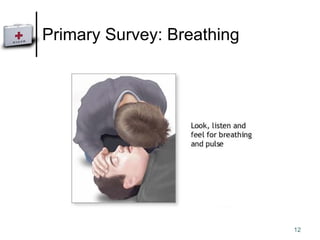
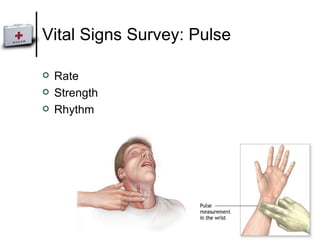
This document outlines the principles of first aid and how to approach an incident. It defines first aid as emergency care provided before medical help arrives. The aims of first aid are to preserve life, prevent further injury, protect the unconscious, promote recovery, and access medical aid. When approaching an incident, one should reduce risks, minimize risks of missing injuries, and prioritize injuries by severity. The primary survey involves assessing danger, response, airway, breathing, and circulation. The secondary survey includes a more thorough history taking and head-to-toe physical examination.