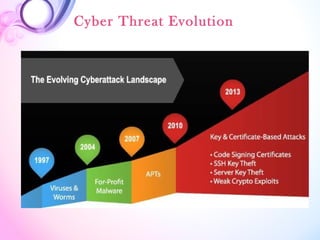
This document discusses cyber crime and its evolution. It defines cyber crime as illegal activity committed using computers and the internet, such as hacking, denial of service attacks, virus dissemination, computer vandalism, cyber terrorism, and software piracy. The types of cyber crimes are then explained in more detail. The document also provides statistics on common types of cyber attacks.