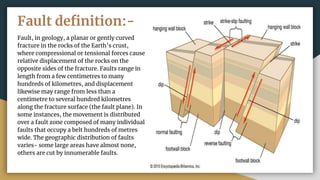
1) A fault is a fracture in the Earth's crust where rocks on either side are displaced relative to each other due to compressional or tensional forces.
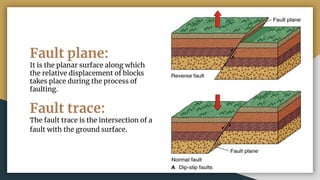
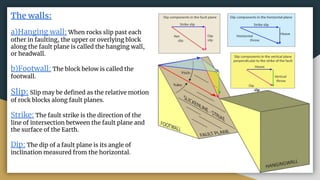
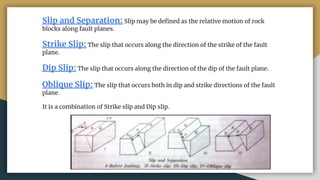
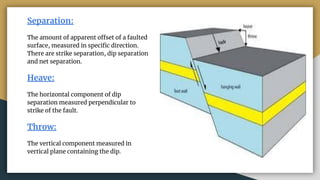
2) Key terms related to faults include the fault plane, fault trace, hanging wall, footwall, strike, dip, slip, separation, heave, and throw.
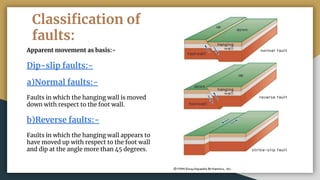
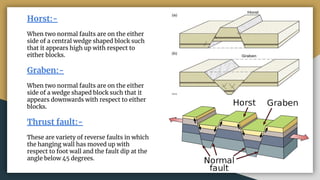
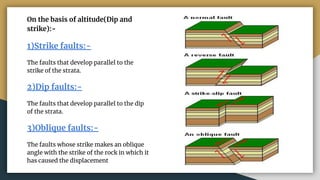
3) Faults can be classified based on their apparent movement (normal, reverse, strike-slip), their orientation relative to bedding (strike, dip, oblique), and their pattern of occurrence (parallel, en echelon, peripheral, radial).