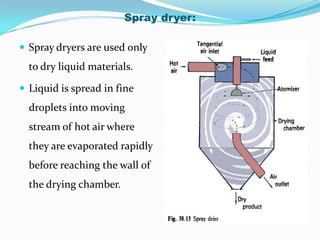
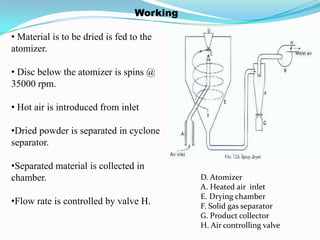
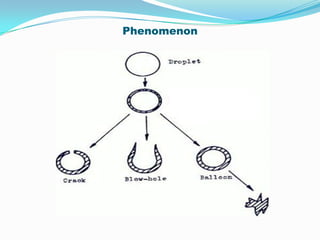
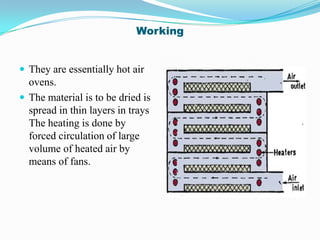
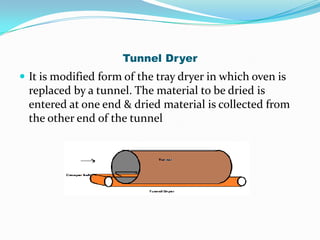
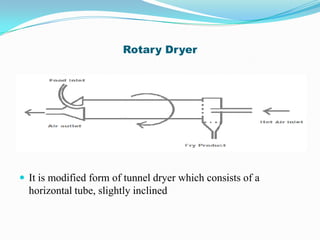
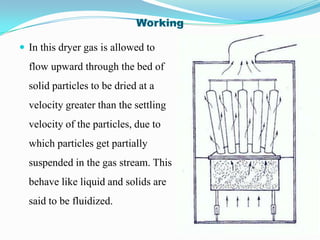
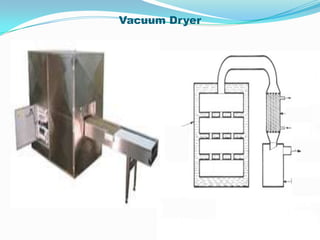
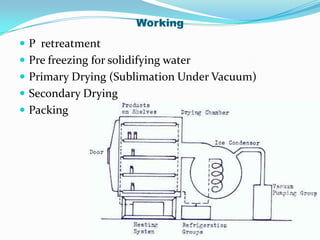
This document discusses various drying methods used in pharmaceutical manufacturing. It defines drying as removing liquid from a material through heat transfer and evaporation. Several dryer types are described, including drum dryers, spray dryers, tray dryers, tunnel dryers, rotary dryers, fluidized bed dryers, vacuum dryers, and freeze dryers. Each method is explained along with its advantages and disadvantages. Freeze drying and vacuum drying allow heat-sensitive materials to be dried at low temperatures. Larger dryers like spray dryers and rotary dryers provide continuous high-volume drying.