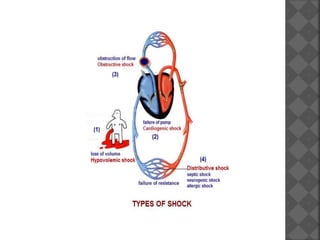
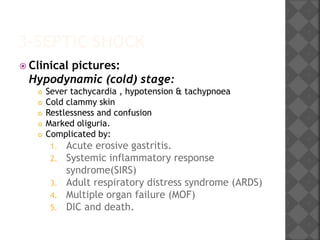
1. Septic shock is caused by infection which releases cytokines that damage microcirculation and cause vasodilation and capillary leakage, leading to tissue hypoxia and multiple organ failure. Early, aggressive treatment of infection along with cardiovascular and organ system support is needed to prevent high mortality rates.
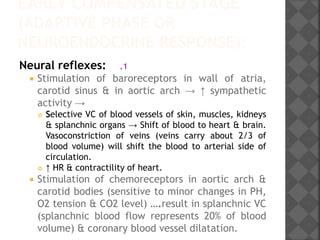
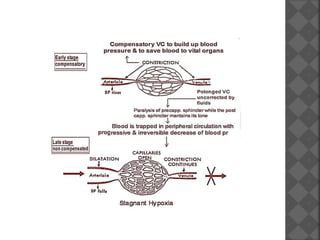
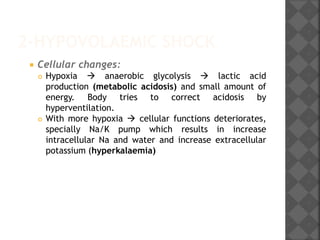
2. Hypovolaemic shock results from decreased blood volume due to blood loss, fluid loss, or fluid shifts. It progresses from mild to severe as compensation fails, leading to cellular changes, metabolic acidosis, and potentially multiple organ failure without timely fluid resuscitation and hemostasis.
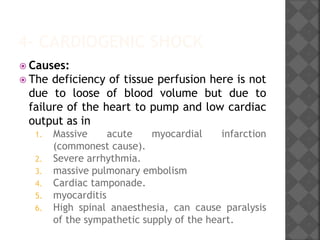
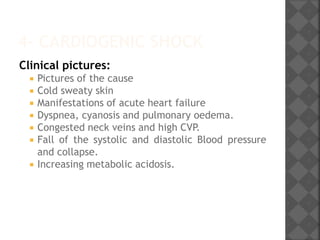
3. Cardiogenic shock stems from heart failure to pump adequately due to causes like myocardial infarction, arrhythmias