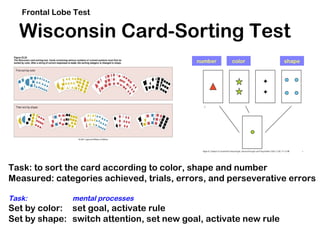
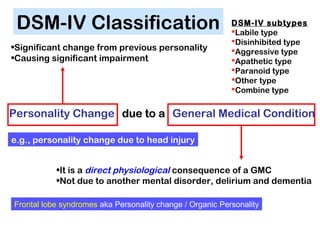
Frontal Lobe Syndromes result from damage to the prefrontal cortex and impairment of executive functions. Executive functions include processes like executive attention, switching attention, response inhibition, sequencing and monitoring. Damage can lead to symptoms like perseveration, impaired judgment and planning, imitative behaviors, and personality changes. Tests of executive functions assess skills like cognitive flexibility on the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test and planning on the Tower of Hanoi. Conditions that commonly involve frontal lobe syndromes include traumatic brain injury, frontotemporal dementia, and vascular dementia.



![Motor Cortex
Superior
Temporal Cortex
Occipital Cortex
Executive Attention
STROOP TEST
State the color as fast as you can
colour
GREEN
word
RED
RED
GREEN
Conflict
Monitor
[cingulate]
Attention
Controller
[DLPFC]
INPUTINPUT RESPONSERESPONSE
DLPFC=dorsolateral prefrontal cortex](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fls2010-170702004929/85/Frontal-Lobe-Syndrome-4-320.jpg)

![PRESS
PRESS
Go trials, when no inhibition is required
Dorsolateral prefrontal [DLPFC] cortex is activated
No-go trials, when response inhibition is required
DLPFC + Orbitofrontal cortex is activated
1) orbitofrontal cortex
2) lateral prefrontal cortex
3) ventromedial cortex
4) limbic system
Response Inhibition](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fls2010-170702004929/85/Frontal-Lobe-Syndrome-8-320.jpg)









![Orbitofrontal Lobe Syndrome
[disinhibited]
Frontal Convexity Syndrome
[apathetic]
Impulsive behavior
(pseudopsychopathic)
Inappropriate jocular
affect, euphoria
Emotional lability
Poor judgment and
insight
Distractibility
Apathy
(pseudodepressive)
Indifference
Psychomotor retardation
Motor perseveration and
impersistence
Stimulus-bound behavior
Motor programming
deficits
Poor word list generation
Frontal Lobe Syndromes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fls2010-170702004929/85/Frontal-Lobe-Syndrome-22-320.jpg)




![Behavior in Dementia
Goldstein (1975) describes the ways in
which behavior can be affected by
cognitive defects. Typically there is
reduction of interests [shrinkage of milieu]
and, rigid and stereotyped routines
[organic orderliness] and, when the person
is taxed beyond restricted abilities, a
sudden explosion of anger or other
emotion [catastrophic reaction]
Oxford textbook of psychiatry, second edition, page 351](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fls2010-170702004929/85/Frontal-Lobe-Syndrome-29-320.jpg)
![Frontotemporal Dementia
FTD is associated with Kluver-Bucy syndrome [KBS]. The most common
symptoms of KBS in FTD is hyperorality manifested as bingeing, altered food
preferences especially for sweets, food fads, weight gain or increased smoking](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fls2010-170702004929/85/Frontal-Lobe-Syndrome-30-320.jpg)