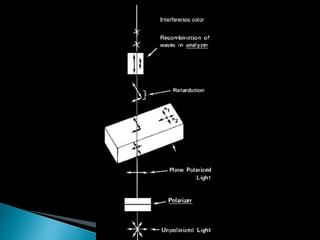
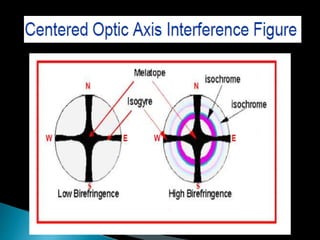
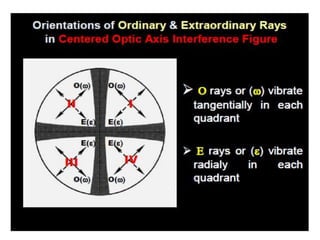
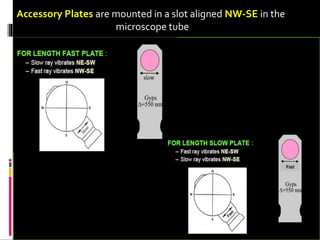
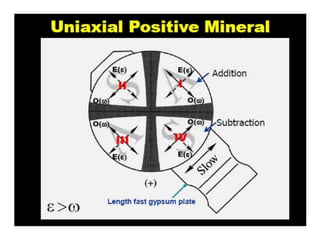
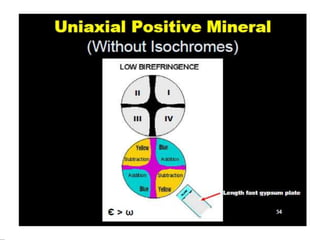
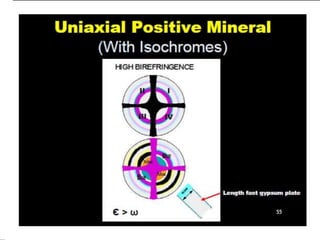
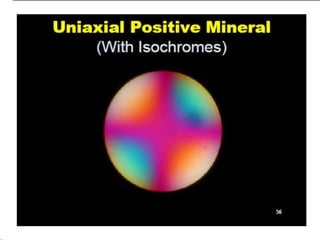
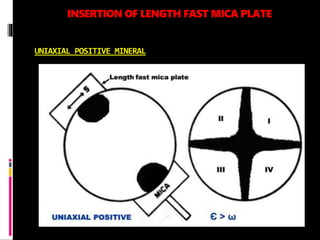
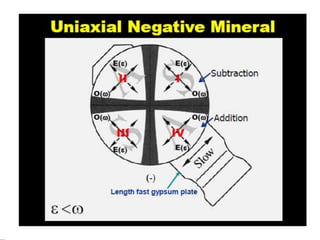
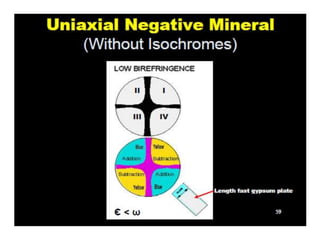
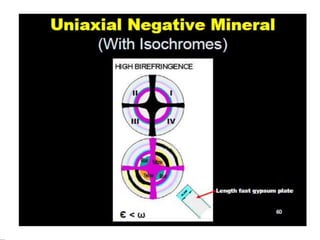
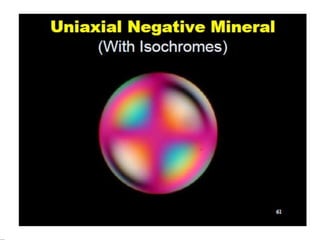
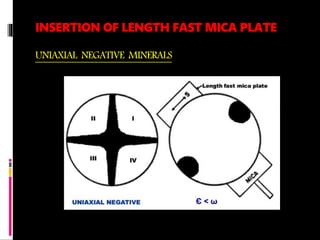
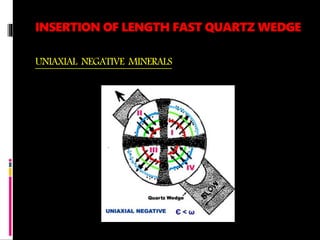
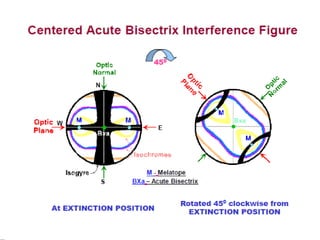
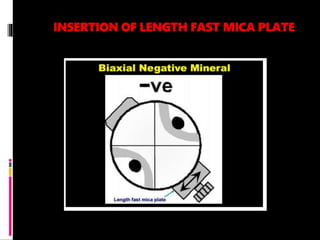
This document discusses interference colors and interference figures seen in anisotropic minerals under polarized light microscopy. It describes how interference colors are produced when minerals are rotated to their extinction positions. It also explains different types of interference figures seen in uniaxial and biaxial minerals, including centered optic axis, acute bisectrix, and how accessory plates can determine optic sign. Accessory plates like gypsum, mica, and quartz wedges are inserted to observe color changes in the interference figures that indicate whether minerals are positive or negative uniaxial and positive or negative biaxial.