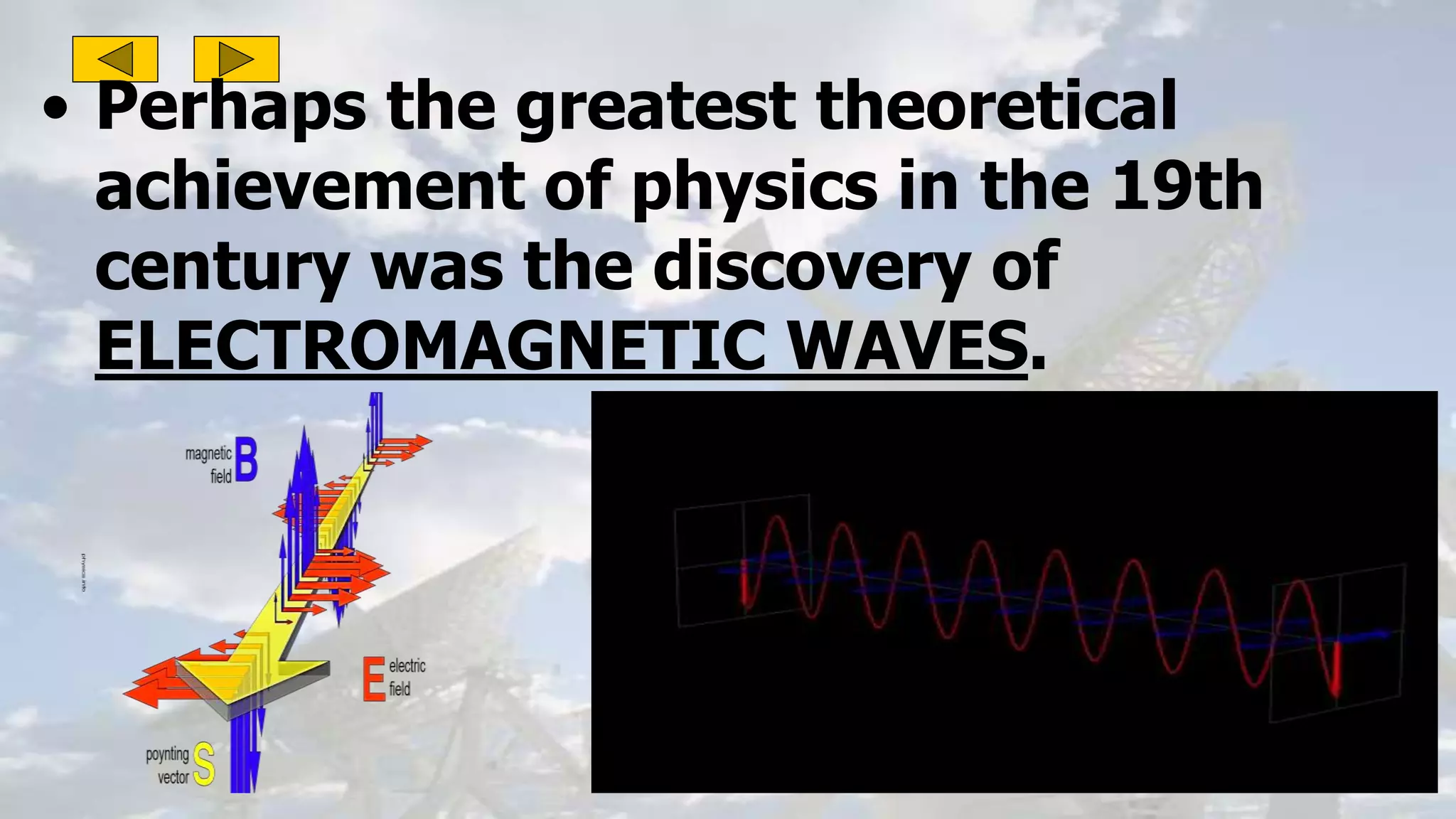
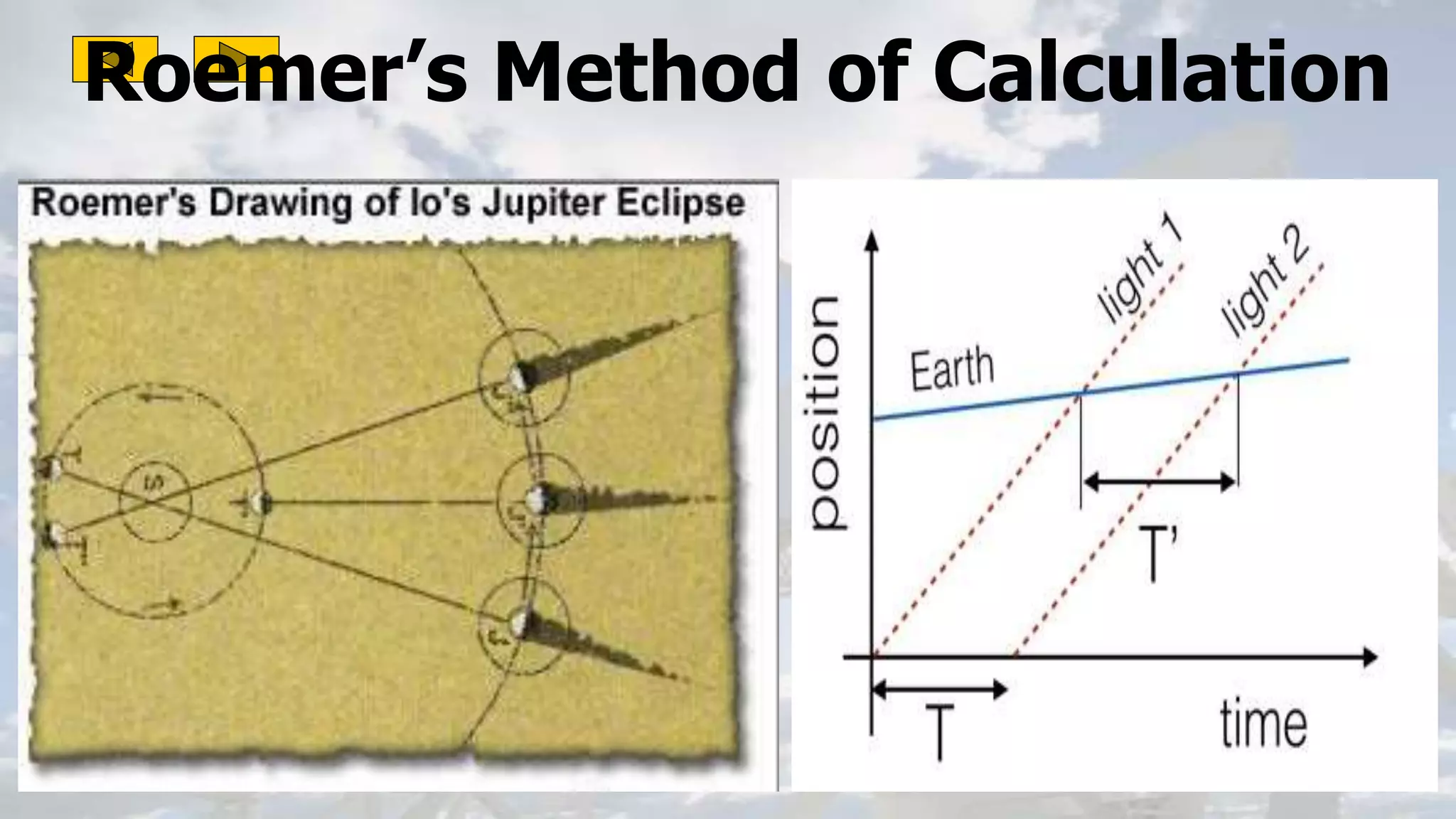
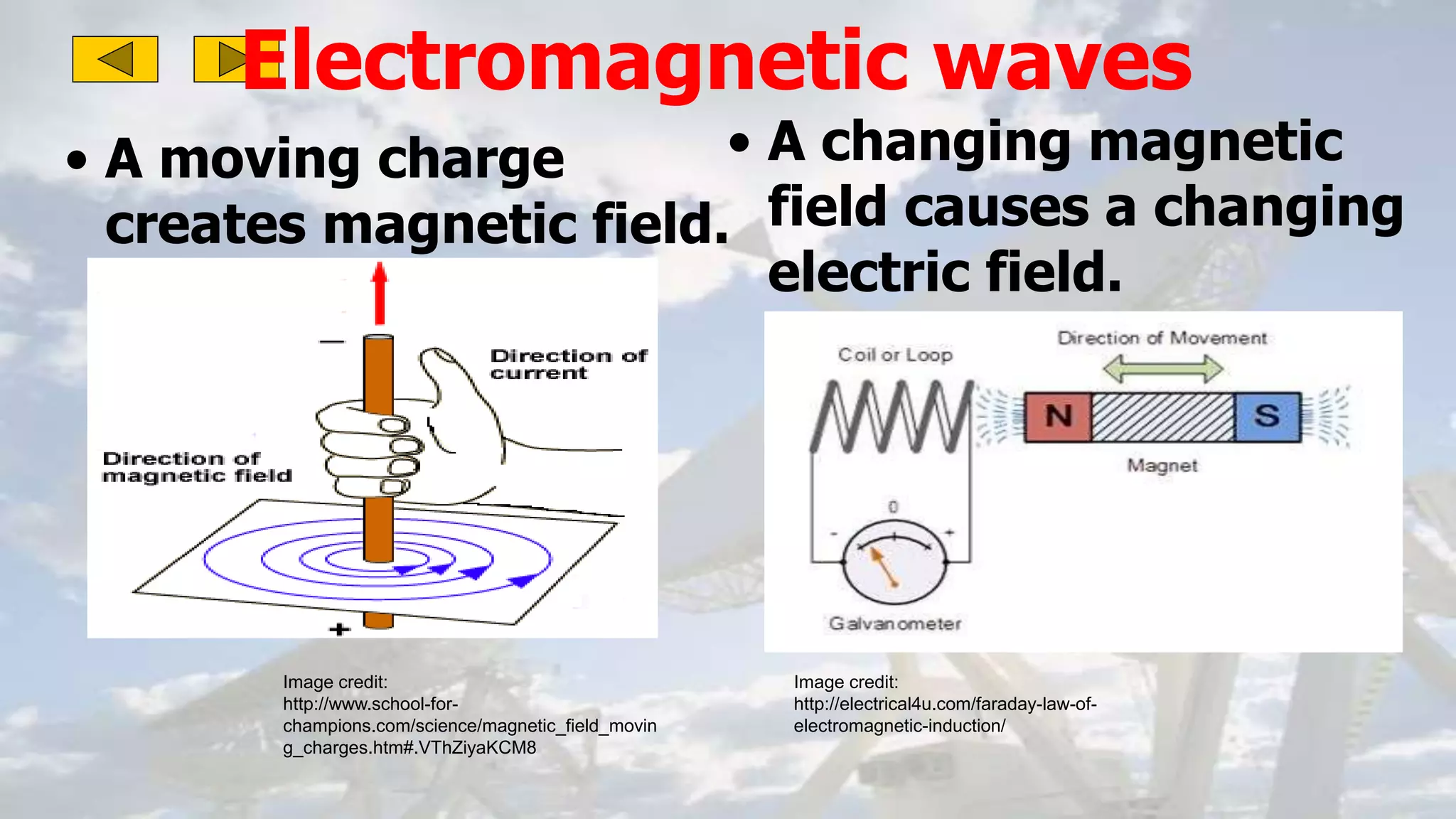
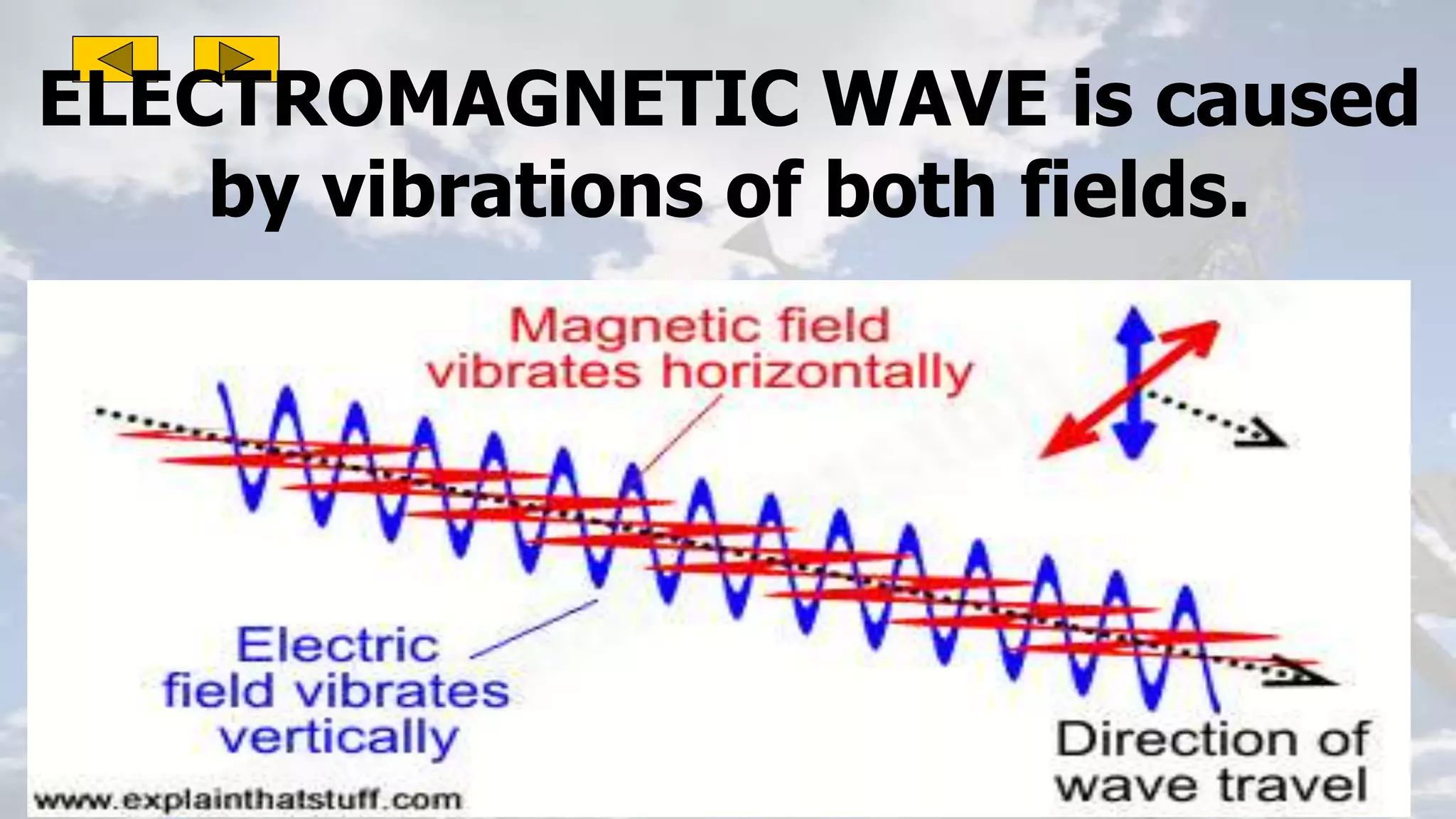
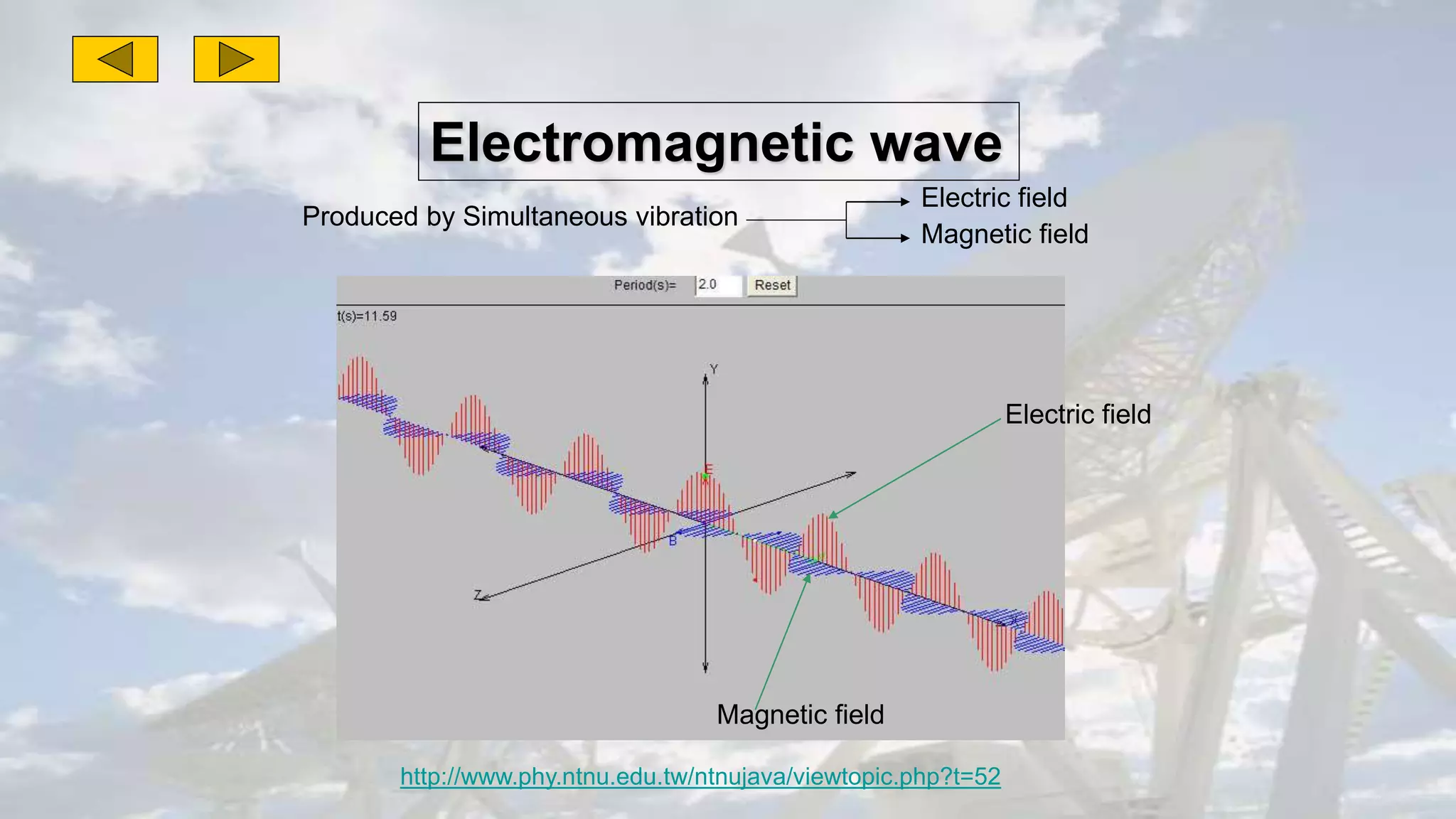
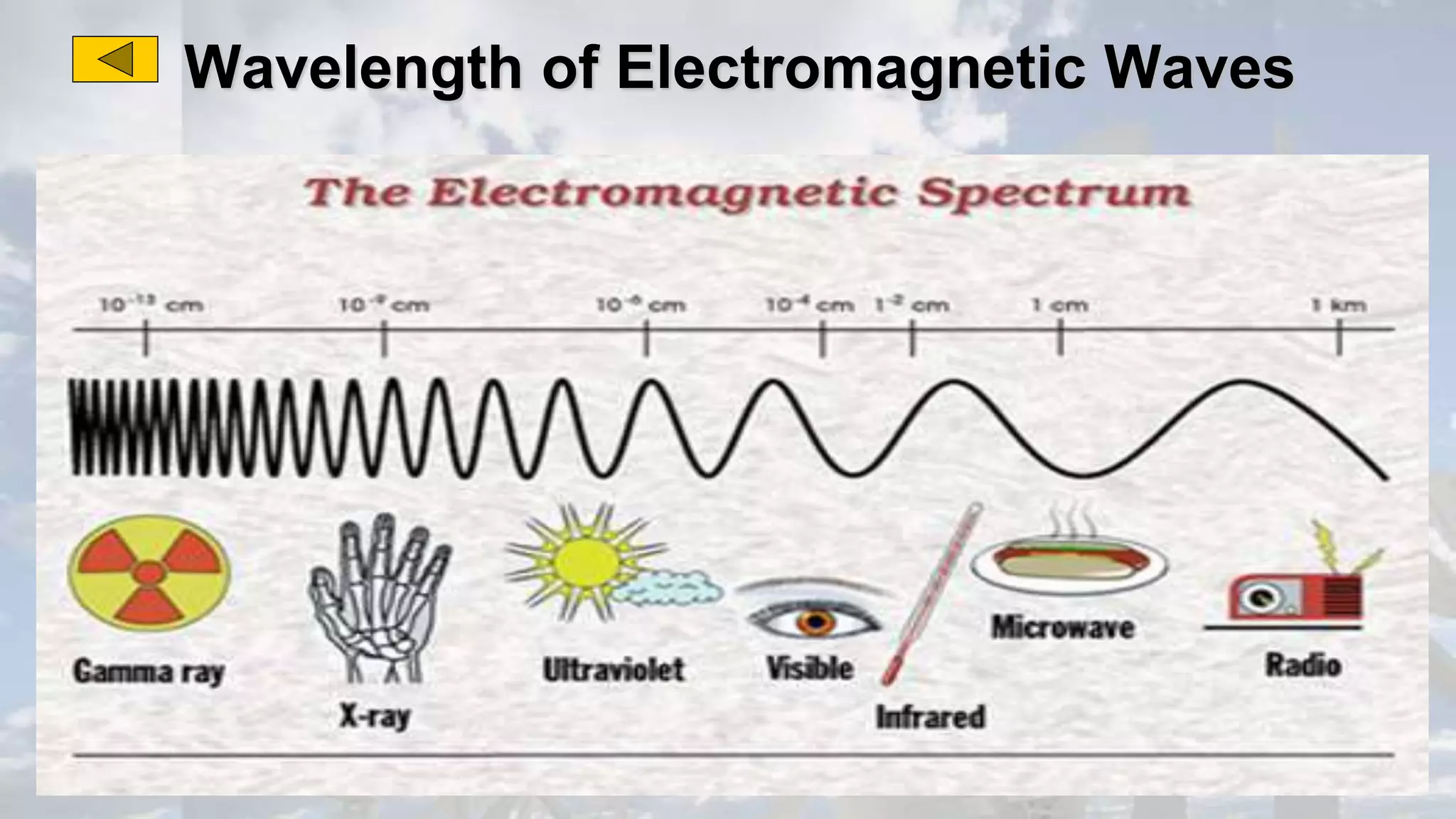
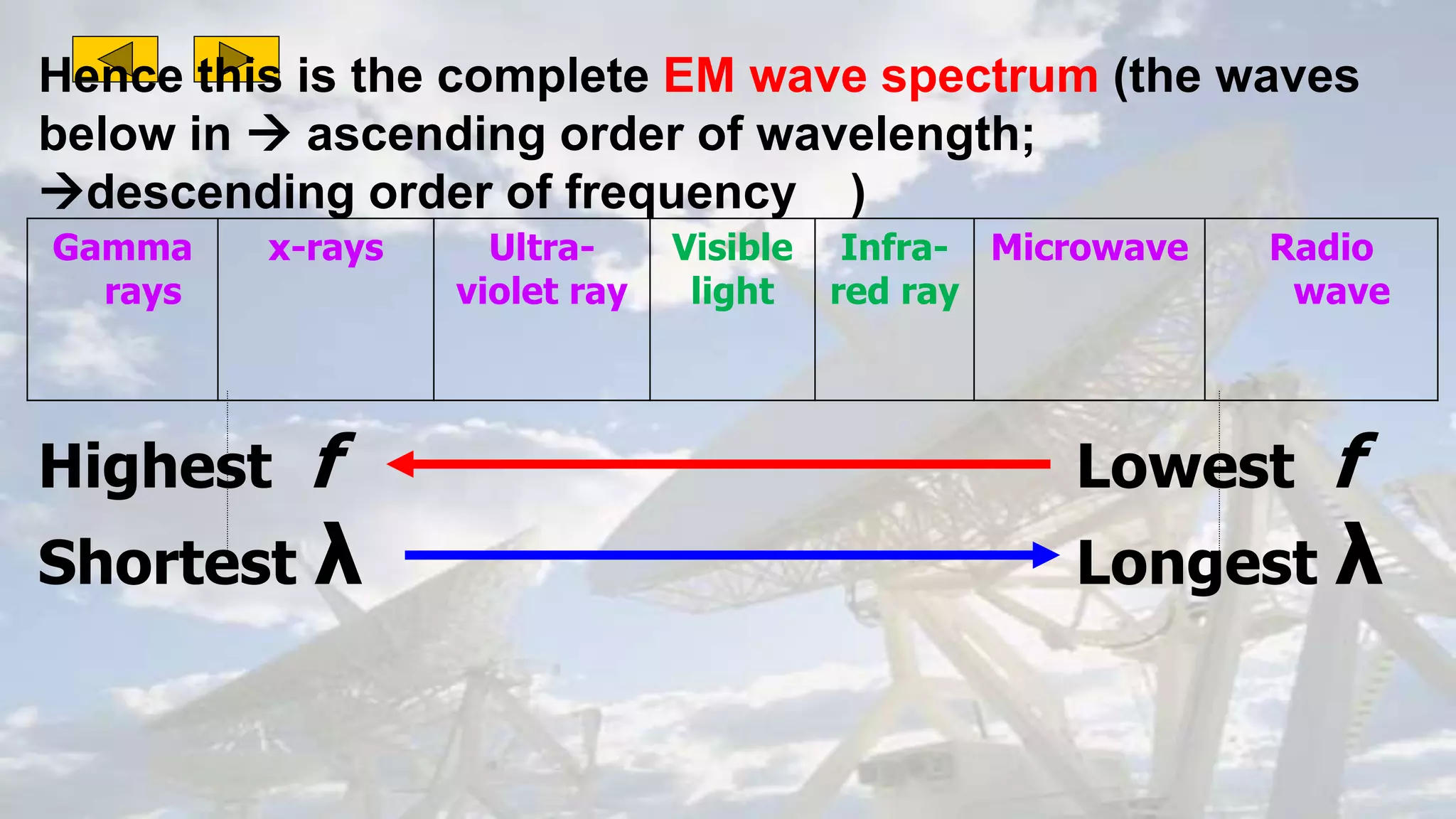
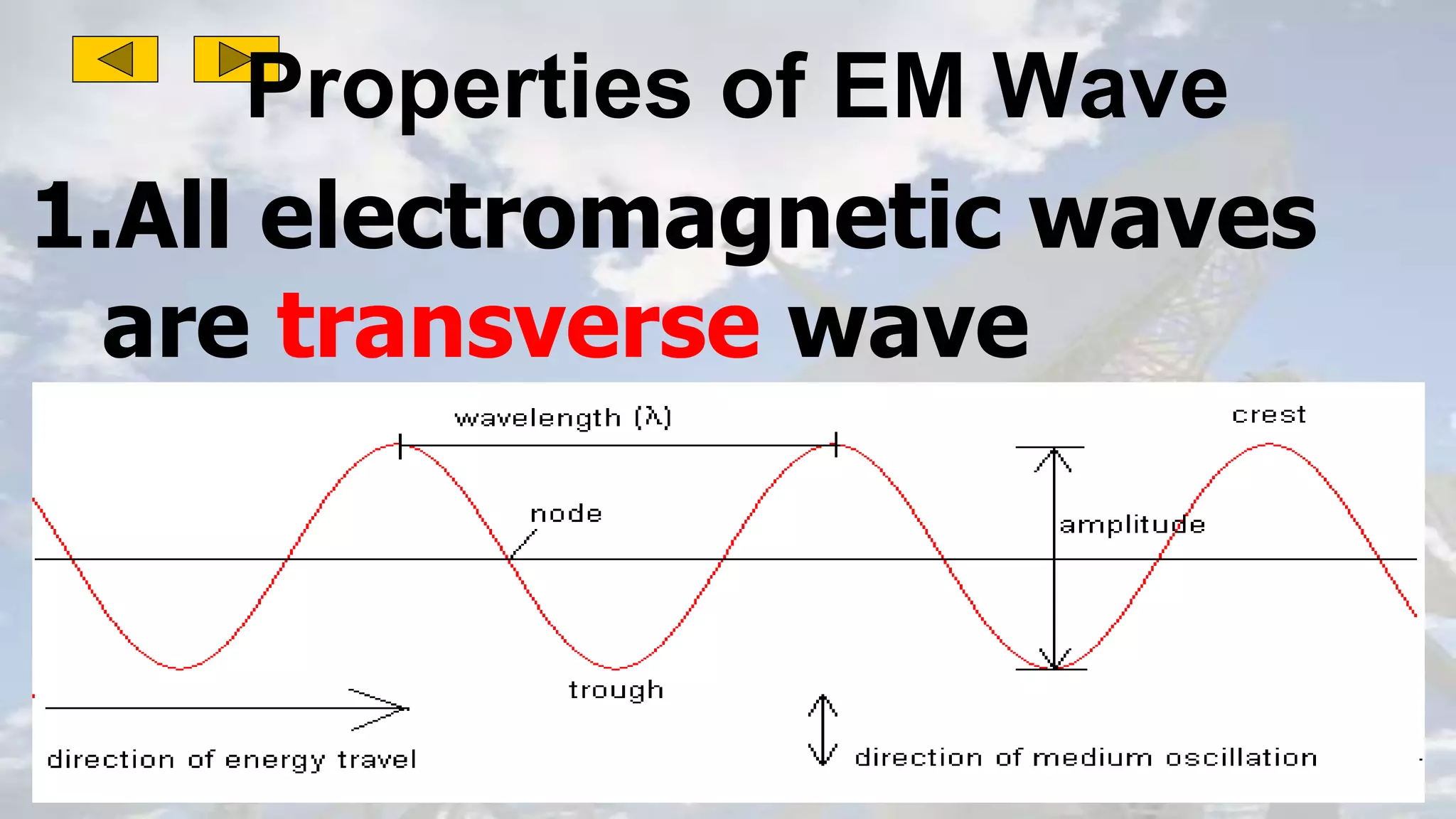
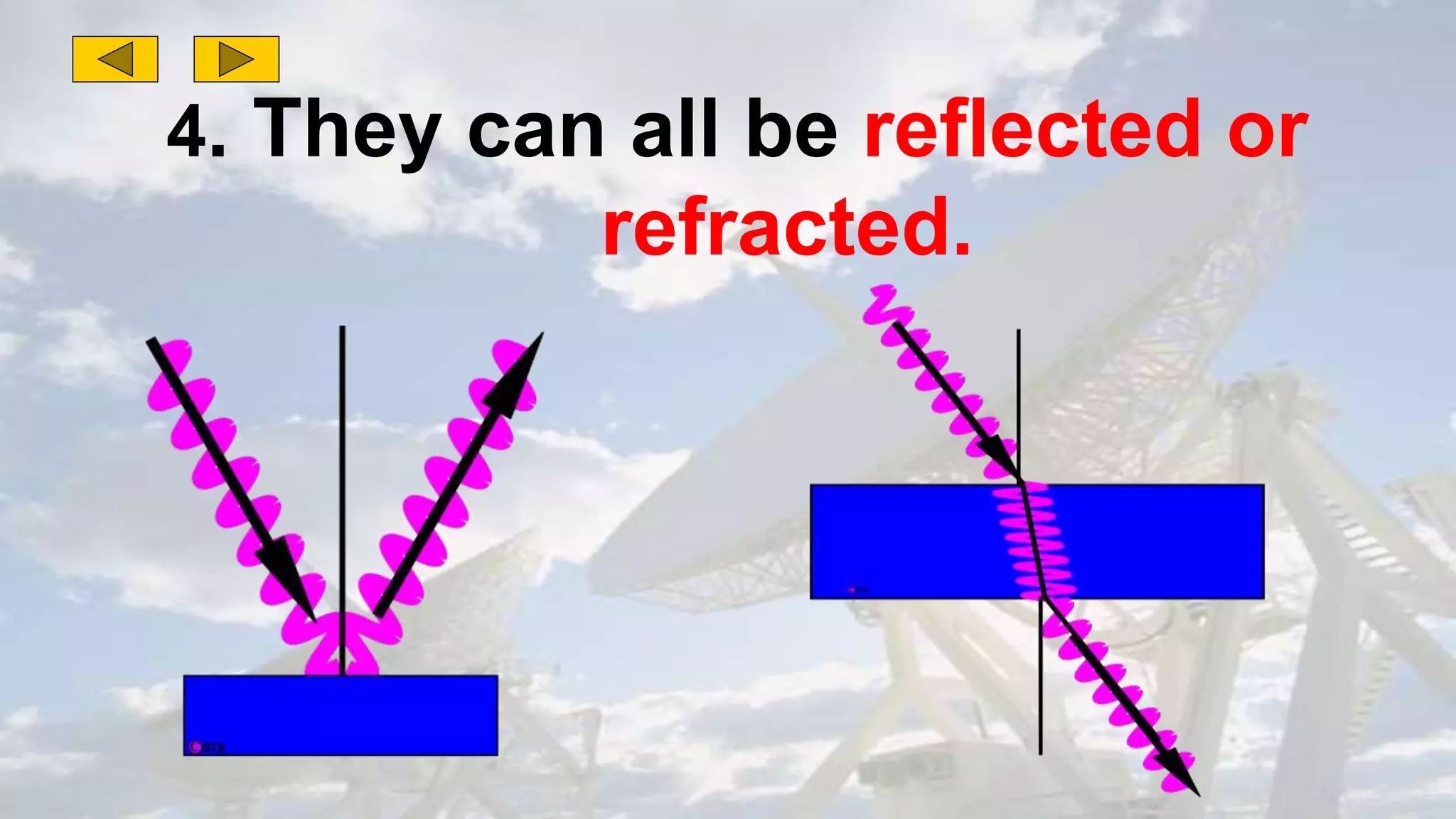
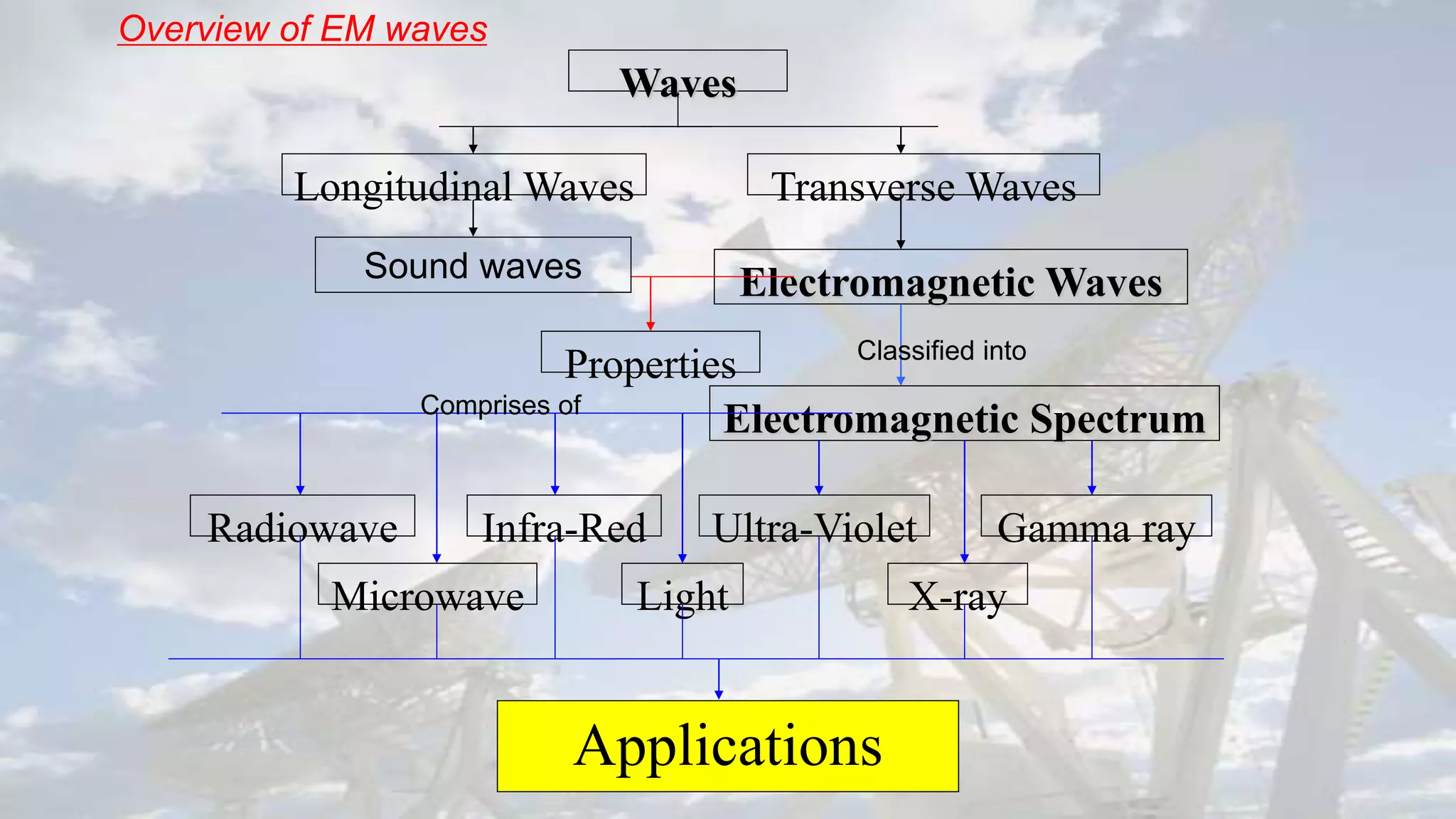
This document discusses the properties of electromagnetic waves. It describes how electromagnetic waves are produced by oscillating electric and magnetic fields and form a spectrum from gamma rays to radio waves. The key properties of all electromagnetic waves are that they are transverse waves that can travel through empty space at the speed of light, carry energy, and have frequencies and wavelengths that are inversely related. Sound waves are longitudinal rather than electromagnetic. Different colors of visible light have different amounts of energy.