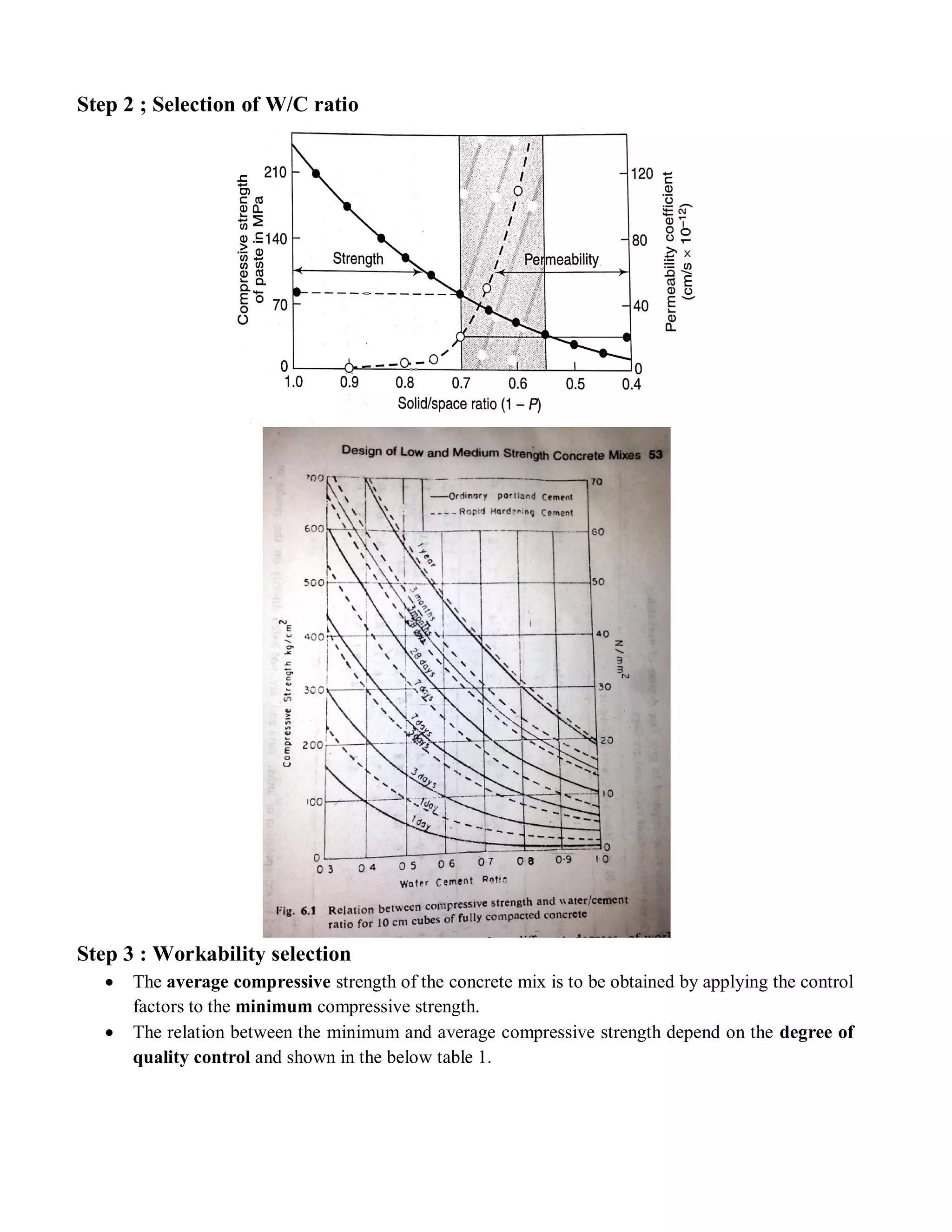
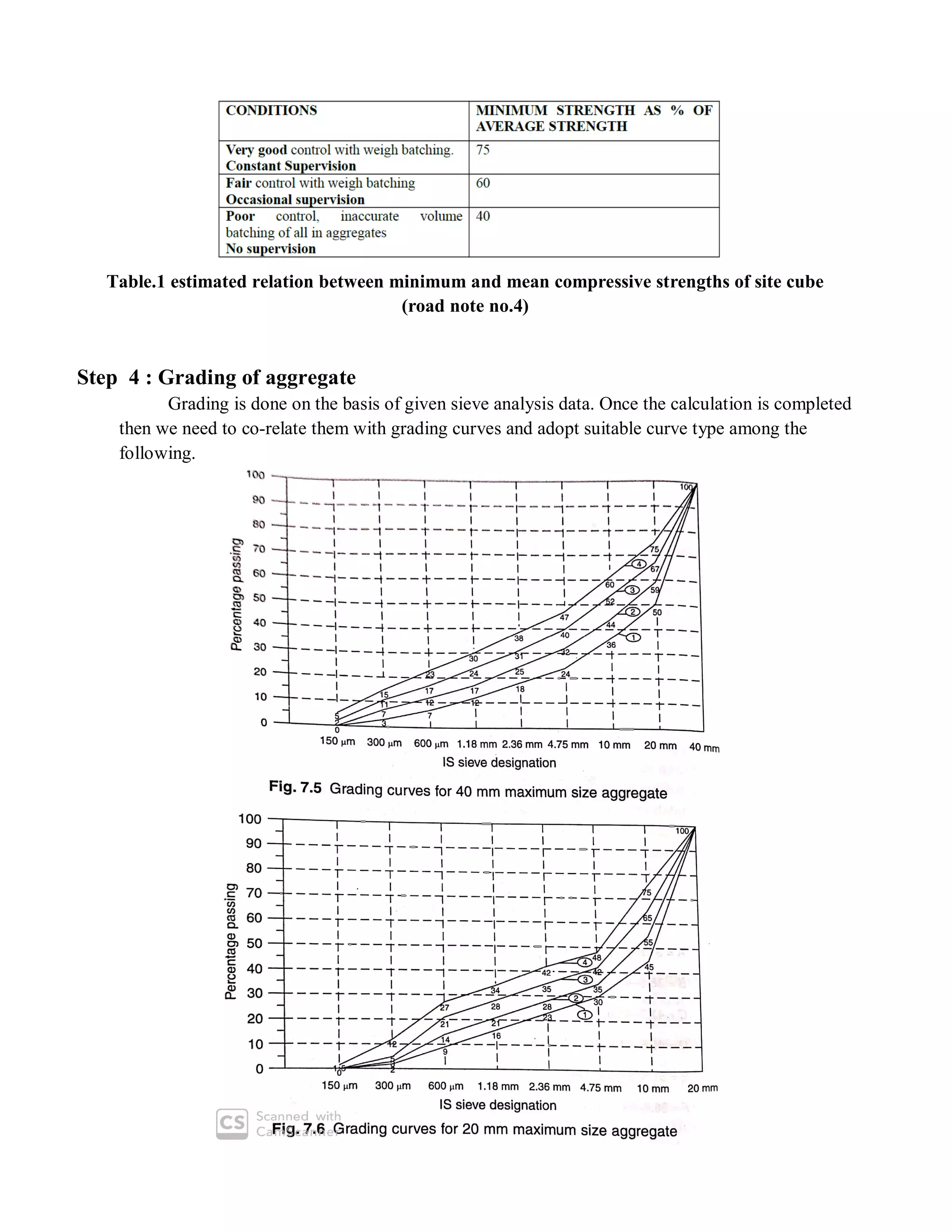
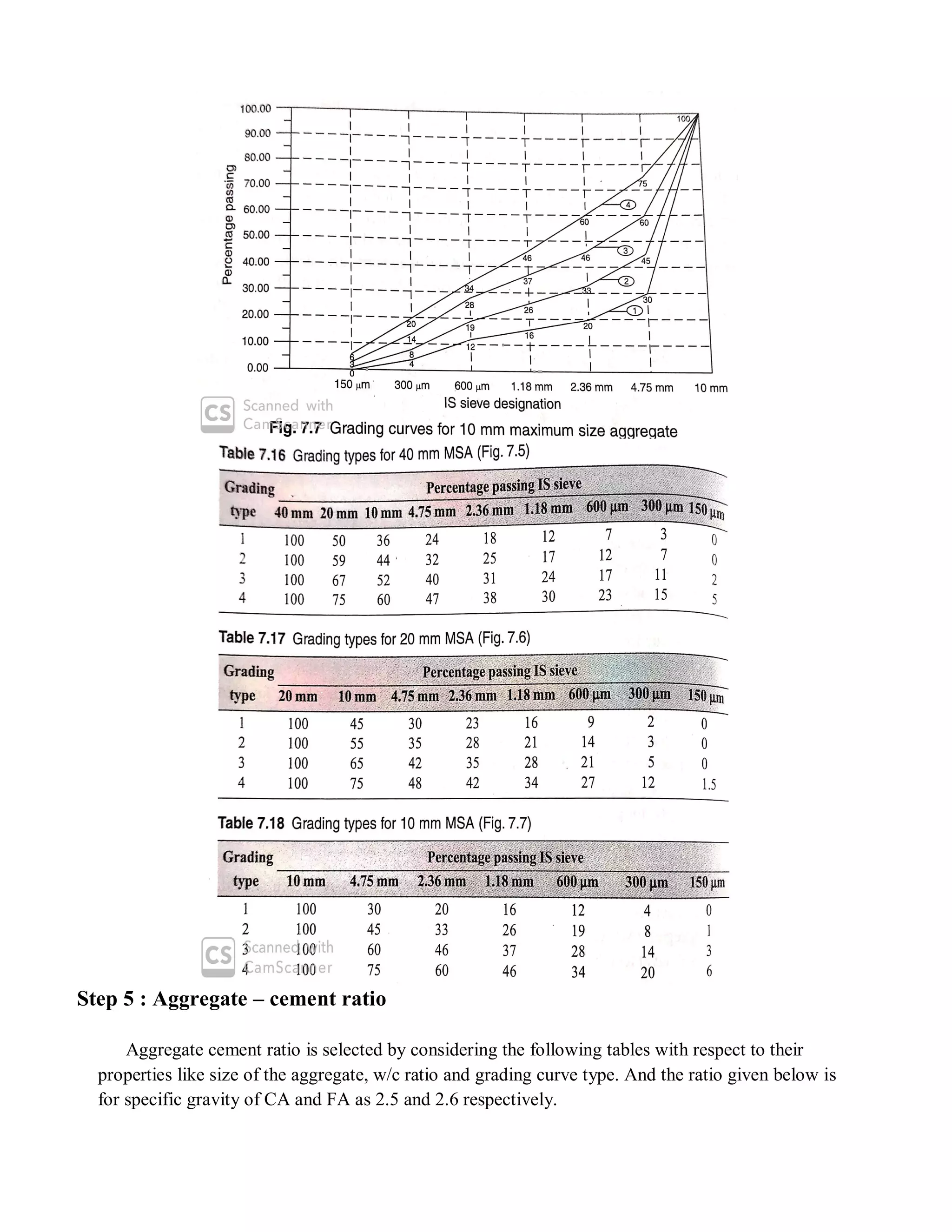
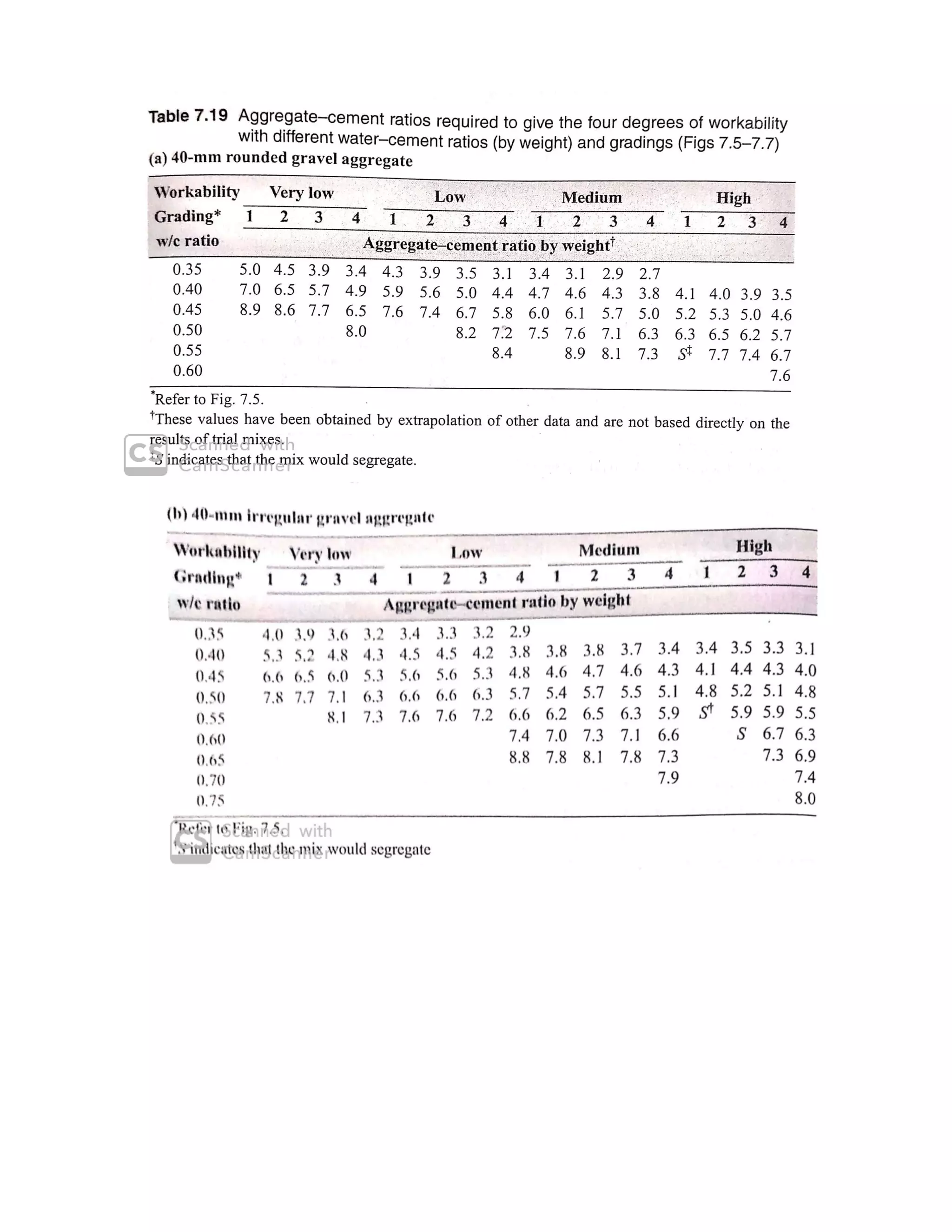
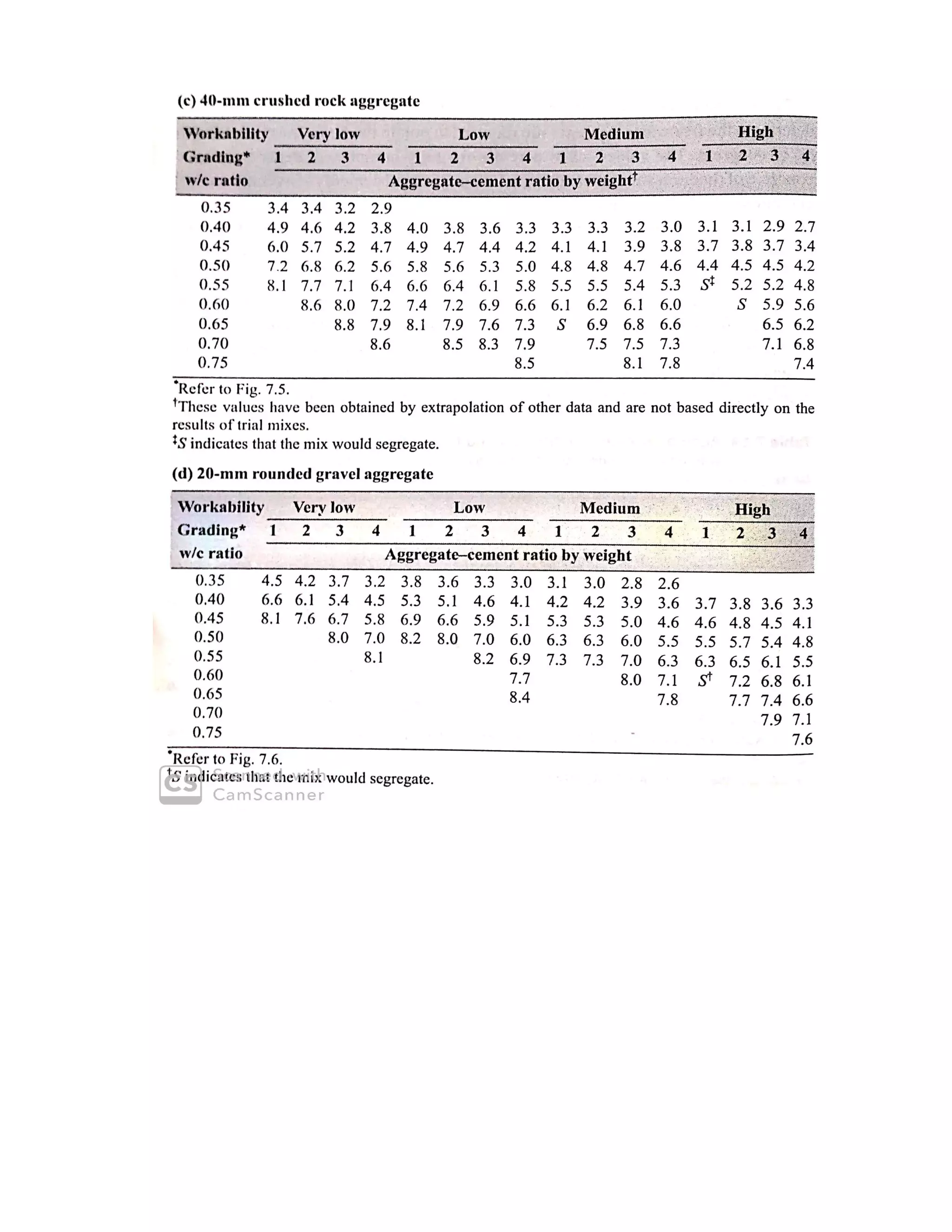
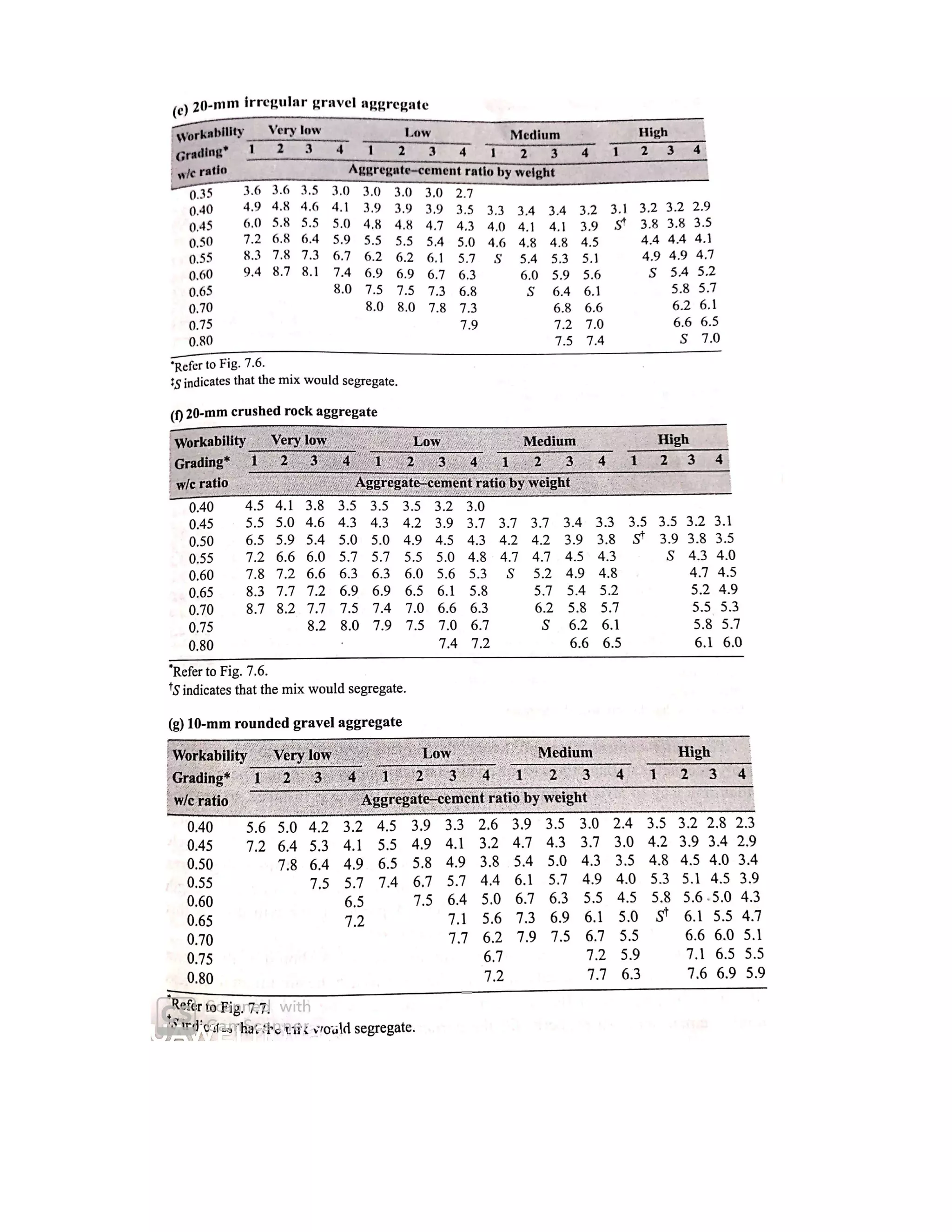
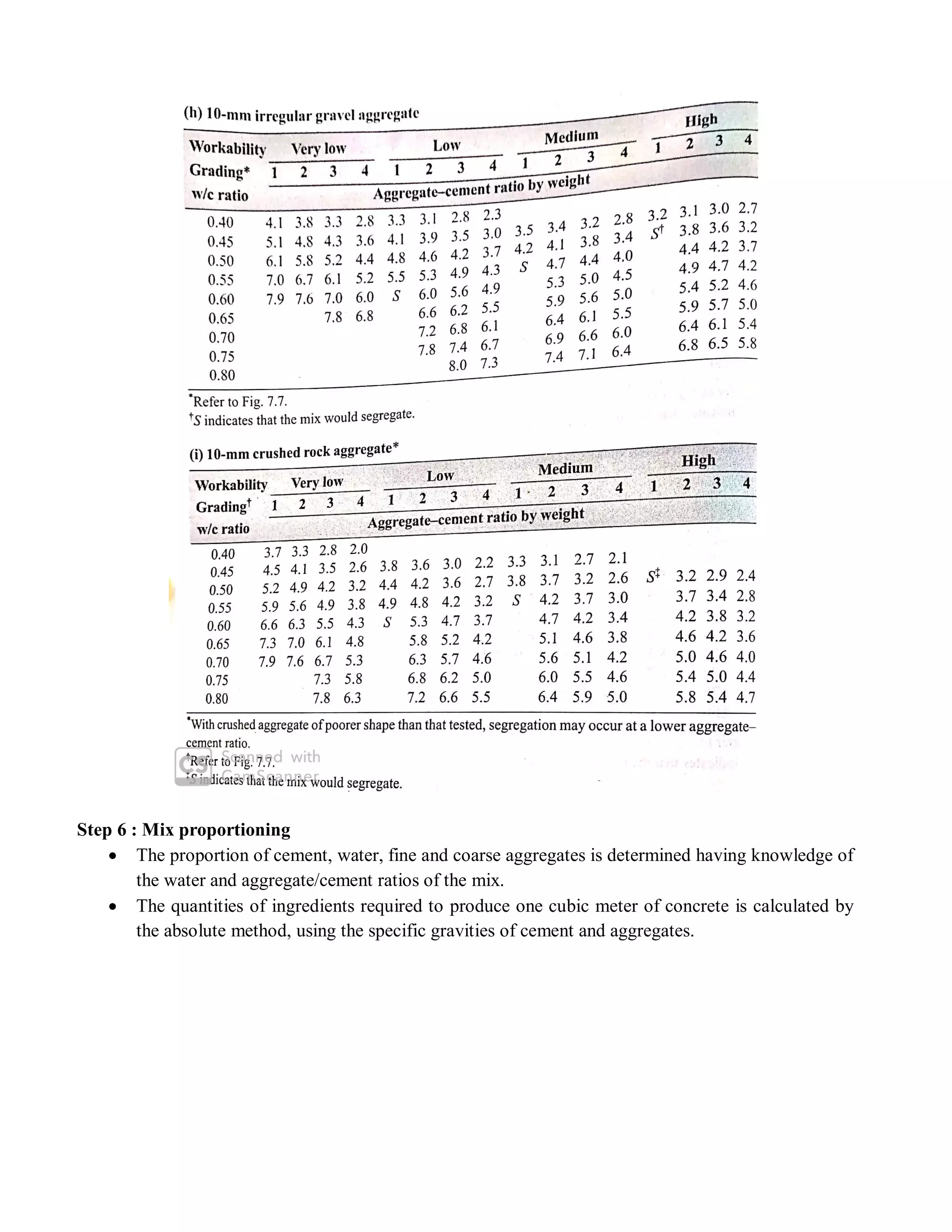
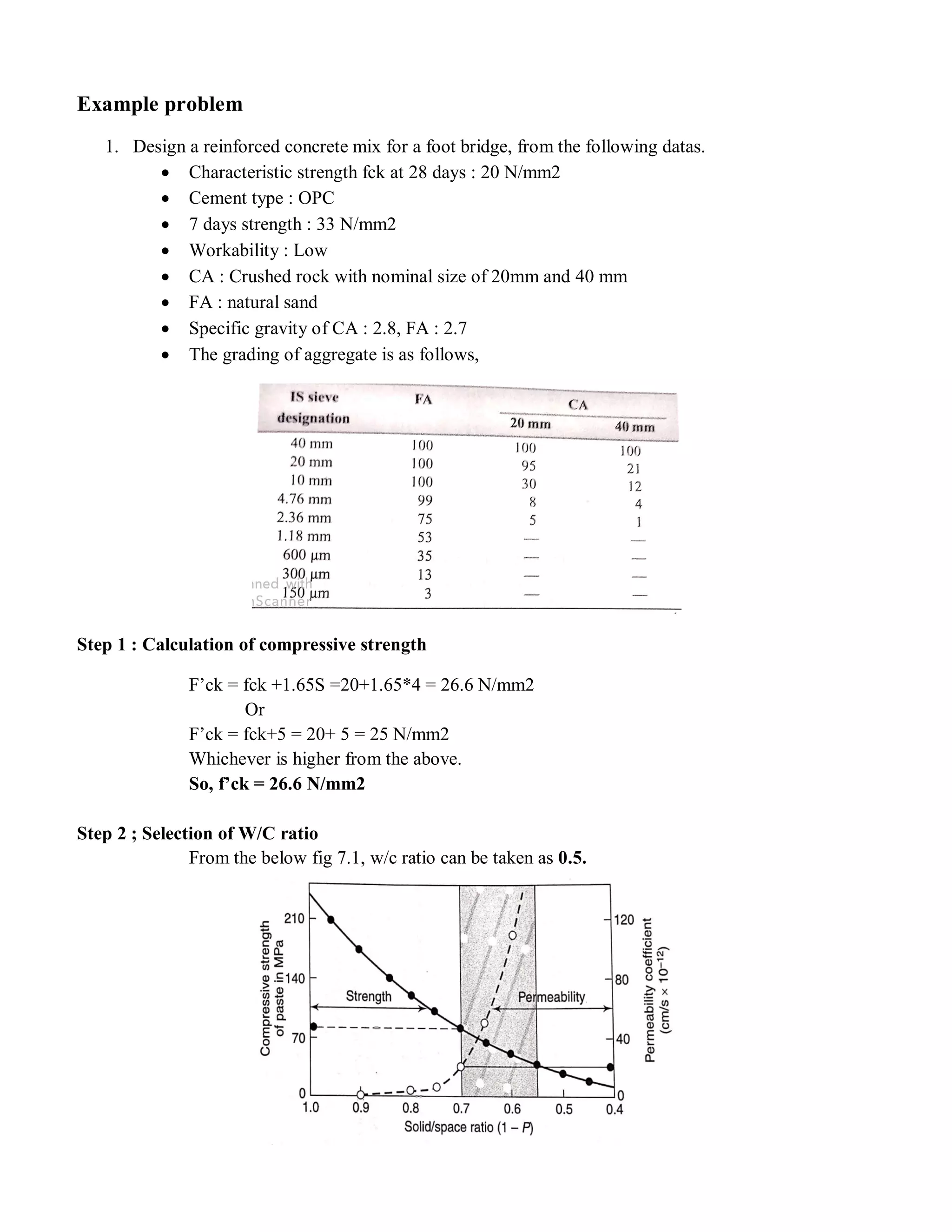
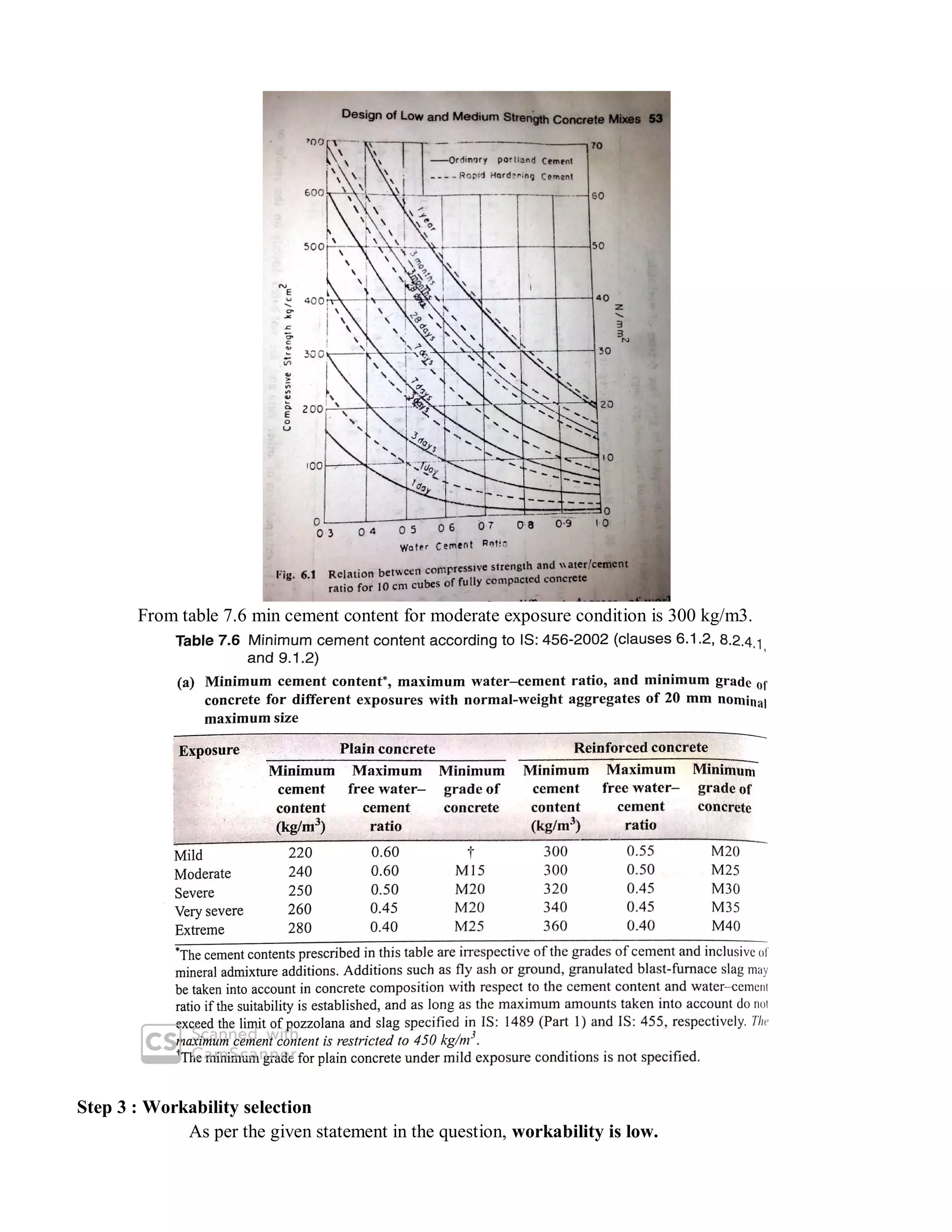
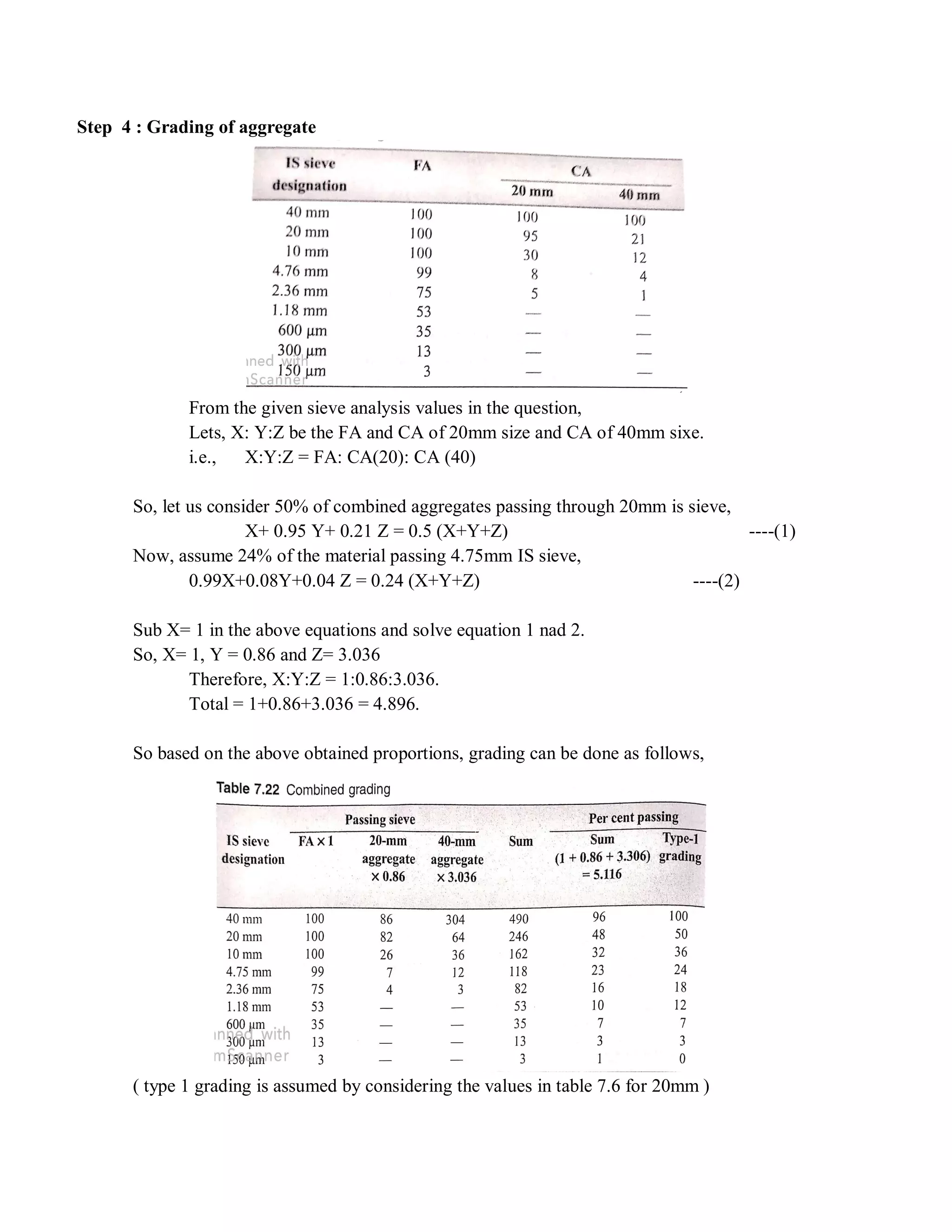
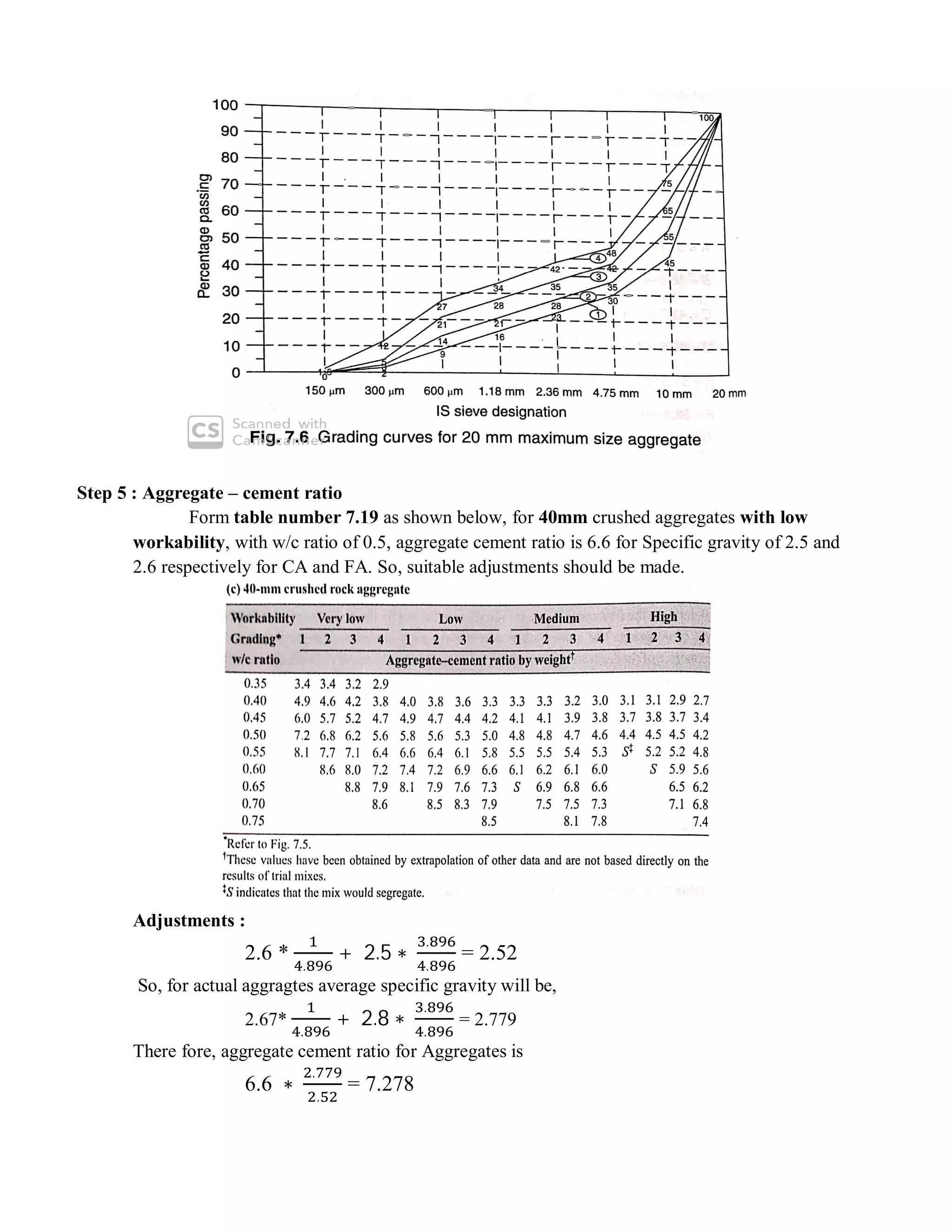
The document describes the Road Note No. 4 method for concrete mix design. It involves selecting proportions of ingredients including cement, water, fine aggregate and coarse aggregate to produce an economical concrete with sufficient workability, strength and durability. The method is based on extensive laboratory investigations of how factors like aggregate-cement ratio, water-cement ratio, grading and aggregate properties influence workability and strength. A six step procedure is outlined for mix design including determining compressive strength, selecting water-cement ratio, workability, grading aggregates, aggregate-cement ratio, and final mix proportions. An example problem demonstrates applying the method to design a mix meeting given requirements.