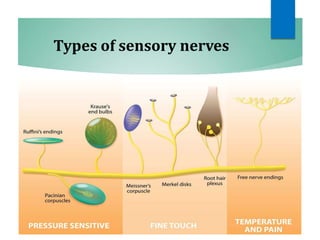
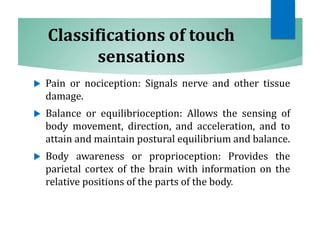
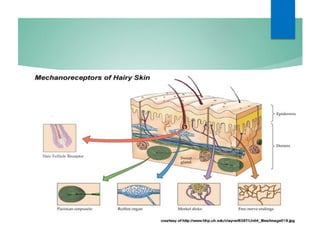
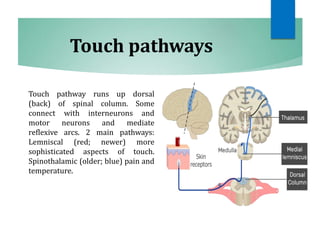
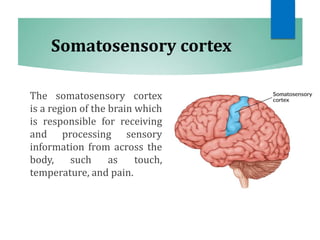
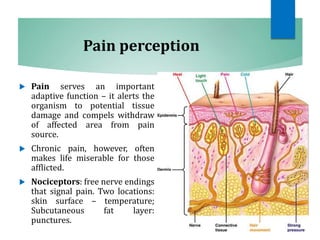
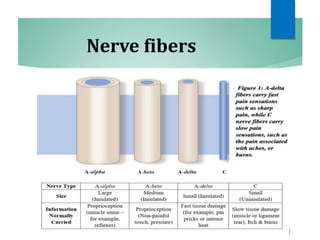
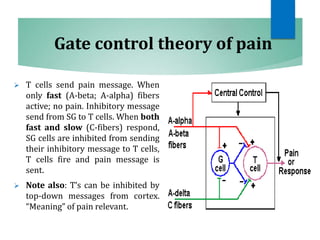
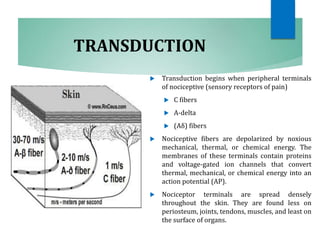
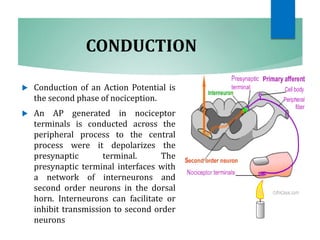
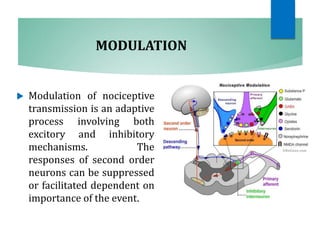
The document discusses the special senses of touch, including the different types of touch sensations like pain, temperature, and proprioception. It describes the receptors in the skin that detect touch sensations and how signals are transmitted through sensory nerves and pathways in the spinal cord and brain. It also discusses methods to measure touch sensitivity and the physiology of touch reception and pain perception.