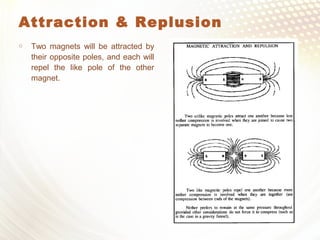
The document discusses magnets, their properties, and history, beginning with the discovery of natural magnets by a shepherd in ancient Greece. It outlines the types of materials that are magnetic and non-magnetic and explains how to test for magnetism, including the use of a compass and the principles of attraction and repulsion between magnets. Additionally, the document highlights various applications of magnets in everyday life and technology.