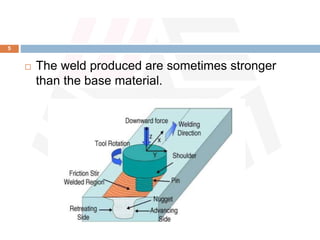
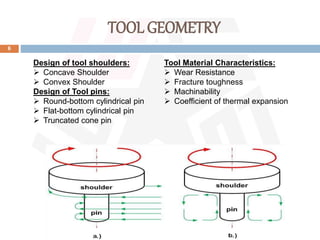
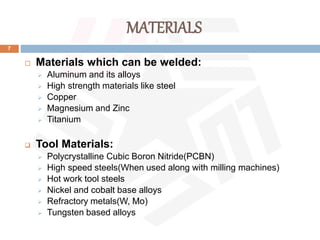
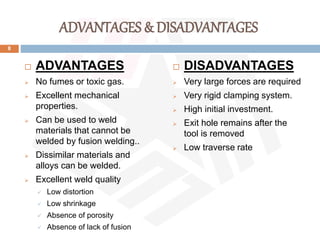
Friction stir welding (FSW) is a patented process developed by TWI in 1991 that uses a rotating tool to join materials, generating heat through friction without melting the base materials. It offers advantages such as excellent mechanical properties, low distortion, and the ability to weld dissimilar materials, though it requires high forces and has a high initial investment. FSW is widely utilized in applications like aerospace, shipbuilding, and large aluminum structures, with ongoing advancements in automation and tool materials.