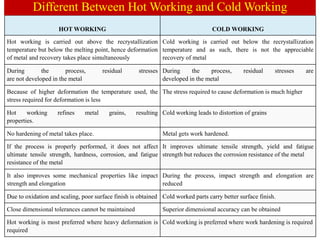
The document discusses the differences between hot working and cold working of metals. Hot working involves deforming metals above their recrystallization temperature but below their melting point, allowing deformation and recovery to occur simultaneously. Cold working deforms metals below the recrystallization temperature, resulting in work hardening rather than recovery. Hot working reduces required stresses and improves properties, while cold working increases strength and hardness but reduces ductility. Both methods have advantages and disadvantages depending on the desired final properties and shape of the metal.