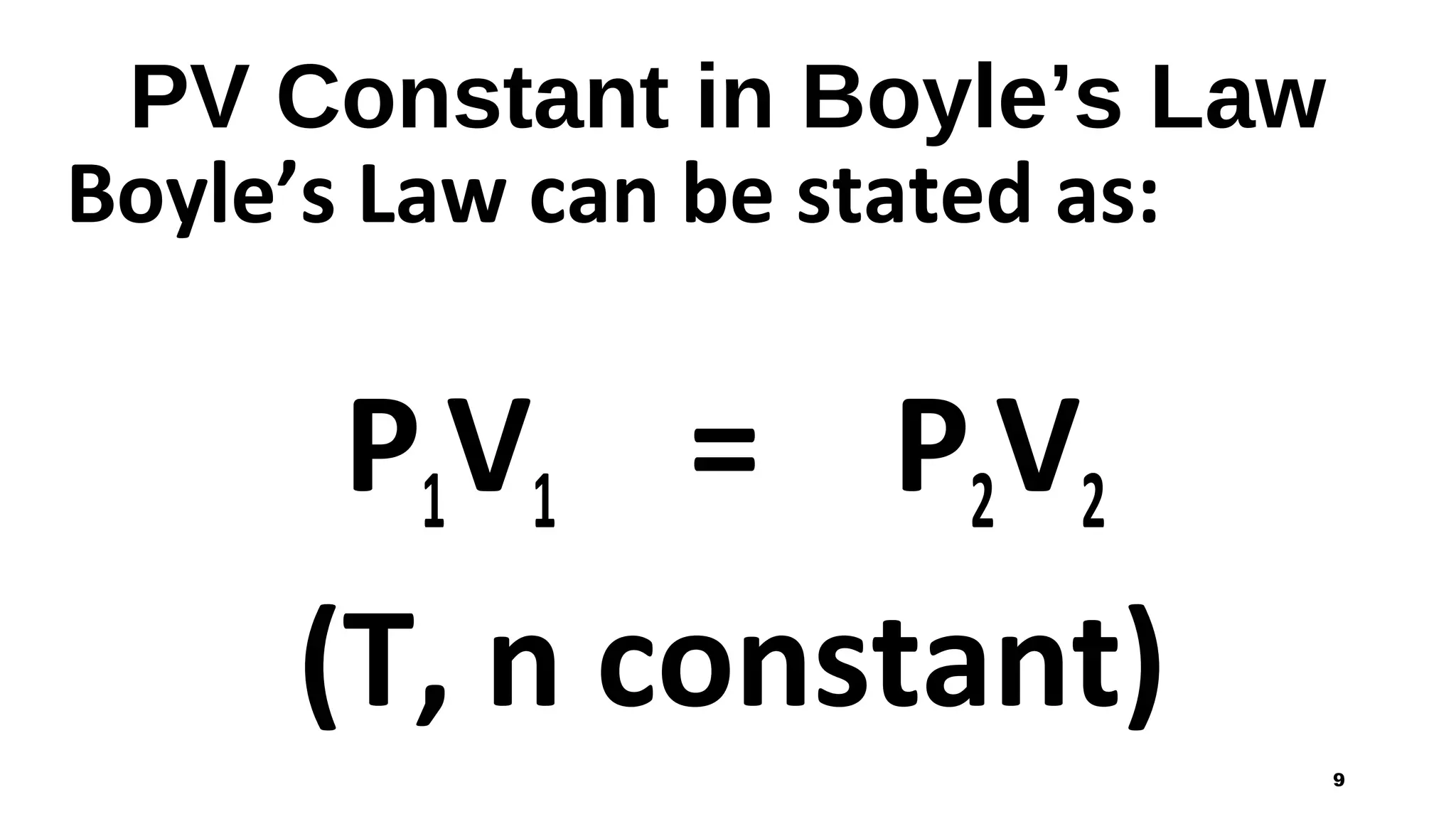
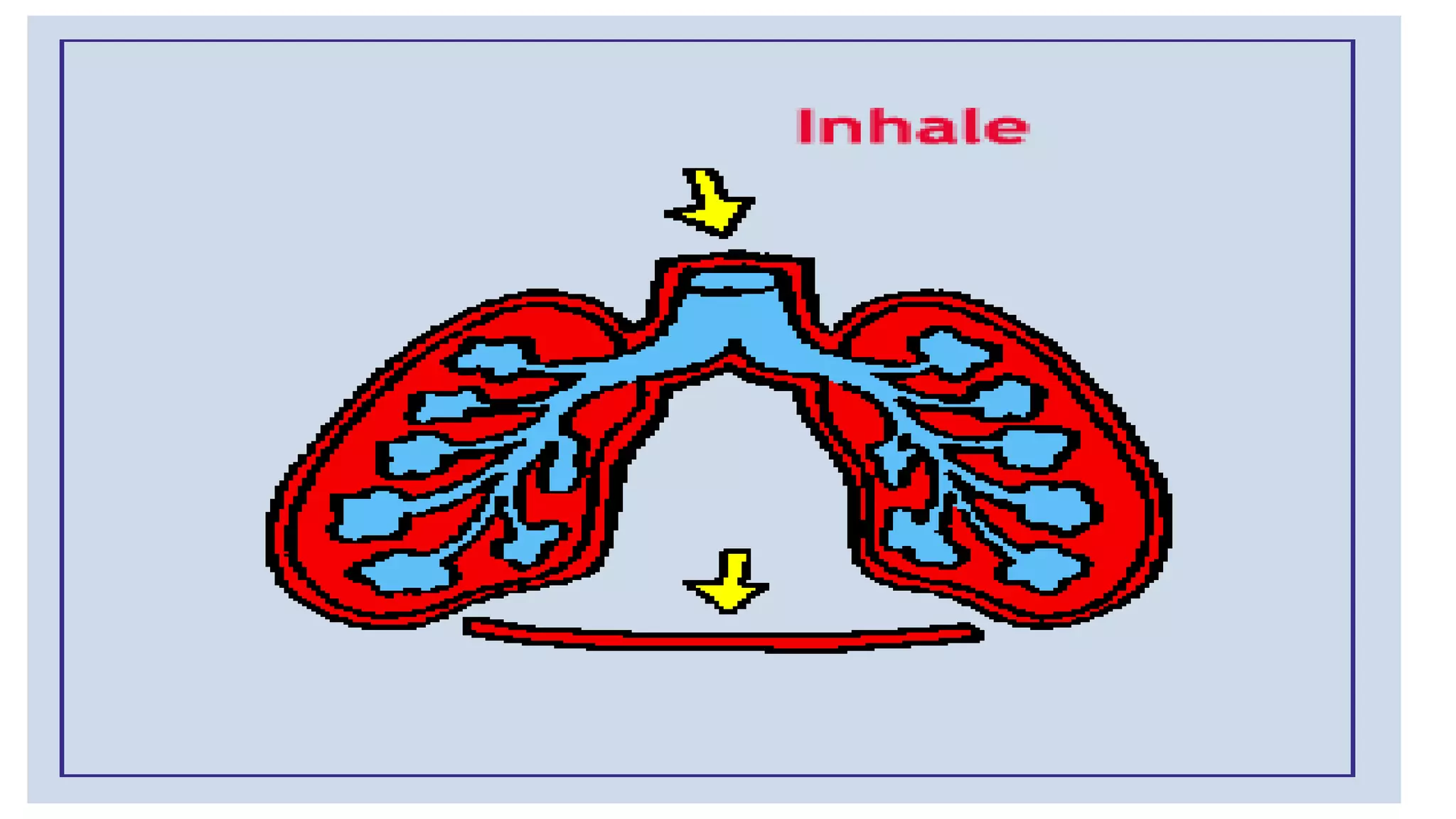
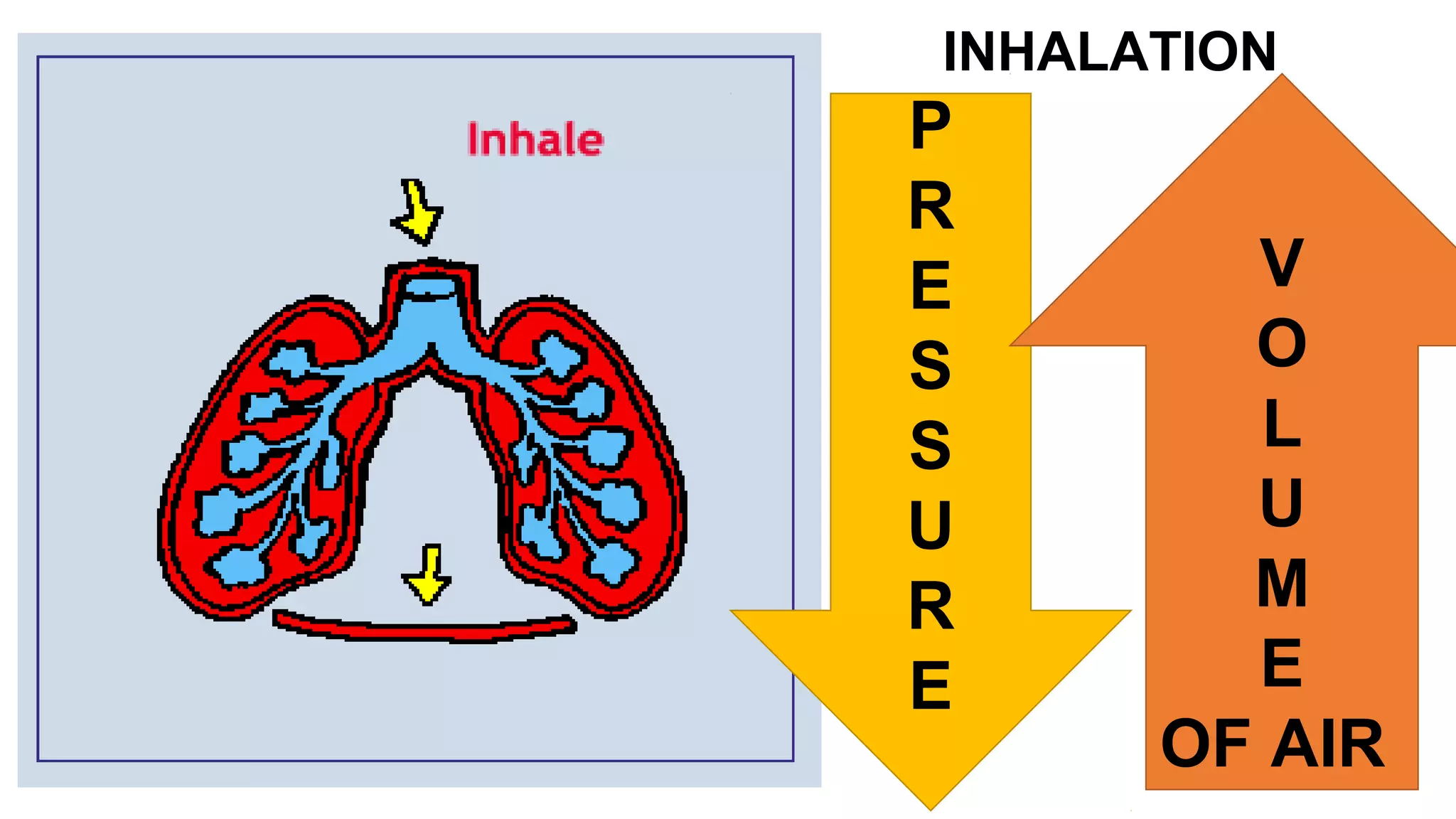
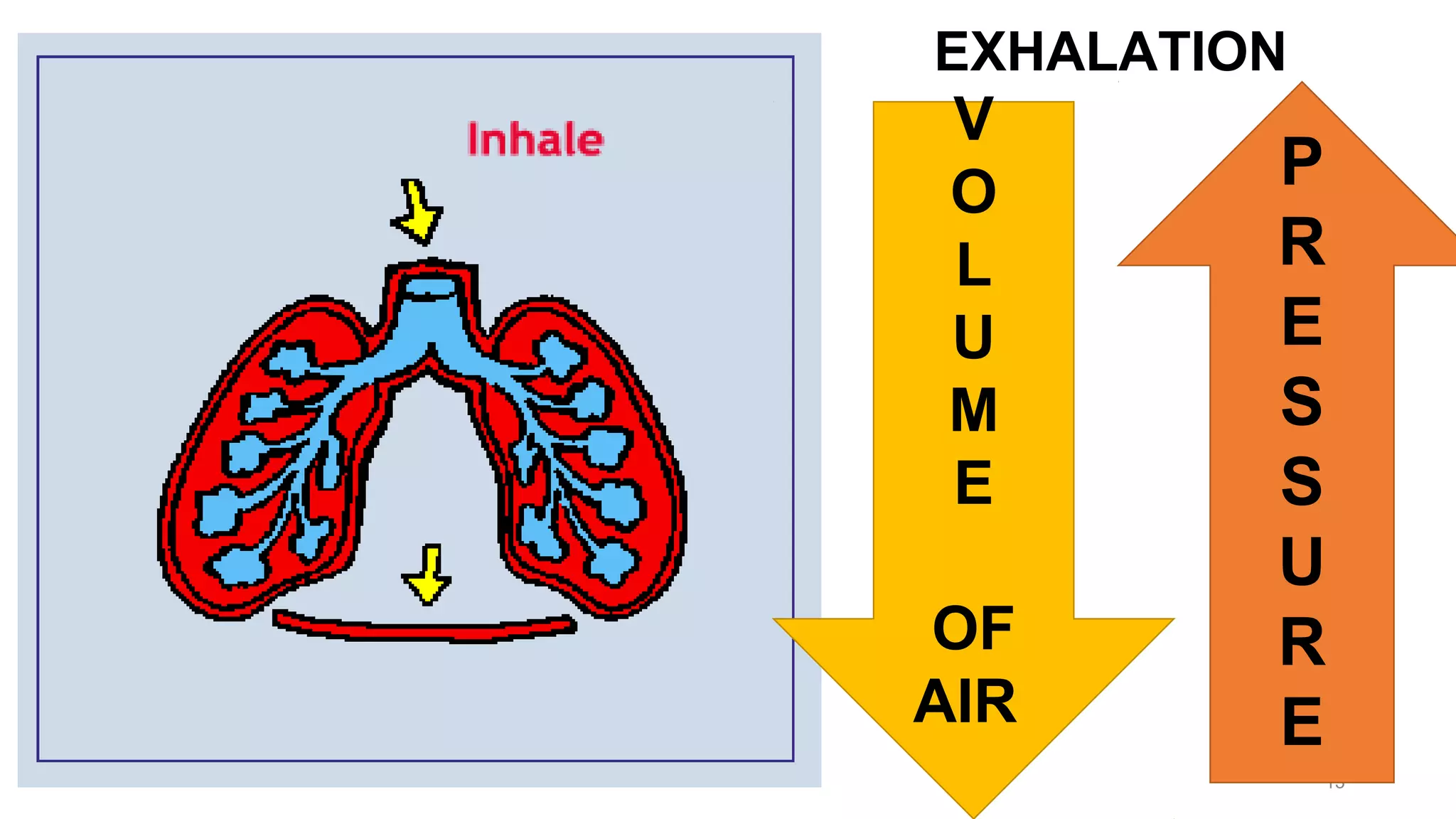
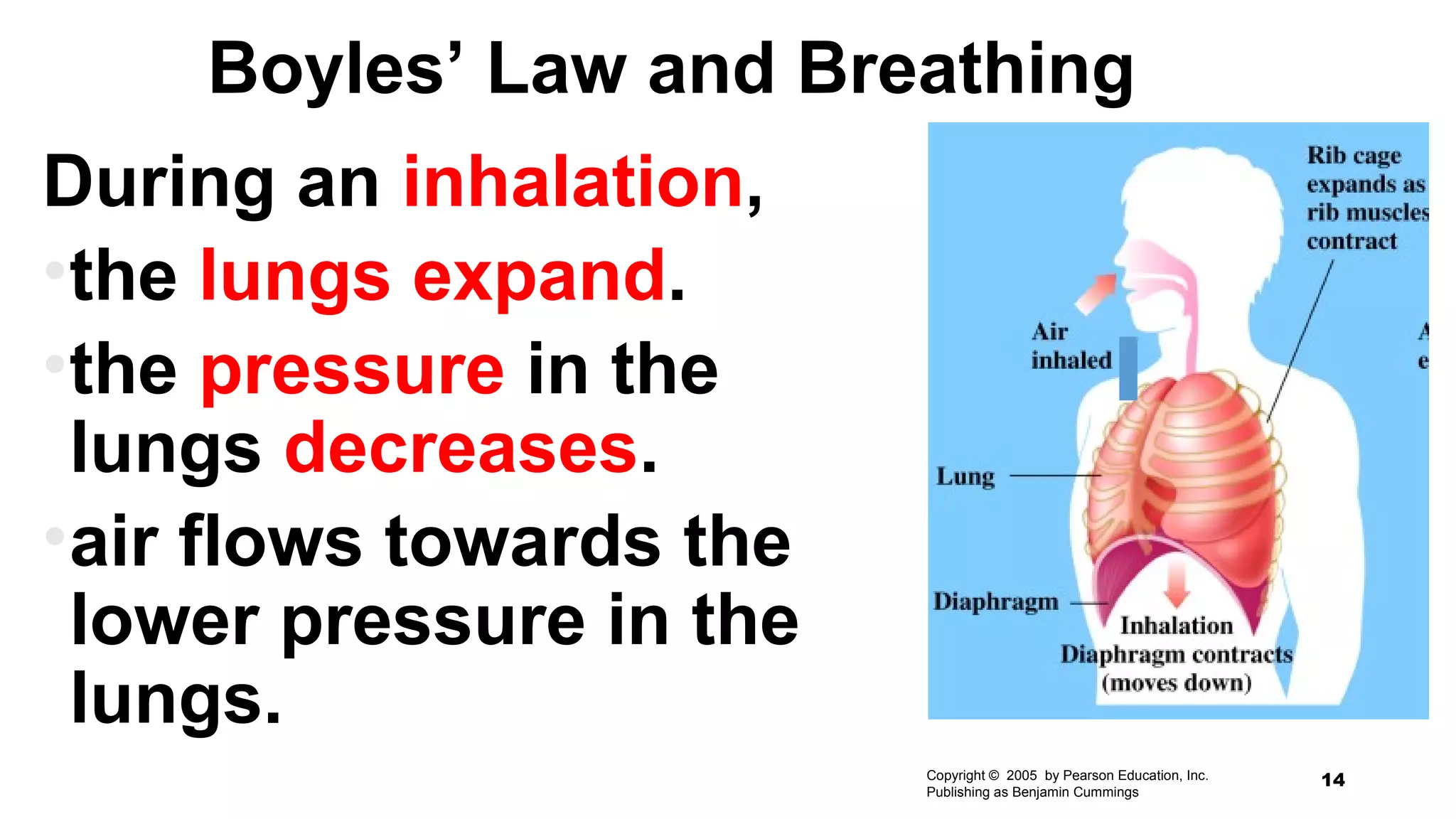
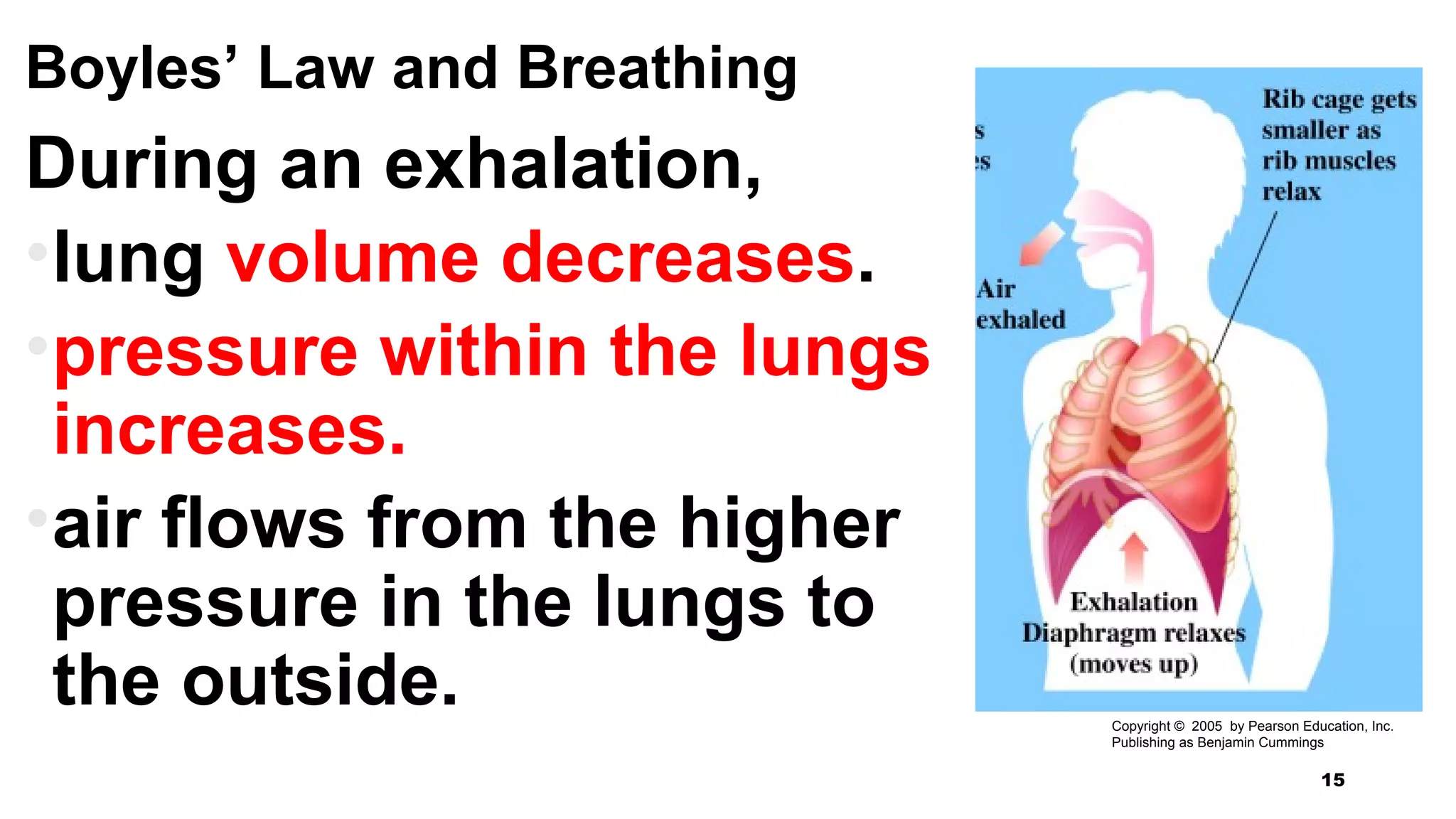
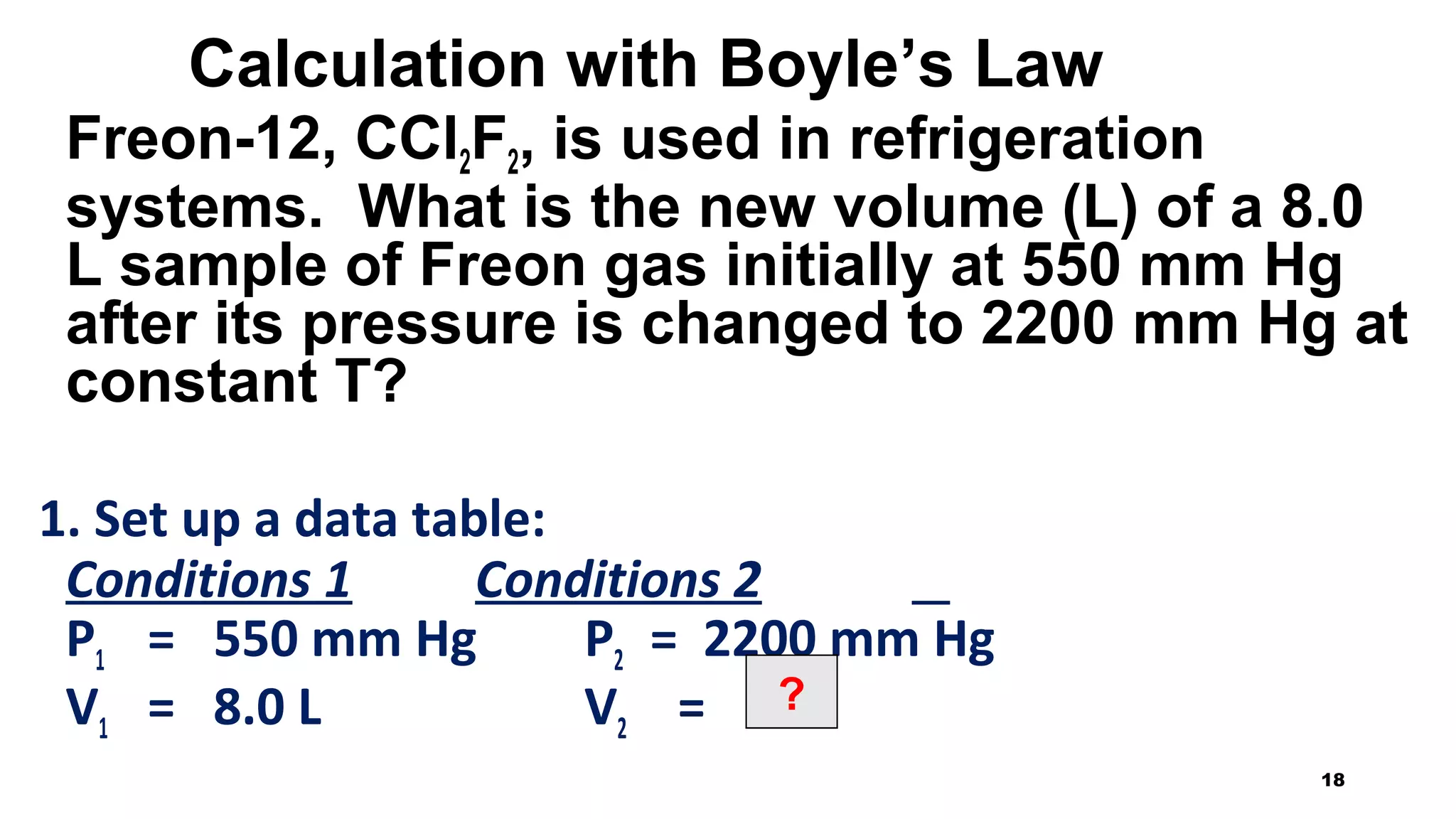
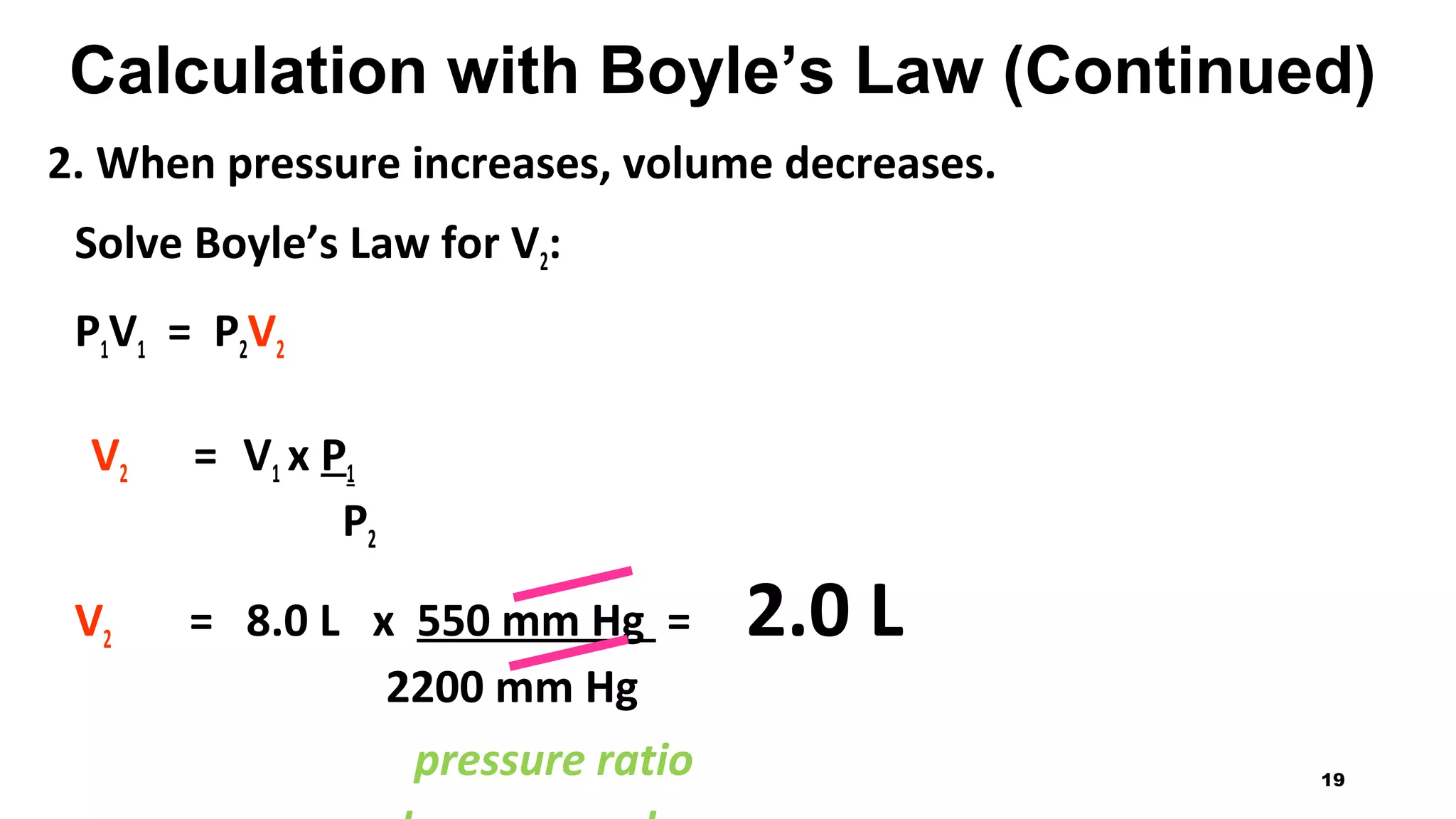
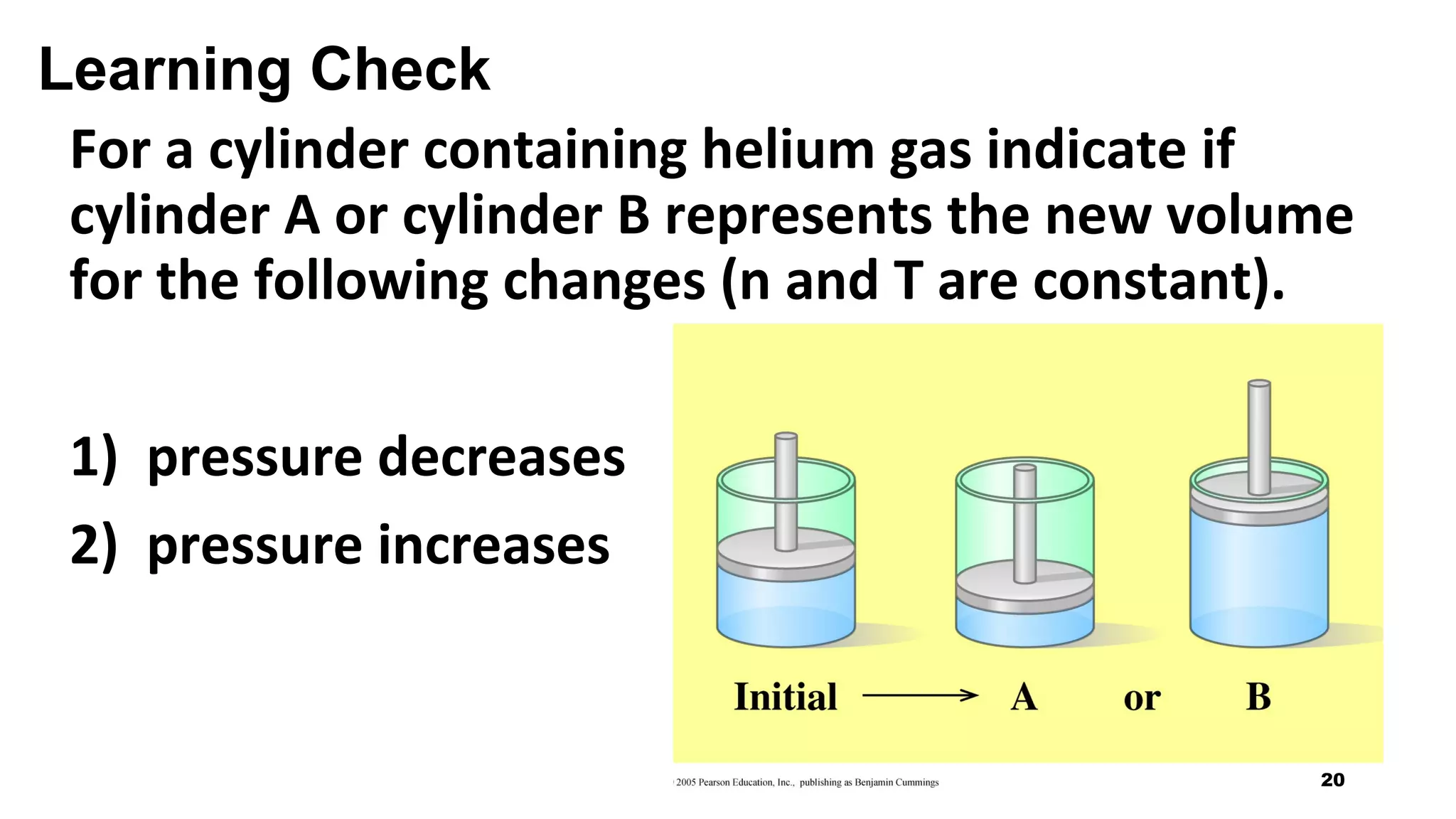
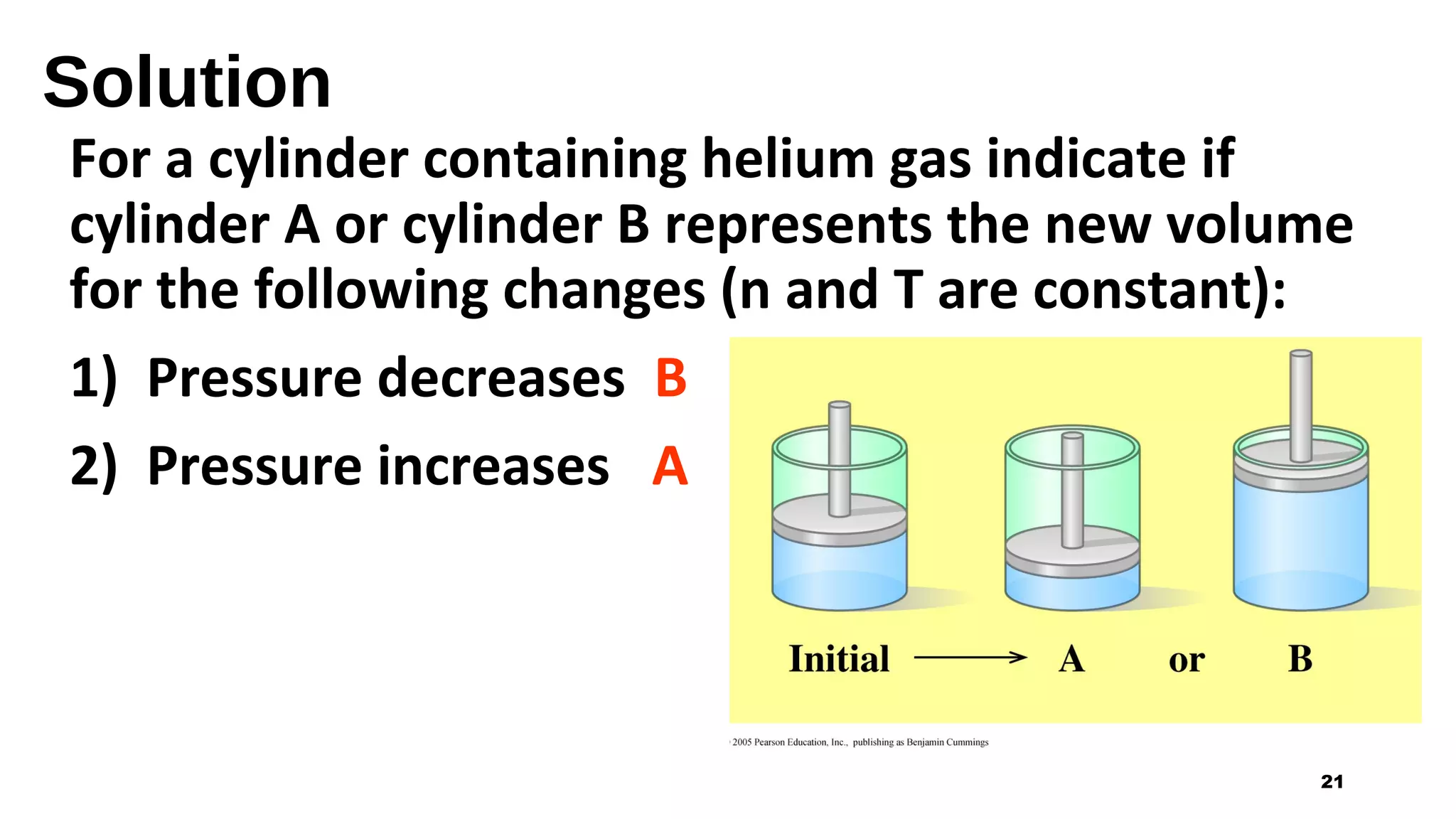
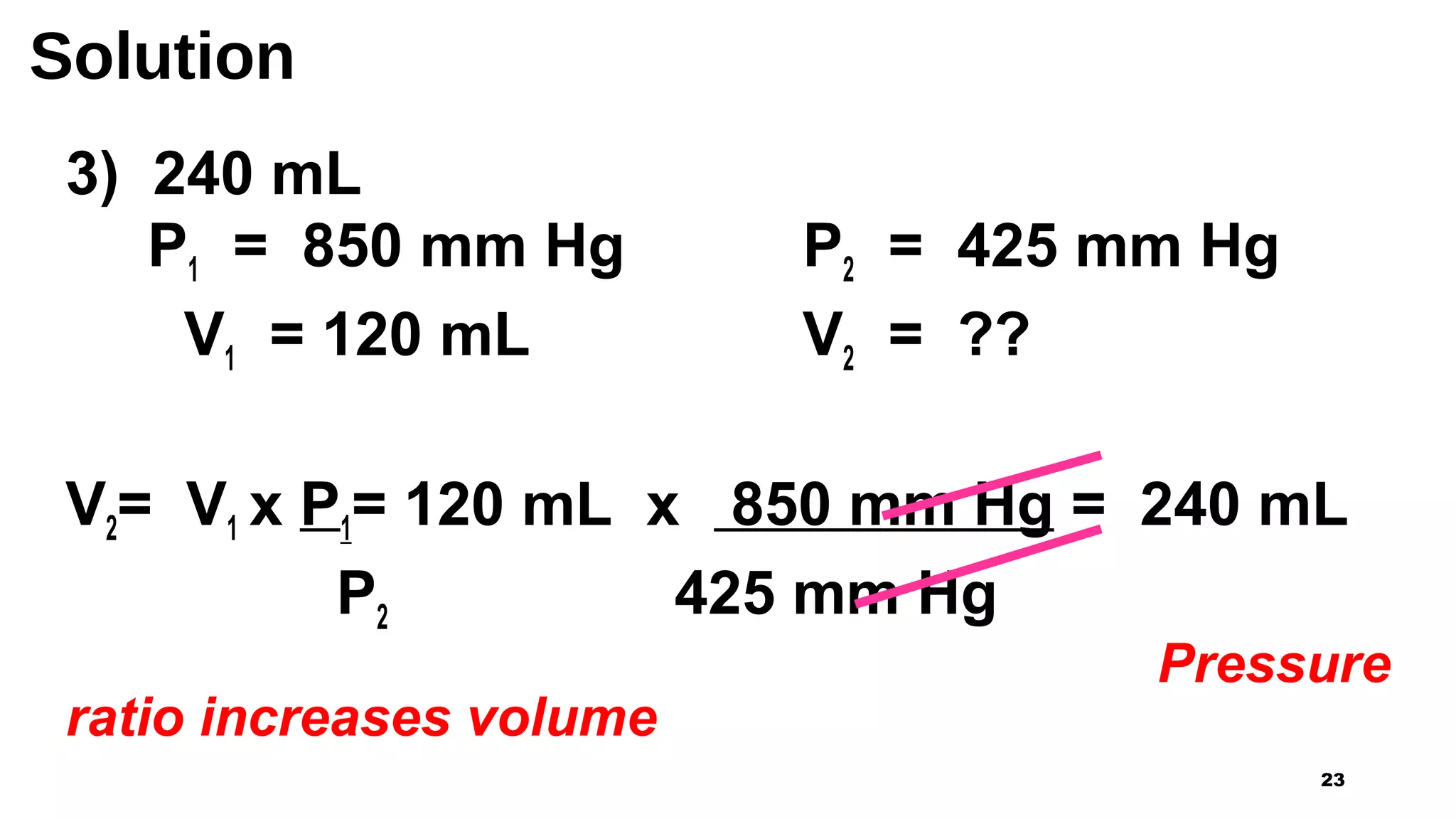
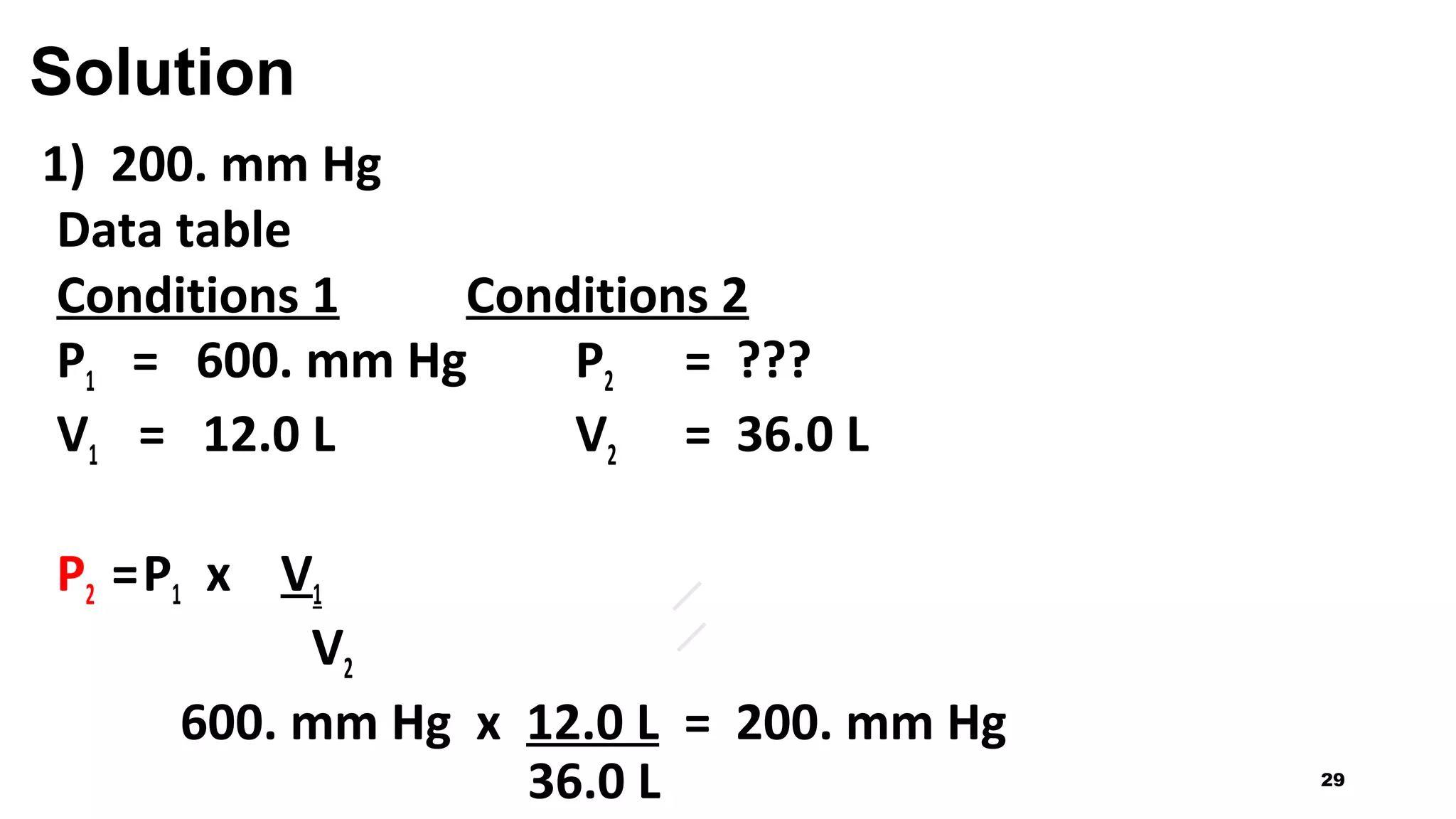
This document discusses Boyle's law, which states that the pressure and volume of a gas are inversely proportional when temperature and amount of gas are kept constant. It provides examples of how Boyle's law can be applied to calculate changes in pressure or volume. For instance, if the volume of a gas decreases, the pressure must increase according to the relationship PV=constant. The document also explains how Boyle's law relates to breathing through examples of how lung pressure and volume change during inhalation and exhalation. It includes sample problems and solutions for calculating new volumes or pressures using the formula for Boyle's law.