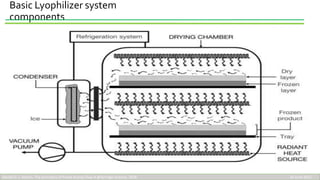
Lyophilization, or freeze drying, is a process used to preserve thermolabile pharmaceutical products and biological materials. It works by freezing the product and then reducing pressure to allow the frozen water in the product to sublime from a solid to gas without passing through the liquid phase. This allows heat-sensitive materials to be dried without excessive heat damage. The process involves freezing the product, primary drying where ice is removed by sublimation under vacuum, and secondary drying where remaining bound water is removed by desorption. Freeze drying is useful for preserving materials like vaccines, blood products, enzymes and other biologics as it prevents degradation and improves stability at low temperatures.















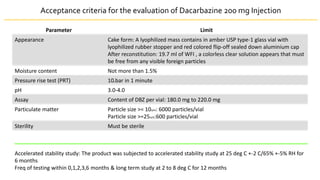
![Case study
• DACARBAZINE is an alkylating agent administered as a first line treatment for
metastatic melanoma. As the stability of dacarbazine in aqueous solution form
was unstable so it was formulated as Lyophilized product
• To develop a stable lyophilized formulation of drug dacarbazine for injection
(200mg/vial)
• Dacarbazine[DBZ] has been administered as a first-line drug treatment for
metastatic malignant melanoma and Hodgin’s disease
• Also used with other drugs for soft tissue sarcoma
• DBZ is supplied as a sterile, lyophilized powder that can be reconstituted for IV
injection.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lyophilizationak-210707151226/85/Lyophilization-17-320.jpg)