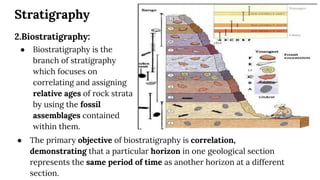
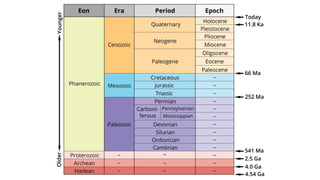
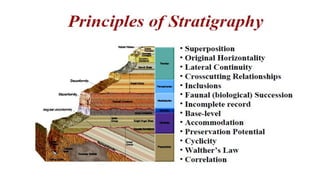
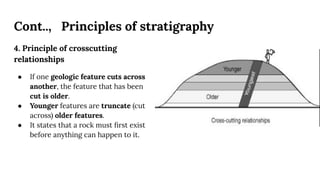
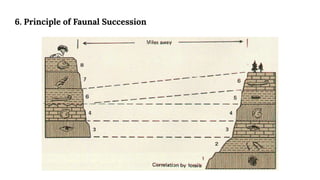
This document discusses structural geography and stratigraphy. It defines structural geography as the study of dip, strike, outcrops, inliers, outliers, discontinuities, folds, faults, joints and unconformities in rock structures. Stratigraphy is divided into lithostratigraphy, which studies rock layers based on lithology, and biostratigraphy, which uses fossil assemblages to correlate rock ages. The principles of stratigraphy include original horizontality, superposition, lateral continuity, cross-cutting relationships, inclusions, faunal succession, and uniformitarianism. Types of stratigraphy are lithostratigraphy, chronostratigraphy, biostratigraphy, magnetostratigraphy, allostratigraphy, geochron