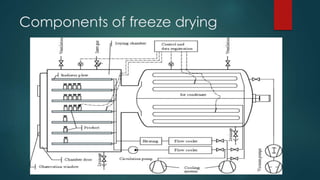
The document provides an in-depth overview of freeze drying, or lyophilization, detailing its principles, process steps, and applications in pharmaceuticals and food preservation. It describes how water is removed via sublimation and desorption after freezing the product under vacuum, resulting in enhanced stability and shelf life. Furthermore, it discusses the technology's advantages and disadvantages, alongside essential equipment components necessary for the freeze-drying process.