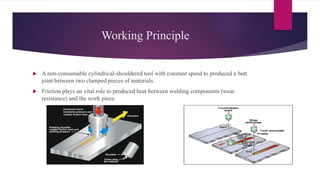
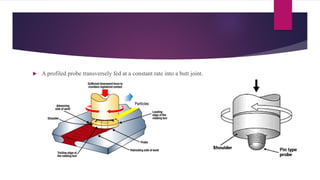
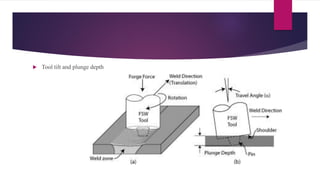
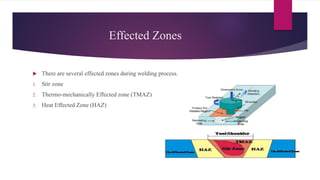
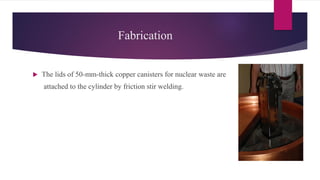
Friction stir welding is a solid state joining process that uses a non-consumable tool to join two touching workpieces without melting. The tool has a shouldered pin that is rotated as it travels along the joint line. Friction between the pin and workpieces generates heat, causing the metals to soften without melting. Benefits include excellent mechanical properties, reduced defects compared to fusion welding, and ability to join difficult-to-weld metals and aluminum alloys. Applications include automotive, aerospace, rail, shipbuilding, and electronics.